Define and provide an example of Adaptation/s
The process or the state of adjusting or changing to become more suited to an environment, the trait as a result of the process.
What is a food chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms in an ecosystem, showing who eats whom. It describes the transfer of energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
What are the scientific words for living and non-living things? Define and provide one example of each.
Biotic factors are the living components present in an ecosystem. More specifically, it includes all flora and fauna.
- Plants
- Animals
- Fungi
- Bacteria
Abiotic factors refer to all the non-living components present in an ecosystem. It typically comprises physical and chemical components.
- Climate
- Humidity
- Precipitation
- Wind
- Altitude
- Type of soil
- Light penetration
- Water depth
- Oxygen content
- Turbidity
Define Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a system that environments and their organisms form through their interaction. The biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
What is a nocturnal animal? Explain a relevant adaptation for a nocturnal animal.
Nocturnal animals sleep during the day because they are adapted to be active and hunt during the night. Their eyesight, hearing, and other senses are well-developed to navigate in low light conditions. Sleeping during the day allows them to conserve energy and avoid predators that are more active during daylight hours. This behavior is common in animals such as owls, bats, and some species of rodents and insects.
Identify one secondary consumer in this food web.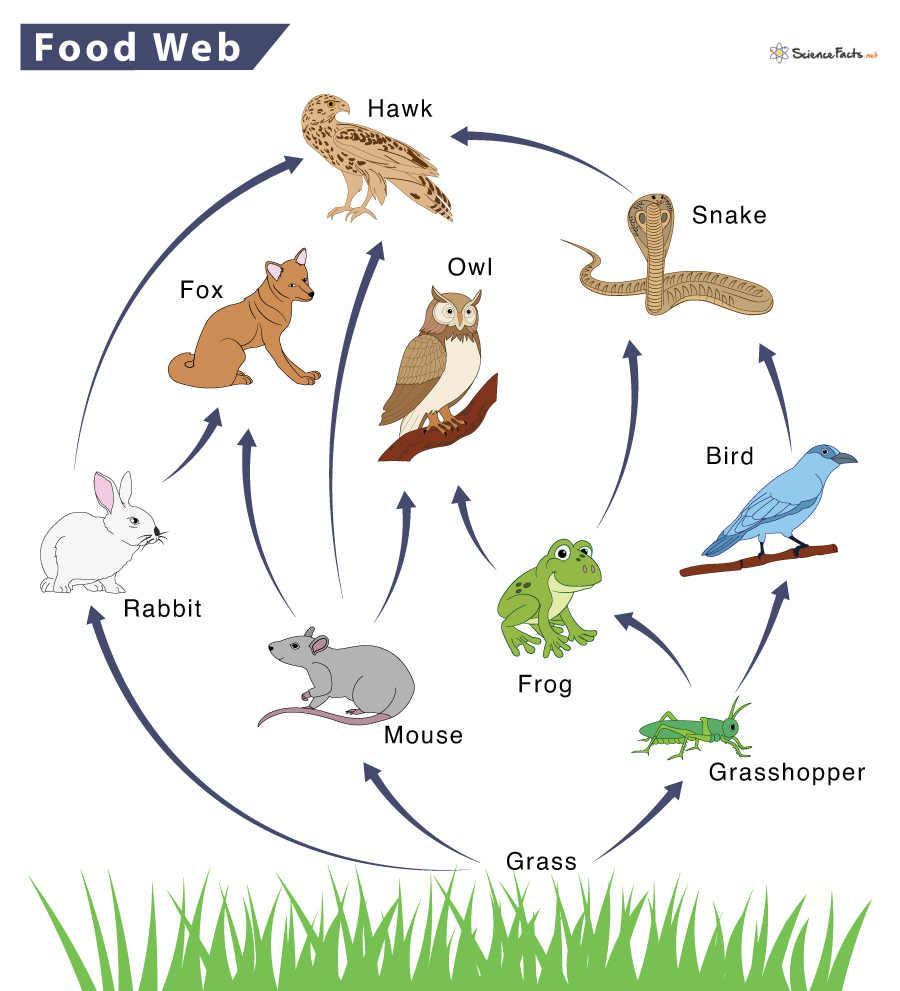
Fox, Owl, Frog, Bird
Identify one way in which light can affect living organisms.
