Which is infinite: Our wants/needs OR Our resources?
Our wants/needs
Does everyone feel scarcity the same way?
No, scarcity is relative, meaning not everyone feels it the same way.
For example, let's say Benny has lots of water but no wood. Billy Bob has lots of wood but no water. Benny feels that wood is scarce, Billy Bob feels that water is scarce.
What type of economy does Venezuela have?
Centralized, Command, Socialism are all correct.
An example of a positive incentive and a negative incentive?
Positive incentives: Rewards (such as a prize) to people to move them to make certain choices and behave in a certain way.
Negative incentives: Punishments (such as a penalty or a fine) to people for making certain choices. They pursue the opposite behavior.
Why might a private beach be seen as an economic good, while a public beach might be seen as a free good?
Public beach is used by everyone, but a private one is used by a few. Public beaches are abundantly available; private ones are not
Economics is the science of _________
Choice
What is an example of a resource?
Natural Resources: Soil, climate, water, minerals, forests, fisheries
Human-made resources: Machinery, buildings and equipment
Human resources: People and their skills
AND other examples that work
Who decides/controls a market economy?
Families and business through the market
(las familias, las empresas a través del mercado)
What is the term for: The cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another.
Opportunity Cost
What is the economic definition for government failure?
Government failures are the lack of efficiency, lack of incentives and lack of initiatives for workers and companies. An example 16might be: If the government raises taxes on high salaries this improves equity. However, high taxes could decrease incentives to work and to save which negatively affect to efficiency.
The 3 basic questions we must ask when making economic decisions
What to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce.
Primary needs or basic needs are those essential things we have to satisfy for survival such as basic food items and shelter
Secondary needs are those things we desire that may include needs such as leisure, communication or luxury items
What are some disadvantages of a command economy (socialism)?
Lack of efficiency
Lack of incentives for business and workers to work harder
Rigidity in the state plans
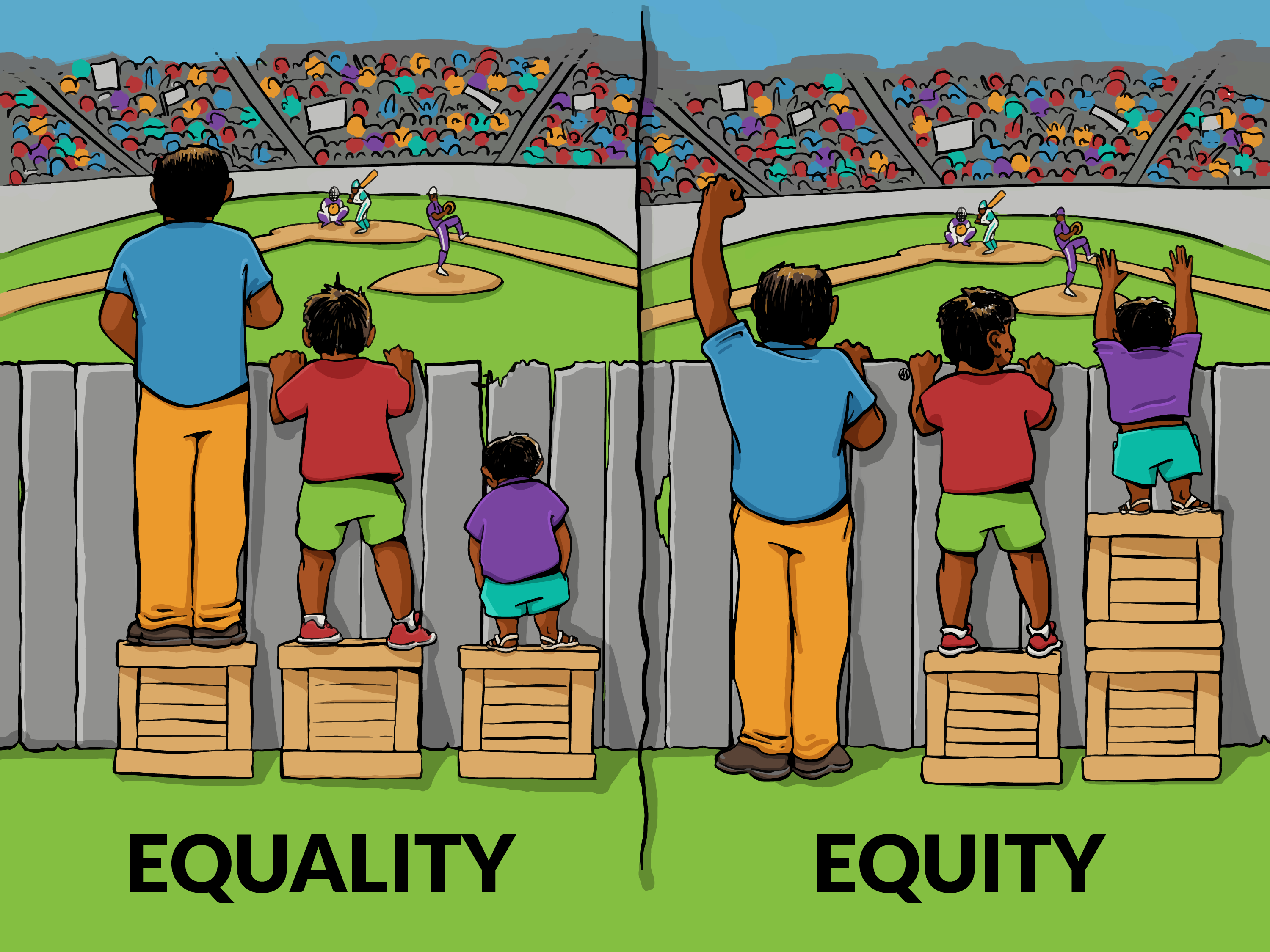
Equality vs. Equity?
What is the "invisible hand" and who first wrote about it?
According to Adam Smith there is an ‘invisible hand’ in the market: consumers and producers act in their own self interest and this leads to the greater public good. In a market economic system, the ´invisible hand´ or natural market forces answers the essential economic questions.
