What general trend is observed in atmospheric CO₂ levels from 2000 to 2020?
The carbon dioxide level is increasing at a fairly constant rate.
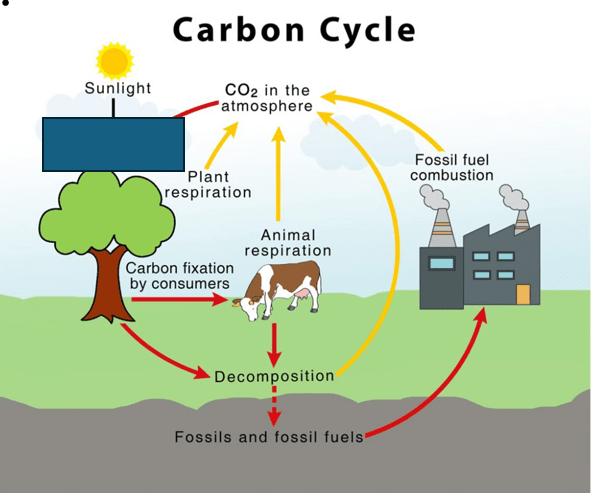
What process is missing?
What is Photosynthesis
What is eutrophication and algae blooms caused by?
Use of fertilizers
Which human activity is most responsible for disrupting the nitrogen cycle?
A. Deforestation B. Use of fertilizers C. Burning fossil fuels D. Overfishing
B. Use of fertilizers
Walking or biking
Washing clothes in cold water
Hanging clothes up to dry
Recycling or repairing things
What are ways to slow climate change
What is happening in this graph?
The lynx population increases after the population of rabbits increases.
90 percent of the energy is lost as heat during body processes, only 10 percent of the energy is available to be used at the next level.
What is the food chain?
Deforestation → How does this impact the carbon cycle?
It causes increased concentrations of atmospheric Carbon dioxide.
An increase in atmospheric CO₂ is most likely to directly result in
A. Eutrophication B. Global warming C. Acid rain D. Ozone depletion
An increase in atmospheric CO₂ is most likely to directly result in: B. Global warming
How can urban planning be adjusted to minimize disruption to ecosystems?
Incorporate green spaces, establish wildlife corridors, institute storm water runoff for watering gardens

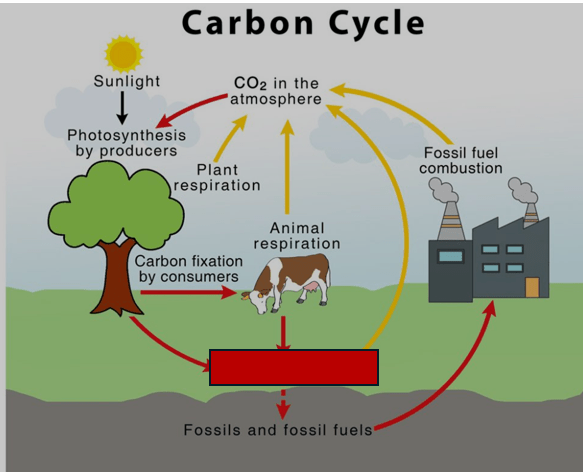
What process is missing between animals and the soil?
What is decomposition?
What are producers
Cause: Overfishing → how can this destabilize a marine food web?
Overfishing causes the populations of organisms below the fish in the food chain to increase
Reduce, reuse, repair and recycle. ...
Eat more vegetables. ...
Throw away less food.
What are ways to help the environment
Why is biodiversity important to an ecosystem's stability?
Different species often perform similar functions within an ecosystem (e.g., pollination, nutrient cycling). If one species is lost, others can take over its role, maintaining ecosystem functions and stability.
If a food chain is missing its producers, what would happen to the levels above?
All levels above the producers will die as well.
Design a food web using at least 4 organisms.
What is a keystone species
What types of animals are in a stable ecosystem?
Producers, consumers, and decomposers
Accidental ingestion: mammals, mistake plastic debris for food and can die.
What is recycling plastics
What effect does loss of species have on an ecosystem?
Fewer species means fewer roles filled (predators, pollinators, SEED DISPERSERS, decomposers, etc.).
With fewer “backup” species, losing even one organism can destabilize food webs.
A HUGE DECREASE AROUND THE TIME OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION.
Squirrels, butterflies, rabbits
What are primary consumers
What effect does urbanization have on the environment?
Loss of animals native to the area
Loss of plants
Reduced biodiversity
Environmental pollution
What can cause eutrophication of water?
Chemical fertilizers and pesticides
Eating less meat
Turning off lights when you leave a room
Buying less plastic
What are ways you will help protect the environment?