Light can affect living organisms in different ways:
- Coloration: Light influences the coloration of animal skin or feathers.
- Growth and Reproduction: Light impacts growth and reproduction in different species.
- Migration and Hibernation: Light affects migration patterns and hibernation.
- Circadian Rhythm: Nocturnal light can interrupt sleep and affect the internal clock.
- Attraction and Repulsion: Light can attract or repel organisms, impacting their habitat and survival.
Define Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living species on Earth, including plants, animals, bacteria and fungi. While Earth’s biodiversity is so rich that many species have yet to be discovered, many species are being threatened with extinction due to human activities, putting the Earth’s magnificent biodiversity at risk.
Explain and justify an adaptation in habitats where food is scarce (little to be found), why some animals may have long necks or humps.
Animals such as Giraffes and turtles have long necks to obtain food or animals such as camels and whales have humps which act as special storage structures for food and water.
List 4 levels (components) of a food chain.
Producer
Primary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Tertiary Consumer
Quarternary Consumer
Apex Predator
How do you identify between living and non-living things? Explain.
MRS GRENC.
Movement
Respiration
Sensitivity
Growth
Reproduction
Energy
Nutrition
Cells.
All of these actions above are essential to life.
If you replied no to any of these (the object does not have them, need them, use them or capable of that action), it is non-living.
Define predation, label 3 sub-types and provide at least 5 examples (of any sub-type).
Predation refers to a flow of energy between two organisms, predator and prey. In this interaction, the prey loses energy, and the predator gains energy.
"Egg -- larva -- pupa -- adult" is one example of the stages of metamorphosis.
Explain how metamorphosis is an example of an adaptation.
The sequence "Egg -- larva -- pupa -- adult" represents the stages of metamorphosis commonly seen in insects like butterflies and beetles. In this process, an organism undergoes a series of distinct physical changes, starting from an egg, then progressing to a larva (caterpillar), followed by a pupa (chrysalis or cocoon), and finally transforming into an adult form. This transformation allows the organism to adapt to different environments and fulfill different ecological roles at each stage.
Name the two additional trophic levels which exist in a food web and not in a food chain
Detrivores and Decomposers