Define scarcity
Scarcity is the universal condition that exists because there is not enough time, money or stuff to satisfy everyone’s needs or wants so that choices must be made.
Difference between economic goods and free goods?
Economic goods are those that are scarce in relation to the demand for it. Therefore, to acquire an economic good a sacrifice must be made.
Free goods are those that are so abundantly available that no sacrifice has to be made to obtain them or use them.
What is a market failure?
Market failure is a situation where market forces give rise to allocative inefficiencies such as: 1) an inequity allocation of resources in an economy (producing at prices that not all consumers can afford). 2) undesirable goods or outputs (such as contamination or bad for health products).
Economic definition of efficiency?
Efficiency consists on reaching maximum production with the available resources, since they are scarce. This implies producing goods at the lower possible cost, minimizing the quantity of resources needed to produce goods and only producing those goods that are needed by people.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs in Order
Physiological, Safety and Security, Love and Belonging, Self-Esteem, Self-Actualization
What is the economic problem?
People have infinite or unlimited needs but there are only limited or finite resources to satisfy those wants.
If something is given away for free, is it always a free good?
No. It is important to know that just because a good is given away for free does not make it a ‘free good’. For example, a supermarket may offer goods that it wants people to try out for free.
However, these are not free goods in the economic sense, because resources have been used to produce these goods and these resources could have been used for something else.
What is a mixed economy?
An economic system where the businesses and consumers control the market, WITH the INTERVENTION of the state/government.
(las empresas, los consumidores con la intervención del estado)
What is marginal analysis?
Marginal analysis assumes that people make their decisions by weighing the additional benefits against the additional costs at the time the decision is made.
It's about comparing the extra benefits (additional benefits or marginal benefits) we get with the additional cost (marginal cost or extra cost) to get them.
What are some classifications of goods and services? (Don't need to name all of them, just 2-3)
shortage, function, degree of elaboration, relationship with each other, character