multiple populations of different species living together
Community:
The 3 MAIN CYCLES that we will study are:
Water (Hydrologic)
Carbon
Nitrogen
plants capture CO2 from the atmosphere and use it to make sugar.
BONUS X7
Photosynthesis
Which organisms are usually the pioneer species in primary succession?
A) Trees B) Lichens and mosses C) Shrubs D) Birds
B) Lichens and mosses
Bacteria (or lightning!) in the soil or water convert nitrogen (from the air or water) into forms that plants can use
Nitrogen fixation
sun heats liquid water to vapor and it rises to the atmosphere
Evaporation
Aspects of the environment that limit the size a population can reach
BONUS x 10
Limiting factors
all of the chemical reactions of each cell in an organism that provide energy for life’s processes and create key molecules.
pick a team do do 5 push ups
Metabolism
some water seeps underground from the surface of the Earth.
Aquifer: An underground layer of permeable rock that can hold water.
Infiltration
CO2 released into atmosphere as waste from metabolism.
Cellular Respiration
Why does primary succession take longer than secondary succession? A) More disturbances B) Soil must first be created
C) Animals arrive slower D) Fewer pioneer species
B) Soil must first be created
decomposers, like bacteria, break down dead matter, returning nitrogen to the soil.
Decomposition
Put these molecules in order
NH4 N2 NO3 NO2
N2, NH4, NO2, NO3
limiting factors have a bigger impact on more dense populations.
These are factors that can be triggered by an increase in population size, and thus
Density-dependent
This process can be both sexual and asexual depending on the species
reproduction
water rises back into the atmosphere as water vapor from plants.
Transpiration:
converts carbon from once-living organisms into fossil fuels through intense heat and compression.
Fossilization
Why might areas with frequent disturbances remain dominated by pioneer species?
A) They never allow soil to form
B) Disturbances favor quick-growing species
C) Pioneer species are climax species
D) Soil is destroyed in climax communities
B) Disturbances favor quick-growing species
Bacteria convert nitrogen from waste (urine and feces) into ammonia.
Ammonification
German Scientist developed system to extract atomospheric N2 into ammonium nitrate
Fritz Haber
There are two kinds of limiting factors
biotic and abiotic
Which is the correct order of organization.
A. Kingdom, class, genus, species, order, phylum, family
B. Species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom
C. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
D. Kingdom, order, class, phylum, genus, family, species
C. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
what is the name of this underground layer of porous, honeycombed, water-bearing rock that is between 300-700 feet thick. #2 name the AQUIFER it creates
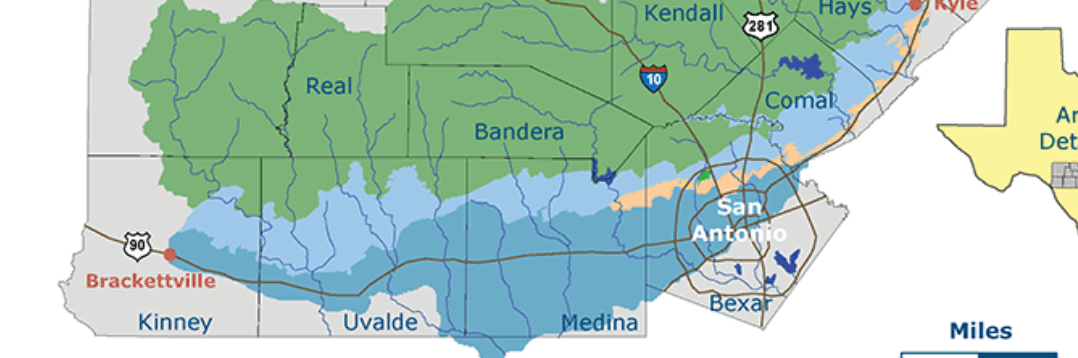
Limestone - Edwards Aquifer
(like bacteria, earthworms, and fungi) break down dead materials and return nutrients (like carbon) to the soil.
Decomposers
Describe one of the main differences in both primary and secondary succession in terms of their starting points.
while both have the same end point (climax community) they have difference starting points and pioneer species
secondary succession has a head start since it already has multiple layers of living soil
Name these molecules.
NH4 NO3 CO2 N2
ammonium
nitrate
carbon dioxide
atmospheric nitrogen
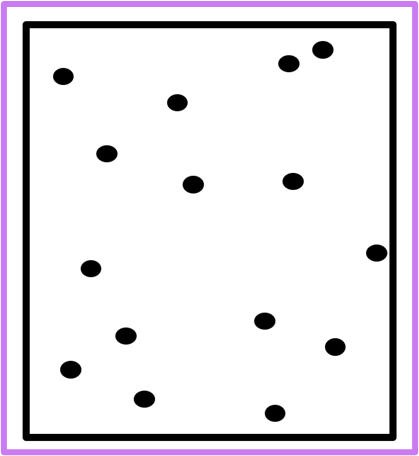
Random dispersion pattern
what kind of pattern AND give an example of a species that follows this pattern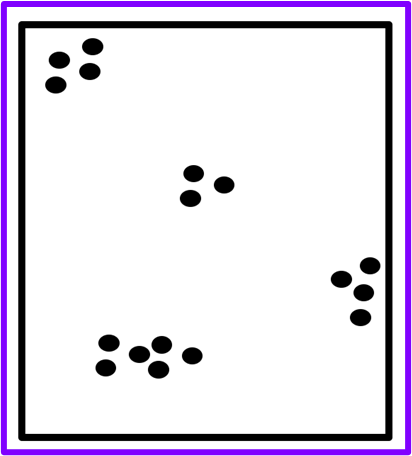
clumped dispersion pattern
Binomial Nomenclature: 2-name naming system by this scientist
Carol Linnaeus
when a body of water becomes overly enriched with nutrients, causing excessive algae growth
Eutrophication
when wood or fossil fuels, which contain carbon, are burned causing the release of CO2 in the atmosphere
Combustion
What is a climax community?
A) An unstable ecosystem B) The first community to form on bare rock
C) A mature and stable community
D) A community destroyed by disturbance
C) A mature and stable community
bacteria convert nitrogen in ammonia to N2 so it can go back into the atmosphere
BONUS X3
Denitrification
the theoretical maximum population that a given environment could support
BONUS TAKE AWAY 500 POINTS FROM ANOTHER GROUP
Carrying Capacity
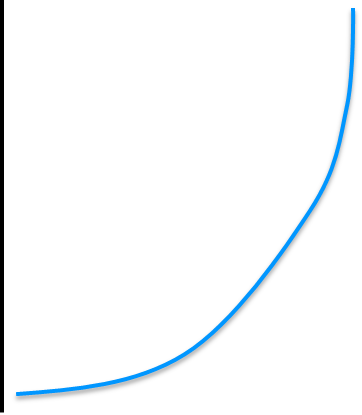
exponential growth pattern