L-Ink
L-Bees
The 3 major bones of the elbow
What is the humerus, radius, and ulna?
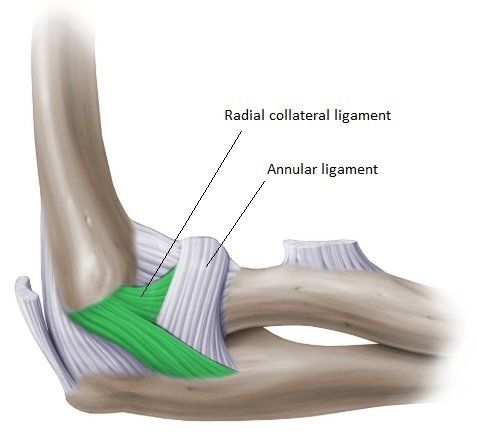
The ligament prevents subluxation of the radial head
What is the annular ligament?
These 3 muscles flex at the elbow

Name the shared nerve root for the muscles?
What are brachialis, biceps brachii,and brachioradialis?
They all share C5 and C6 (brachialis and brachioradialis have some C7 as well)
In a child patient, the inability to bend the elbow after falling on outstretched hand can result in this posterior type of injury
What is dislocation?
The annular ligament links the ulna to this structure
What is the radial head?

The triceps brachii inserts onto this bony landmark
What is the olecranon process? 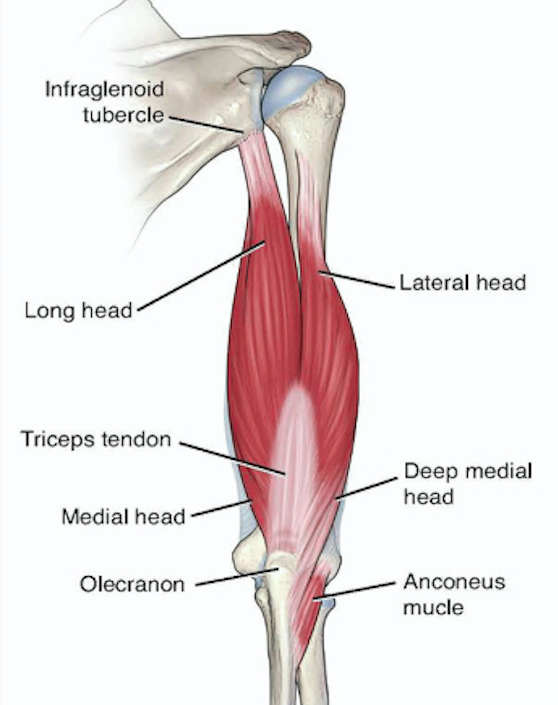
Excessive throwing can cause injury to this ligament
What is the Ulnar collateral ligament?

Name all of the motions that occur at the elbow and the ROM for each +/- 15 degrees
Flexion: 150 degrees
Extension: 0 degrees
Supination: 90 degrees
Pronation: 90 degrees