Provide a definition and example of Competition
Competition is a relationship between organisms or species that require a resource that is in limited supply123. Competition can be direct or indirect, and can occur within or between groups2. Competition lowers the fitness of both organisms or species involved, but can also improve the adaptations of the same species.
E.g, Baby birds in a nest trying to get food from a parent.
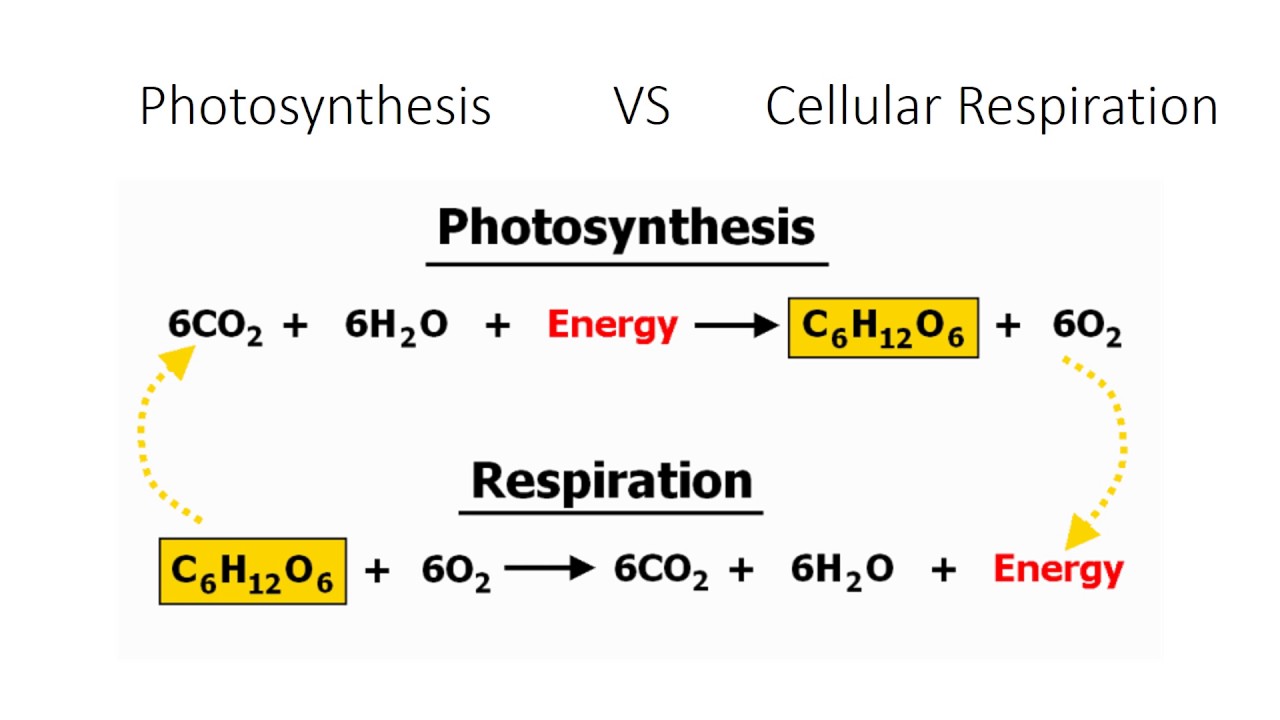
What is Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration? What is the difference between the two? Provide the formula for at least one of these.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy.
Cellular respiration is a process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules to produce energy.
Photosynthesis is performed by plants whilst cellular respiration is performed by animals. This is how living things respirate (by one or the other).
List three ways a polar bear is adapted to live in cold climates.
- White appearance: Camouflage from prey on the snow and ice.
- Thick layers of fat and fur: Insulation against the cold.
- Small surface area to volume ratio: Minimizes heat loss.
- Greasy coat that sheds water after swimming: Helps reduce heat loss.
Name a secondary consumer which is not a tertiary consumer or apex predator.
Whiptail.
Provide a definition and example of Commensalism
Commensalism is a relationship between two species in which one obtains benefits from the other without harming or benefiting it.
E.g,
- Barnacles on the back of a whale: Barnacles attach to whales and benefit from their movement.
- Bait Fish and Manta Rays: Small bait fish are protected by their proximity to larger manta rays.
Explain the events in the infographic below.
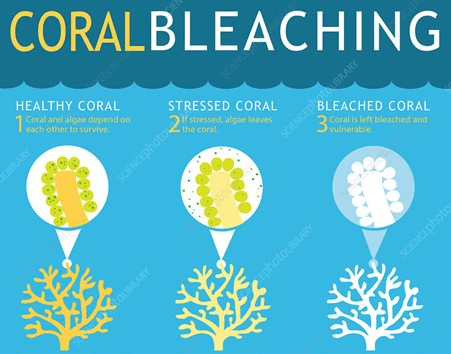
Coral bleaching is an example of what happens when abiotic factors move out of the zone of tolerance.
Coral live in a mutualistic relationship with an algae called zooxanthellae. The algae live inside the structure of the coral. The coral provides the algae with a home and the algae photosynthesise and provide the coral with 90% of its energy requirements. The algae are also responsible for the corals colour.
If the water temperature or pollution levels (which affects the pH of the water) increase to outside the corals zone of tolerance, the coral expels the algae and becomes bleached. If temperatures and pollution levels return to normal, the coral allows the algae to return and so it will recover. If the levels remain too high for a long period of time, then the coral will die because it is not receiving the energy it needs.