Perfectly competitive firms are ____ which means they have no control over price. They maximize profits by setting Q where MR ___ MC. (<,>, or =)
Monopolies are _____ which means they have pricing power. They maximize profits by setting Q where MR ___ MC. (<,>, or =)
Price Takers
Price Makers/Setters
Both maximize profits by producing the Quantity of output where MR = MC.
In monopoly, MR ___ P
(>,<, or =)
Explain your reasoning.
MR < P
(A monopolist is a large share of the market, so it faces the entire downward-facing demand curve. This means that the monopolist has to lower the price to sell more units, which means they have to lower the price for every unit when the decrease the price)
Which 2 of these statement are false:
The short run is the period before exit or entry can occur.
The long run is the period after all exit and entry has occurred.
Constant Cost Industries have a downward sloping supply curve while Increasing Cost Industries have an upward sloping supply curve
Firms immediately exit an industry when P < AC and immediately enter when P > AC
Constant Cost Industries have a horizontal supply curve while Increasing and Decreasing Cost Industries have an upward and downward sloping supply curve respectively.
Firms don't immediately exit an industry when P < AC because of entry and exit costs, or sunk costs. They exit when the Expected Price > Minimum Average Costs long enough to recover entry costs.
Given this function, calculate fixed, variable costs and Total Costs.
Calculate for y = 2
5y^2 + 2
Fixed Costs = 2
Variable Costs = 5(2)^2 = 20
Total Costs = FC + VC = 22
____ is a type of price discrimination where the base good is sold with another good called the variable good. This tends to increase output and social welfare.
____ requires that 2 or more products must be sold as a package. This is especially effective for 0 marginal cost products.
Tying. (Example: Printer is base good, ink is variable good)
Bundling. (Example: Microsoft Office, which contains Excel, Word, and Powerpoint)
Accounting Profit = Total Revenue - ____ Costs, which are out-of-pocket costs like wages, rent, and materials.
Economic Profit = Total Revenue - ___ Costs and ____ Costs, which are opportunity costs of resources already owned, like land used for a factory instead of selling it.
Accounting Profit = Total Revenue - Explicit Costs
Economic Profit = Total Revenue - (Explicit Costs + Implicit Costs)
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry that results in a monopoly:
Legal barriers (patents, trademarks), technological innovation, excess competition, control of physical resources, economies of scale
Which of the following is incorrect:
- Monopoly power is the power to raise prices above average cost without facing new entry of firms.
- If governments removed all patent laws, the future supply of new drugs would increase
- Monopolies have market power, which is the firm's ability to influence the market price for a product
Excess competition is not a barrier to entry.
- If governments removed all patent laws, the future supply of new drugs would decrease because there would be less incentive to tolerate R&D costs if the product is less likely to earn a profit across a long period of time.
If P > AVC, a firm will enter the industry and will maximize profits by producing the Quantity where MR ___ MC. (<,>, or =)
If P < ___, a firm will shut down in the short run.
If P < ___, a firm will exit in the long run.
If P > AVC, a firm maximizes profit by producing the quantity where MR = MC.
If P < AVC, a firm will shut down in the short run.
If P < ATC, a firm will exit in the long run.
Find Marginal Cost if y = 2 and m = 5. Use formula 2*m*y
5y^2 + 2
10y = 10(2) = 20
Label each as either 1st, 2nd, or 3rd degree price discrimination.
- Perfect price discrimination. Producers charge customers based on their maximum willingness to pay and capture their entire consumer surplus.
- Companies charge different prices for customers with different backgrounds or demographics.
- Charge based on amounts or quantities consumed. Bulk purchases receive a discount.
1st Degree - Perfect price discrimination. Producers charge customers based on their maximum willingness to pay and capture their entire consumer surplus.
2nd Degree - Charge based on amounts or quantities consumed. Bulk purchases receive a discount.
3rd Degree - Companies charge different prices for customers with different backgrounds or demographics.
Match Each with either a perfectly competitive firm or a Monopoly:
A) Free entry and exit
B) Barriers to entry
C) Firms can control price
D) Firms have no control over Price
E) Firms produce nearly identical products
F) Consumers have relevant information to make rational decisions
G) Firms is a relatively large share of the market
Perfect Competition:
A) Free entry and exit
D) Firms have no control over price
E) Firms produce nearly identical products
F) Relevant information to make rational decisions (This includes information about the quality, price, availability, and other characteristics of the products)
Monopoly:
B) Barriers to entry
C) Firms control price
G) Firm is a relatively large share of the market
Which of the 2 graphs represent a more elastic demand curve? Which would generate the most profit from a markup?


In a constant cost industry, P = AC. Which sequence of events follows an increase in demand?
P __ AC, (<,>, or =) firms make an economic profit and existing firms expand output.
New firms enter the industry, the short-run supply curve shifts ____ (left or right), which causes profits to ___(fall or rise) until profits return to $0.
When P > AC, firms make an economic profit, existing firms expand output, new firms enter the industry, the short-run supply curve shifts right, price falls until profits return to $0.
Economic profits = 0 in the long run. Short run means the period before new firms can enter the market

Find Average Variable Costs, Average Fixed Cost, and Average Total Cost for y = 3
5y^2 + 2
ATC = (5(3)^2 + 2) / 3 = 15.67
AVC = (5(3)^2) / 3 = 15
AFC = 2 / 3 = 0.67
What should Microsoft price the Microsoft Office Bundle at, assume MC = 0?