The injury known as golfer's elbow
What is Medial Epicondylitis?
This is the formal name for Little Leaguer's elbow
What is traction apophysitis of the medial epicondyle?
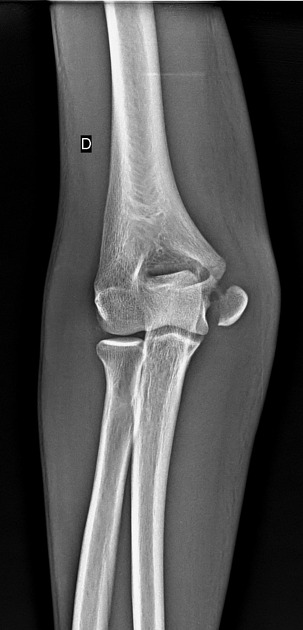
Two bony prominences on the ulna that form the articulating surface with the humerus
Coronoid process, olecranon process 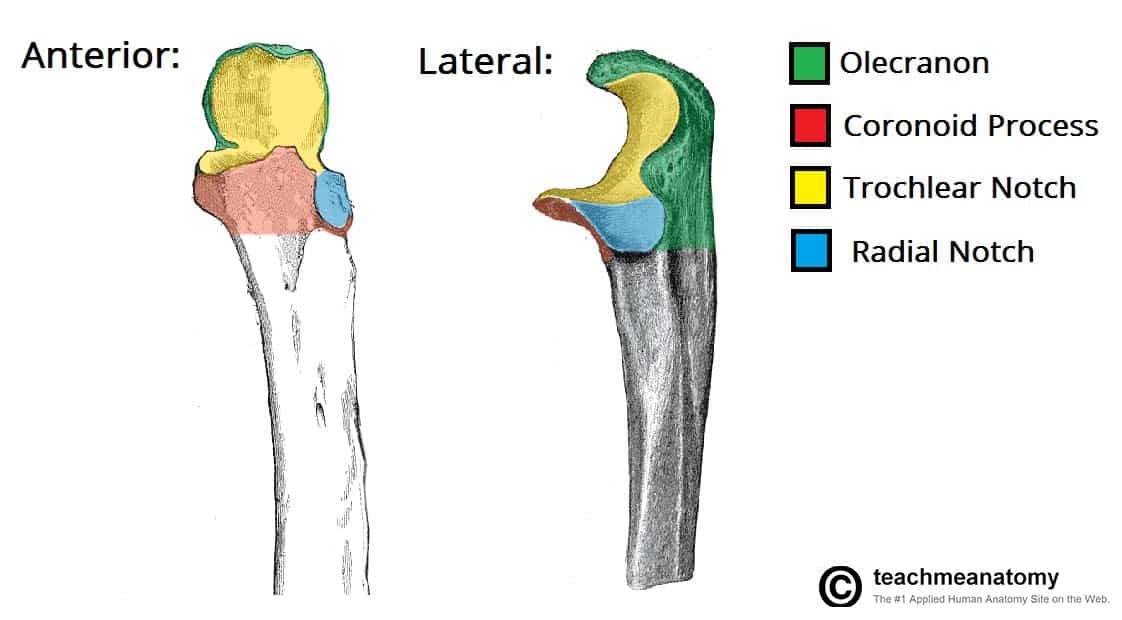
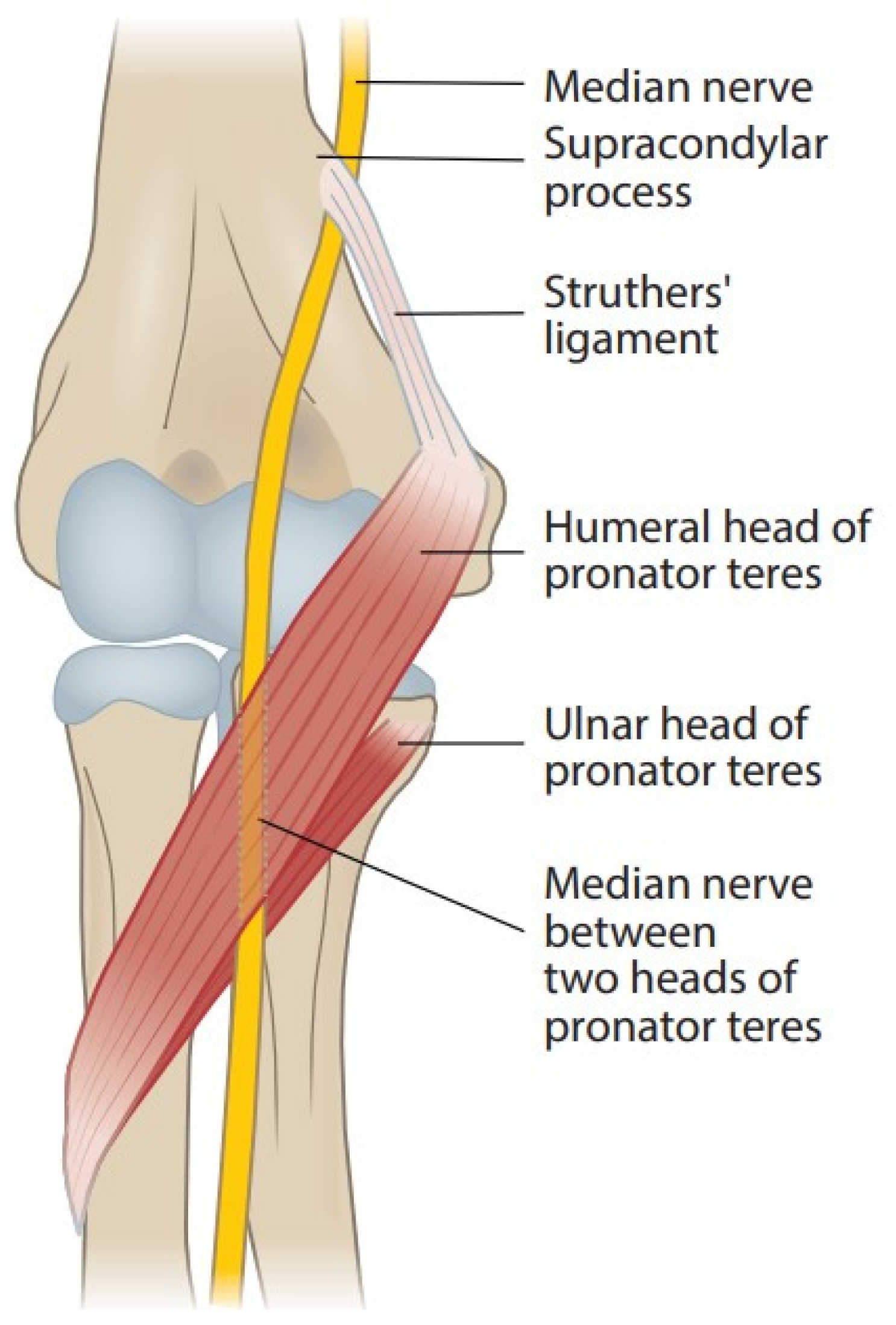
This ligament can compress the median nerve in the elbow
What is the ligament of Struthers?

