Trees, plants, insects, and bacteria are examples of what type of factors?
Biotic, Abiotic, or limiting?
what is biotic?
How much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next?
What is 10%
Which letter represents evaporation?
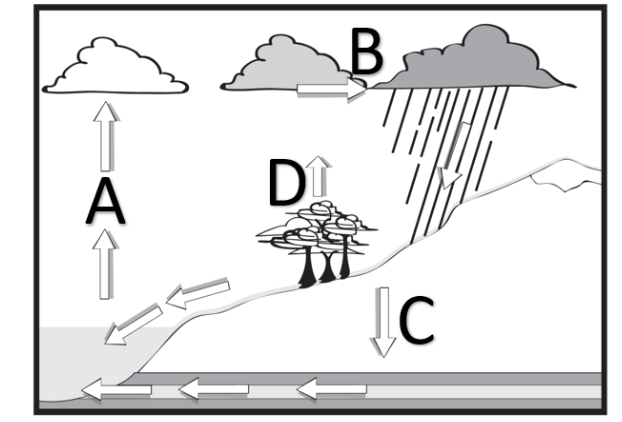
What is A?
What does the image below represent? 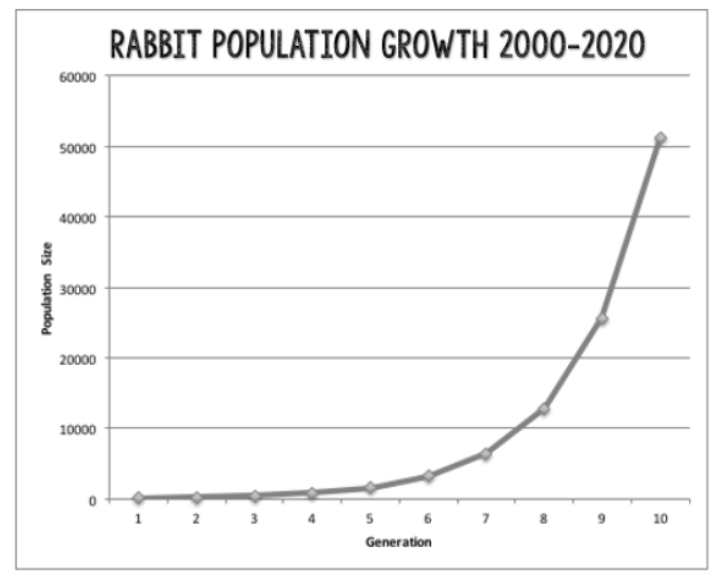
What is exponential growth?
What type of succession occurs where there is no soil?
What is primary?
Name 3 examples of abiotic factors
air, water, temperature, sunlight, any solid object in the classroom, etc.
The ultimate source of energy is...
What is the sun?
Which of the four biogeochemical cycles does not enter the atmosphere?
What is phosphorus?
Space, food, water, predation, competition, and human disturbances are examples of what?
What are limiting factors?
After a fire, what type of succession would occur?
what is... secondary succession
In ecology, which of the following is considered the largest?
A. Organism
B. Ecosystem
C. Community
D. Biosphere
What is Biosphere
What is the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
What is...
autotrophs: make their own food (producers)
Heterotrophs: eat their food (consumers)
What is a biogeochemical cycle?
what is...process in which elements and matter are passed from one organism to another and through the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem
What is carrying capacity?
What is the number of individuals the environment can support over a long period of time
What is a climax community?
what is... a stable community
Name four of the eight characteristics of life
What is...
1. Made up of cells 5. Energy
2. Contain DNA 6. Respond to environment
3. Reproduce 7. Maintain homeostasis
4. Grow 8. Adapt and change over time
What are the four types of heterotrophs?
What is... Herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, and detritivore (decomposer)
Organisms can't use most of the nitrogen available in the atmosphere, how do they get the nitrogen they need?
What are bacteria?
What type of dispersion is shown in the image?

What is clumped?
What species are not necessary for secondary succession
Name and describe the three main symbiotic relationships
What is...
Mutualism: both benefit
Parasitism: one helped, one harmed
Commensalism: one helped, other is neither helped or harmed
Label each organism in the food chain as primary consumer, tertiary consumer, producer, and secondary consumer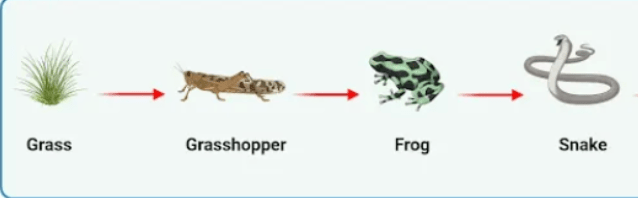
What is...
Grass: producer
Grasshopper: primary consumer
Frog: Secondary Consumer
Snake: tertiary consumer
What organism removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to produce glucose through the process of photosynthesis?
What are plants?
Determine if each will increase or decrease a population size...
1. Increase number of births
2. Increase number of deaths
3. Immigration
4. emigration
What is
1. increase
2. decrease
3. increase
4. decrease
What are pioneer species?
What are.. the first species to colonize an area