A non-native species whose introduction causes or is likely to cause economic harm, environmental harm, or harm to human health.
Invasive Species
Invasive plants can disrupt this cycle. 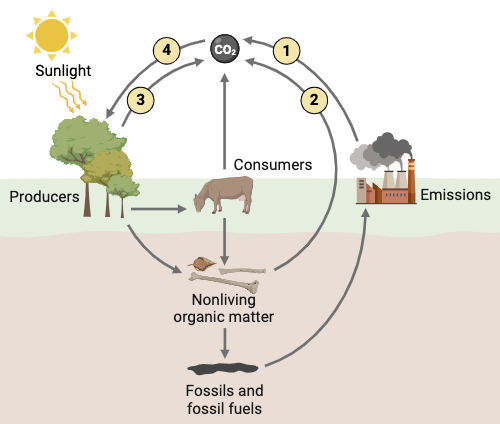
The Carbon Cycle.
Invasive species are the cause of more than (10, 20, 50) percent of native species being classified as either endangered or threatened.
50%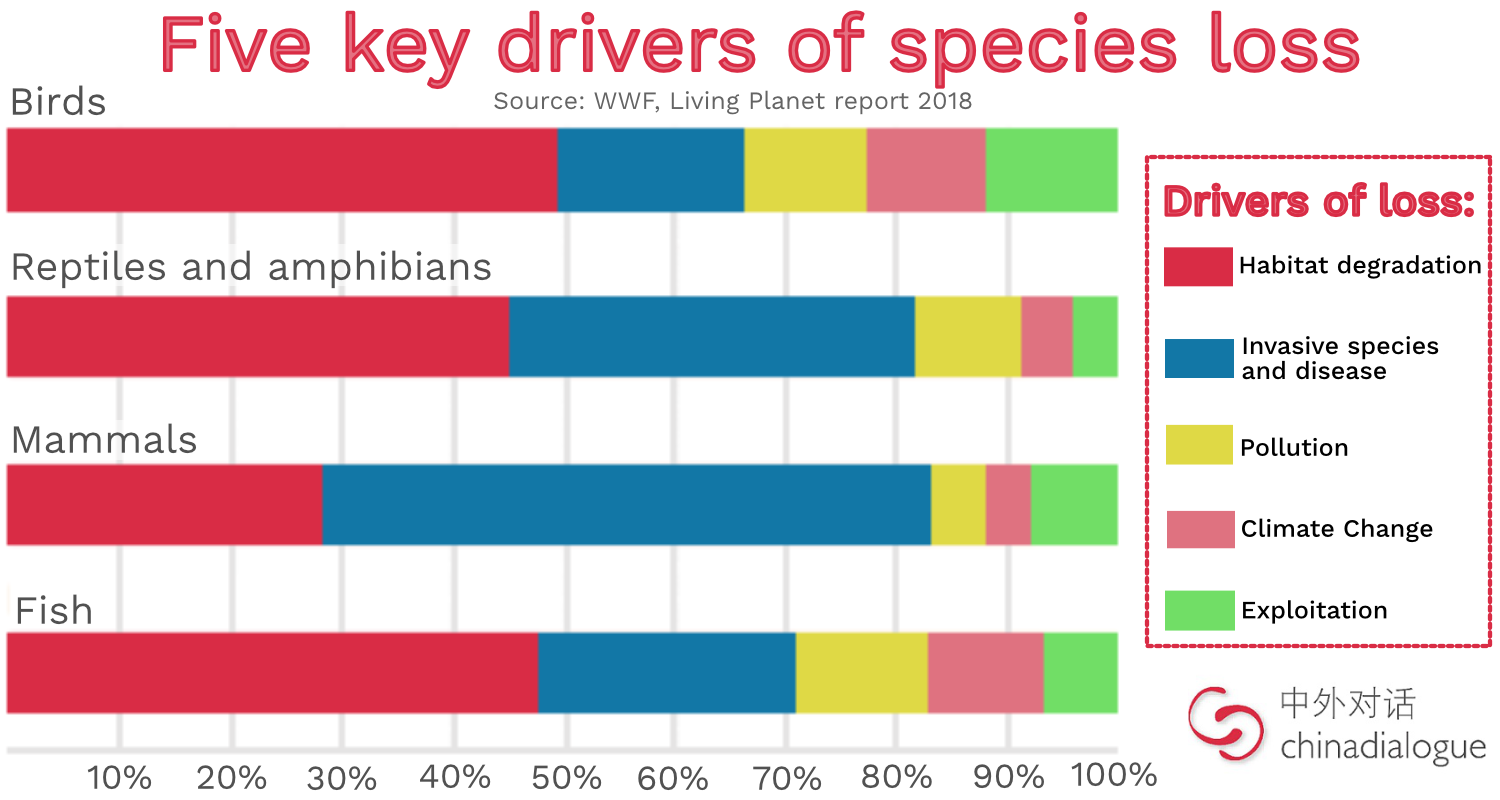
Invasive species can severely impact water ________ by changing nutrient dynamics.
Water quality.
