Which of the following is the simplest level of organization in an ecosystem?
A. Population
B. Organism
C. Community
D. Ecosystem
Organism
Which of the following is a biotic factor in an ecosystem?
A. Rocks
B. Water
C. Trees
D. Sunlight
Trees
What is the best definition of a habitat?
A. An animal's diet
B. The place where an organism lives
C. A type of symbiotic relationship
D. A predator-prey relationship
The place where an organism lives
What is a limiting factor in an ecosystem?
A. A resource that organisms have unlimited access to
B. A factor that restricts population growth
C. An animal at the top of the food chain
D. A plant that produces oxygen
A factor that restricts population growth
What is an example of a predator-prey relationship?
ex. lynx and hare, snake and mouse, etc
Which of the following correctly represents the flow of energy in a food chain?
A. Rabbit → Sun → Grass → Fox
B. Fox → Rabbit → Grass → Sun
C. Sun → Grass → Rabbit → Fox
D. Sun → Fox → Grass → Rabbit
C. Sun → Grass → Rabbit → Fox
Which type of symbiotic relationship benefits both organisms?
A. Parasitism
B. Mutualism
C. Commensalism
D. Predation
B. Mutualism
Which of the following is NOT part of the water cycle?
A. Condensation
B. Evaporation
C. Nitrogen fixation
D. Precipitation
C. Nitrogen fixation
Which level of organization includes only biotic factors?
A. Ecosystem
B. Community
C. Biome
D. Biosphere
Community
Name an abiotic factor that affects ecosystems?
Sun, Temperature, Weather, Water, etc.
What does an organism’s niche describe?
A. Its reproductive cycle
B. The physical space it occupies
C. Its predators
D. The food it eats and its role in the ecosystem
The food it eats and its role in the ecosystem
Which of the following is a density-dependent limiting factor?
A. Natural disasters
B. Disease
C. Climate
D. Sunlight
Disease
What happens to a predator population if the prey population increases?
The predator population increases
Which organism is always found at the base of a food web?
A. Herbivores
B. Carnivores
C. Producers
D. Decomposers
C. Producers
What is an example of commensalism?
A. A tick feeding on a dog
B. A remora fish attaching to shark without harming it
C. Bees pollinating flowers
D. A snake eating a frog
B. A remora fish attaching to shark without harming it
What process moves carbon from plants to animals?
A. Respiration
B. Photosynthesis
C. Consumption
D. Decomposition
C. Consumption
What is a group of the same species living in the same area called?
A. Population
B. Community
C. Ecosystem
D. Biome
Population
Which of these is a way that abiotic factors influence an ecosystem?
A. Temperature affects the types of plants that can grow
B. Birds build nests in trees
C. Wolves hunt deer for food
D. Fungi decompose dead organisms
Temperature affects the types of plants that can grow
Two bird species, a warbler and a woodpecker, live in the same forest. The warbler eats insects from leaves, while the woodpecker drills into tree bark for insects. What does this example best demonstrate?
A. The two birds compete for the same resources
B. The two birds share the same niche and habitat
C. The two birds share the same habitat but have different niches
D. The two birds are in a predator-prey relationship
The two birds share the same habitat but have different niches
What happens when a population exceeds its carrying capacity?
A. It continues growing indefinitely
B. Resources become scarce, and the population declines
C. The ecosystem expands to accommodate the population
D. Predators disappear
Resources become scarce, and the population declines
Which graph shape best represents a predator-prey cycle over time?
A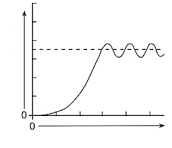 B
B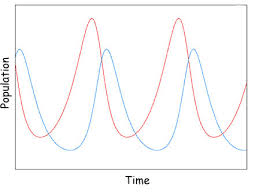 C
C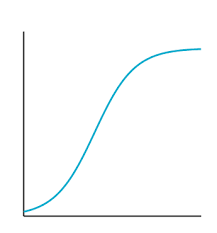

What is the primary reason energy decreases at each level of an energy pyramid?
A. Organisms store most energy in their bones
B. Energy is lost as heat during metabolism
C. Energy is destroyed at each level
D. Producers do not create enough energy
B. Energy is lost as heat during metabolism
Which of the following is an example of parasitism?
A. A bird eating insects off a buffalo
B. A flower being pollinated by a bee
C. A tapeworm inside a dog’s intestine
D. A deer eating grass
C. A tapeworm inside a dog’s intestine
Which of the following is a major contributor to increased carbon in the atmosphere?
A. Decomposers
B. Burning fossil fuels
C. Absorption by plants
D. Formation of limestone
B. Burning fossil fuels
Which of the following is an example of a biome?
A. A herd of deer
B. A tropical rainforest
C. Earth
D. A group of oak trees
A tropical rainforest
Which of the following pairs correctly shows an abiotic factor affecting a biotic factor?
A. Soil nutrients affecting plant growth
B. Birds eating insects
C. A fox chasing a rabbit
D. A tree providing shade for animals
Soil nutrients affecting plant growth
What would likely happen if two species occupied the same niche?
One species would outcompete the other
Which factor would likely increase the carrying capacity of an ecosystem?
A. A prolonged drought
B. An increase in available food and water
C. A new predator introduced to the ecosystem
D. A decrease in plant growth
An increase in available food and water
Which of the following could cause a decline in both predator and prey populations?
A. An increase in prey reproduction
B. A decrease in available resources
C. An increase in predator numbers
D. More prey migration into the area
A decrease in available resources
Which organism would be classified as both a primary and secondary consumer?
A. A wolf that eats a rabbit
B. A hawk that eats a field mouse
C. A bear that eats berries and fish
D. A rabbit that eats grass
C. A bear that eats berries and fish
How is parasitism different from predation?
A. Parasites kill their hosts immediately
B. Predators kill their prey, while parasites usually do not
C. Parasites are beneficial to their hosts
D. There is no difference
B. Predators kill their prey, while parasites usually do not
Why is nitrogen fixation important in the nitrogen cycle?
It allows plants to absorb nitrogen in a usable form
Which level of organization includes both biotic and abiotic factors interacting together?
A. Organism
B. Population
C. Community
D. Ecosystem
Ecosystem
Why is oxygen considered an abiotic factor?
A. It is produced by plants
B. It is necessary for many organisms but is not living itself
C. It is part of the food web
D. It is only used by animals
It is necessary for many organisms but is not living itself
Which scenario demonstrates the competitive exclusion principle?
A. Two fish species feeding on different parts of a coral reef
B. One species of bird driving another species away from a nesting site
C. A wolf pack hunting deer in a forest
D. A parasite feeding off a host without killing it
One species of bird driving another species away from a nesting site
Why do predator-prey relationships help maintain population balance in an ecosystem?
A. Predators ensure that prey species never overpopulate
B. Prey species always outnumber predators
C. Predators eat all the prey and cause extinction
D. Prey species control predator numbers
Predators ensure that prey species never overpopulate
What would most likely happen if a top predator, like a wolf, was removed from an ecosystem?
D. Prey populations would increase unchecked, leading to resource depletion
What is the job of decomposers?
B. They break down organic material and return nutrients to the soil
What would likely happen if all mutualistic relationships disappeared?
A. Many species would struggle to survive
B. Ecosystems would remain the same
C. Organisms would become predators
D. More food would be available
A. Many species would struggle to survive
Which biogeochemical cycles that we examined does NOT involve the atmosphere?
C. Phosphorus cycle