What is the difference between a vertebrate and an invertebrate? Identify an example of vertebrate and invertebrate animals in the food web below.
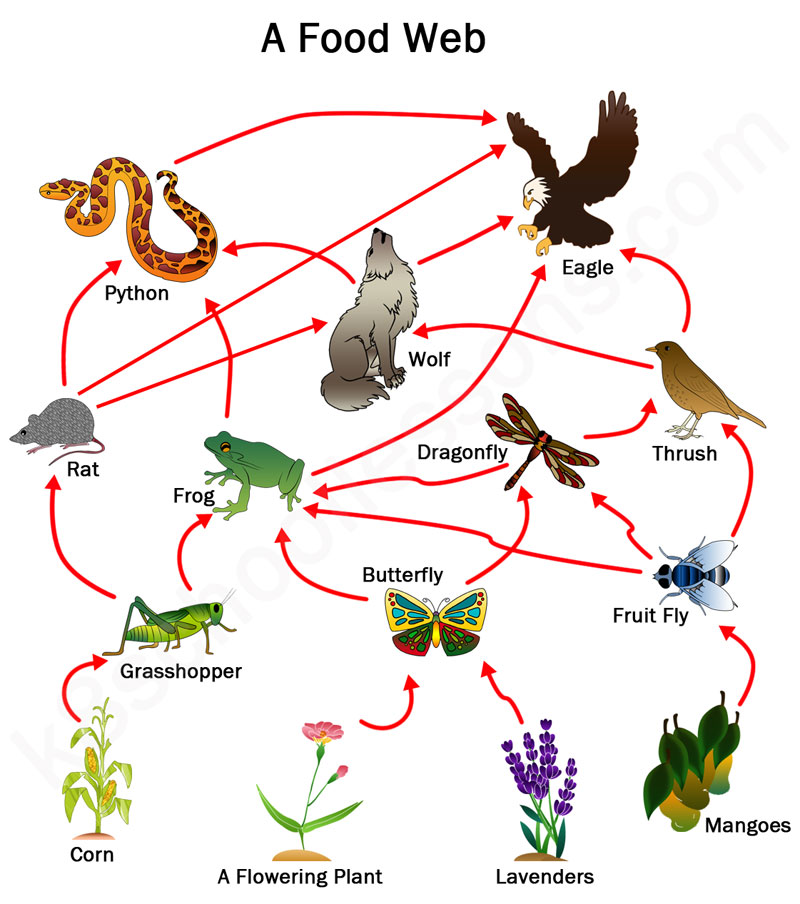
Vertebrate - An animal that has a backbone. E.g., frog, eagle.
Invertebrate - An animal that does not have a backbone.
E.g., grasshopper, fruit fly
What are predators and prey?
Predator - animal that eats another animal
Prey - animal that gets eaten (organism must be able to move and hide from predator to be classified as a prey)
What do arrows in a food chain/web mean?
The arrows represent the direction of energy transfer in an food chain/web.
If the number of grasshoppers decreases, the number of mice and owls will ___________ (increase/decrease).

Decrease
What is the difference between a habitat, environment and ecosystem?
A habitat is the natural home of an organism. Environment refers to the surroundings in which an organism lives. Ecosystem is the interaction between an environment and its components (e.g., water, plants, animals).
What is a competitor?
Competitor- an animal that competes with another animal for the same food
What is a first-order consumer? Give an example from the food web below.

First-order consumers are animals that eat producers. They are always herbivores.
E.g., grasshopper, fruit fly, butterfly
List one advantage and one disadvantage of deforestation
Advantage - wood used by humans for building, paper, land for agriculture, and infrastructure.
Disadvantage - takes away homes and sources of food for animals.
Which ecosystem is expected to have greater biodiversity, a rainforest or a desert?
Rainforests have more biodiversity than any other habitat type due to the moist climate. In contrast, few organisms are adapted to survive in the dry, harsh conditions typical of deserts.
Identify two predator-prey relationships in the food web.

Butterfly (prey), Dragonfly (predator)
Snake (prey), Eagle (predator)
What is a second-order consumer? Given an example from the food web below.

Second-order consumers are animals that eat first-order consumers.
E.g., dragonfly, frog, rat, thrush
List 3 human activities that negatively impact ecosystems. Explain how they impact ecosystems.
Pollution - contaminating air, water, and soil, making it difficult for plants and animals to survive.
Overfishing - disrupting marine food chains and affecting species that rely on fish for food.
Deforestation destroys habitats, leading to the loss of biodiversity and disrupting the balance of ecosystems.
Using the dichotomous key, identify the characteristics of a crocodile.
Vertebrate, does not have feathers, has dry skin --> reptile
Identify two animals that compete with each other for the same food (frog) in the below food web.

Eagle, python
Identify any two food chains in the food web below.

lavender - butterfly - frog - python - eagle
Cane toads are introduced to the food web below. It eats all plants and insects in the food web. How would this impact the food web?

Other animals in the ecosystem that get energy from insects and plants will not have their sources of food. As a result, the population of animals like rats, dragonflies and thrush will decrease, which will further reduce the population of wolves, pythons and eagles.
Are viruses biotic or abiotic? Explain your answer.
Viruses are abiotic. They are not alive because they are unable to reproduce by themselves.
Are animals that are predators also prey? Explain your answer.
Yes. Animals that hunt for food can also be hunted (i.e., become food for other animals).
A keystone species is an organism that holds the ecosystem together. By removing keystone species, the ecosystem will be significantly disrupted. Identify one keystone species that holds the food web together in the food web below.

Wolf, frog
Rabbits were introduced to Australia in the 1800s and soon became an invasive species. Propose three methods scientists might have used to manage the rabbit population.
Setting up traps, creating a virus to control their numbers, and allowing farmers to hunt rabbits.