With shallower roots systems invasives may (increase/ decrease) rates of erosion. 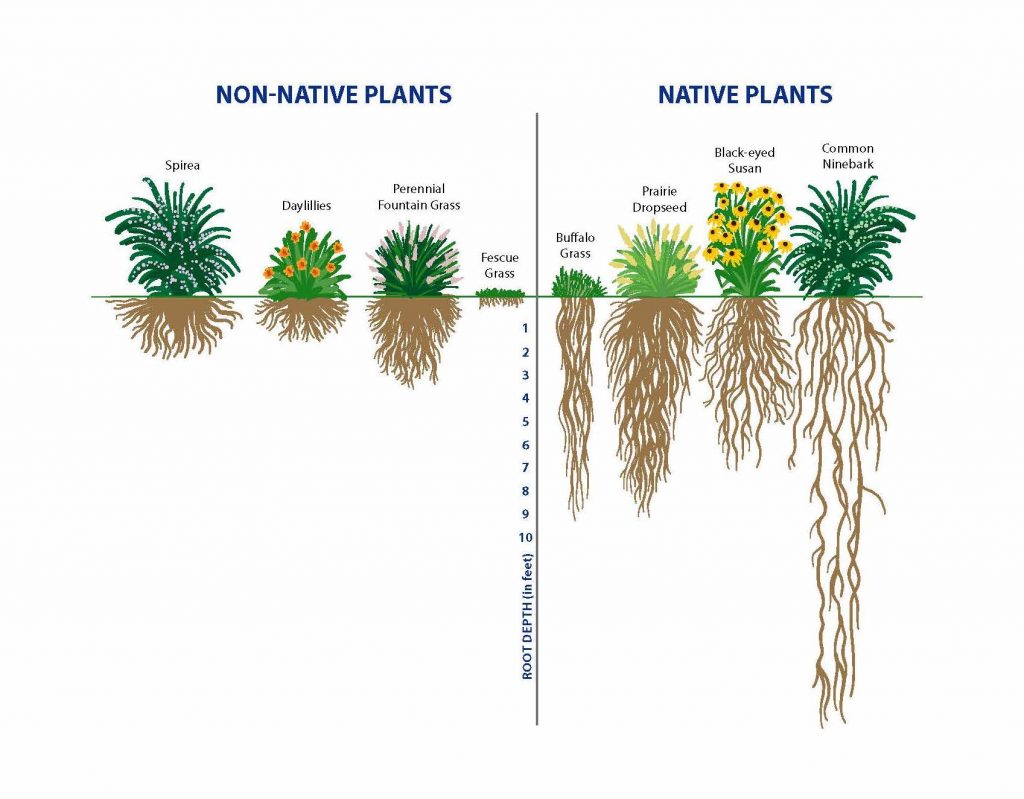
Increase.
An organism, plant, or animal that occurs naturally in a given area or ecosystem, meaning its presence is the result of natural processes, not human intervention
Native Species
Invasives may store (more/less) carbon than native species increasing the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Less
The global phenomenon, related to life, that invasives are contributing to.
Biodiversity Loss.

Water flow disruption.
The sustained potential of a soil to function as a growth medium for plants and soil organisms, through the provision of nutrients, water and habitat, for the long-term health and benefit of man and the environment
Soil Health.
One reason they are introduced.
Accidental, landscaping, aquariums, shipping, hitchhikers, intentional.
Invasives may increase the risk of this phenomenon, causing more CO2 to be released into the atmosphere.
Wildfires.
Invasives disrupt the balance of these essential units of nature.
Ecosystems.
Aquatic invasive species can harm our water supply by:
Clogging pipes that decrease water flows for drinking water and agriculture
1) soil acidification, 2) competition with other plant species, thereby decreasing above-ground and below-ground diversity, 3) release of allelopathic* compounds suppressing growth potential of other plants, and 4) changing of the soil microbiome through the alteration of fungal and bacterial associations.
One of the invasive species in Coachella Valley.
Fountain grass, Sahara mustard, Tamarisk, Giant reed, Barbed goat grass, Italian thistle, Red gum, Mexican fan palm, Yellow fever mosquito
The global phenomenon, related to the atmosphere, that invasives are contributing to.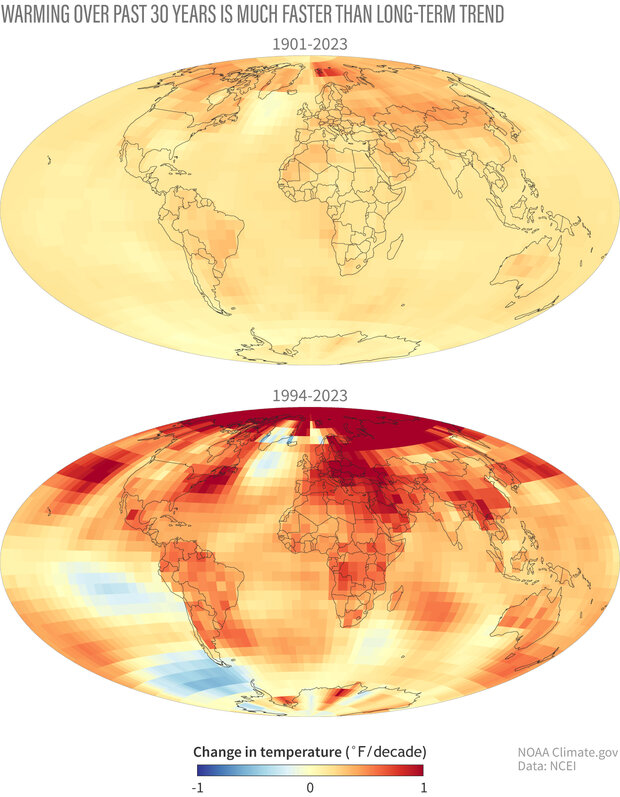
Climate Change
Two ways invasives can directly reduce native population numbers.