Microsoft should sell the bundle at $120
Now, instead of selling Word or Excel individually, Microsoft can increase profits by selling both products as a bundle. The bundle is useful since Amanda and Yvonne have a different maximum willingness to pay for both products.

Determine which of the following represents Monopolistic Competition and which represents an Oligopoly:
- Many firms vs Small number of firms
- Similar but slightly differentiated products
- Significant control over price from limited competition vs Some degree of market power to charge a slightly higher price
- Easy entry and exit
- Focus on maintaining market position rather than making new products vs Focus on non-price competition like advertising and product differentiation vs
- Price collusion/ choice of each affects profit of others
Monopolistic Competition:
- Many firms
- Similar but slightly differentiated product
- Some degree of market power to charge a slightly higher price
- Easy entry and exit
- Focus on non-price competition like advertising and product differentiation
Oligopoly:
- Small number of firms
- Choice of each affects profit of others
- Significant control over price from limited competition
- Price collusion
- Focus on maintaining market position rather than making new products

In this graph of a monopoly, determine where the profits would be located. If P = 10, P' = 5, Q = 40 , what is the value of the total profit?

The profit maximizing move is still where MR=MC, so the profit-maximizing level of output is where the MR intersects with the MC curve. Then, the Price is located at the point on the Demand Curve for that Quantity. The profit would be the (AC - PxQ)
40 x 10 - 400, 40 x 5 = 200, 400-200 = 200,
Profit = 200
Identify which illustrates a profit, loss, and breakeven point

If P ↑ AC Curve = Profit
If P ↓ AC Curve = Loss
AC Curve's minimum intersects with MC Curve = Breakeven Point
or
Price > ATC
Firm earns an economic profit
Price = ATC
Firm earns zero economic profit
Price<ATC
Firm earns a loss
What happens to ATC when it is less than MC and What happens to ATC with is more than MC?
When is ATC at its minimum?
When MC < ATC, ATC is decreasing as Q increases.
When MC > ATC, ATC is increasing as Q increases.
ATC is at its minimum when MC = ATC.

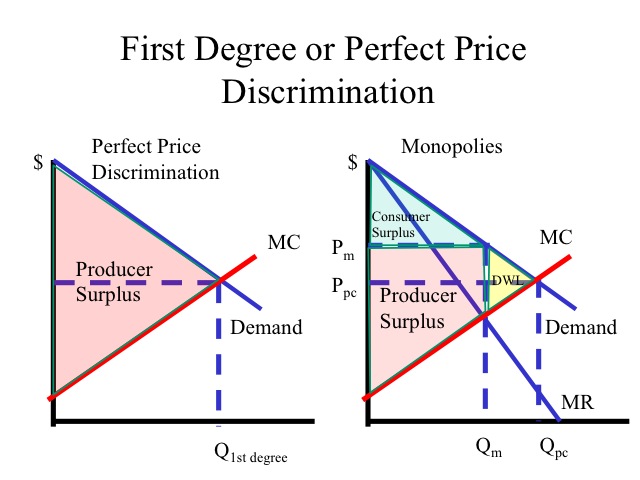
In a monopoly with perfect price discrimination, where is the producer and consumer surplus? Where is the deadweight loss?
The producer surplus is the entire area above the MC and below the D curve. Since the monopoly produces exactly the Q where MR=MC and at the Q the market is Demanding, (40 Units) there is no DWL. Since profits have been maximized for the monopoly under price discrimination, there is no consumer surplus.
Perfectly competitive firms are _____ which means they produce the optimal Q of output.
Monopolies produce ____ (<,>, or =) the optimal Quantity, which has what result on consumer surplus and deadweight loss?
Perfectly competitive firms are allocatively efficient which means they produce the optimal Q of output.
Because P>MC in a monopoly, the monopolist produces < the optimal Quantity because it is not profitable.Consumer then lose some potential surplus and DWL occurs from the value of trades that don't take place.
Where would Consumer and Producer surplus be located at Price Pm and Quantity Qm? Where is the deadweight loss?

Consumer surplus is area a, producer surplus is area b + d, and deadweight loss is area c+e.
Calculate profits for chart (a) and (b)
Assume Q = 90, P = 5.00, P2 = 3.50 for (a)
Assume Q = 70 and P = 3.00 for (b)

Profits = P x Q - AC x Q or (P - AC) x Q
(90 x 5) - (90 x 3.50) = 135
(70 x 3.00) - (70 x 3.00) = 0
At what level of production is AVC at it's minimum?
When is the firm able to cover Variable Costs?
The firm will be able to cover variable costs as long as MC (which = Price in perfect competition) is above the AVC curve.

What type of activity does this graph represent if it displays a "buying low, selling high" strategy to make a profit?
Which of the 2 graphs indicate the market containing the lower price, and which is the market containing the higher price?
This is graph illustrates arbitrage, the strategy of "buying low and selling high" where a person purchases a good at one market so they can sell it at another market for a higher price. This makes it difficult to price discriminate since it tends to smooth prices.
Graph 1 (France) illustrates the rightward shift of the supply curve and decrease in price while graph 2 illustrates the rightward shift in the demand curve due to increased demand from arbitrage.