Predation and competition.
Invasive algae blooms can deplete oxygen causing these occur in water bodies.
Dead Zones.
One way invasives can change soil structure.
The root systems can compact soil and reduce its ability to absorb water.
Where did Saharan mustard come from? How did it get here, we think. 
Africa, seeds hitchhiked on date palm trees or other agricultural products.
Invasives may change the composition and structure of these, influencing local climate by affecting temperature and humidity levels.
Forests. (ecosystems)
One example of an invasive animal in Coachella.
Red imported fire ant, Brown widow spider, House sparrow, European starling, Bullfrog, Domestic cat, European honeybee, Rock dove, Mediterranean gecko, Aedes mosquito
Types of human activity that invasives can disrupt, related to water.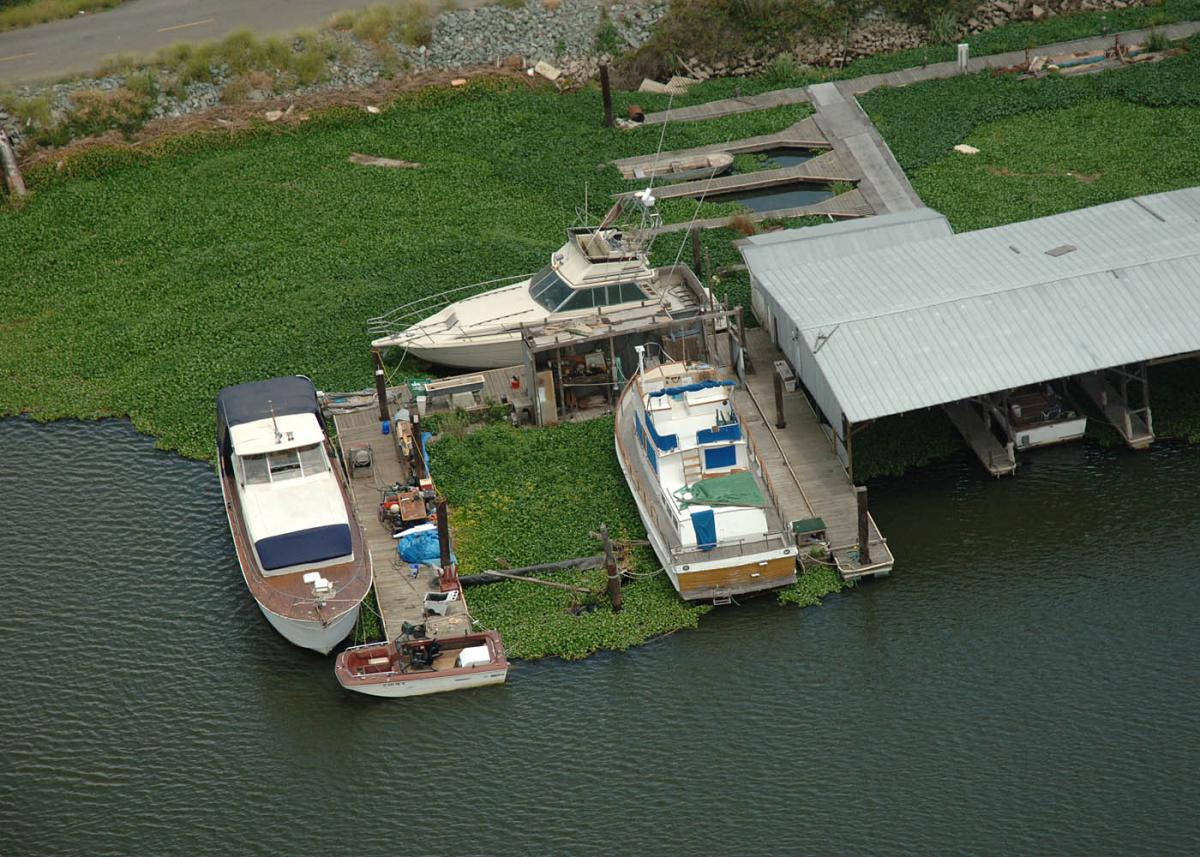 
Recreation, agriculture, fishing, boating, irrigation, water storage, water quality management, flood control, habitat restoration, wildlife conservation, drinking water supply, hydroelectric power generation.
The global phenomenon, related to soil degradation, that invasives are contributing to.
Desertification.