This is the most common angle for fusion (can name either unilateral or bilateral elbow fusion)
What is 90 degrees if unilateral, or 110 in one arm and 65 in the other if bilateral


Name and show the two provacative tests for lateral epicondylitis.
What is Cozen's and Mill's test?
Cozen: The examiner stabilizes the elbow with a thumb over the extensor tendon origin just distal to the lateral epicondyle. Pain in the lateral epicondyle is seen with the patient making a fist, pronating the forearm, and radially deviating and extending the wrist against resistance by the examiner.
Mill’s test – Passive extension of the elbow with forced flexion of the wrist with radial deviation may precipitate pain at the lateral epicondyle

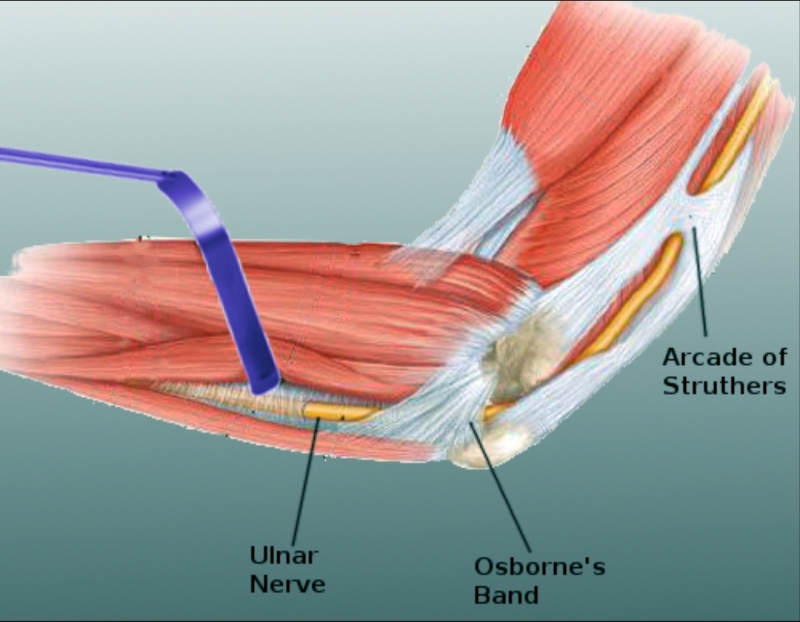
The ulnar nerve can be compromised at the elbow by many factors. The most likely anatomic cause is via compression with what?
What is the Arcade of Struthers?
A midshaft humeral fracture can nerve injury which leads to weakness of these muscles (name 3)
What is:
- Extensor digitorum
- Supinator muscle
- Extensor digiti minimi (EDM)
- Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
- Abductor pollicis longus (APL)
- Extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
- Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
- Extensor indicis proprius (EIP)
This is a named syndrome which occurs when the median nerve is compressed at the elbow by a pronator in the forearm
What is Pronator Syndrome?
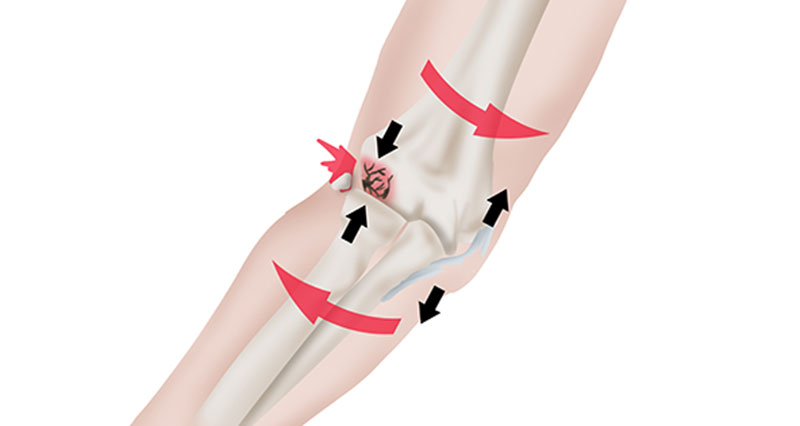
Carrying angle for men and women
What is 5 degrees of valgus in men and 10-15 degrees in women?
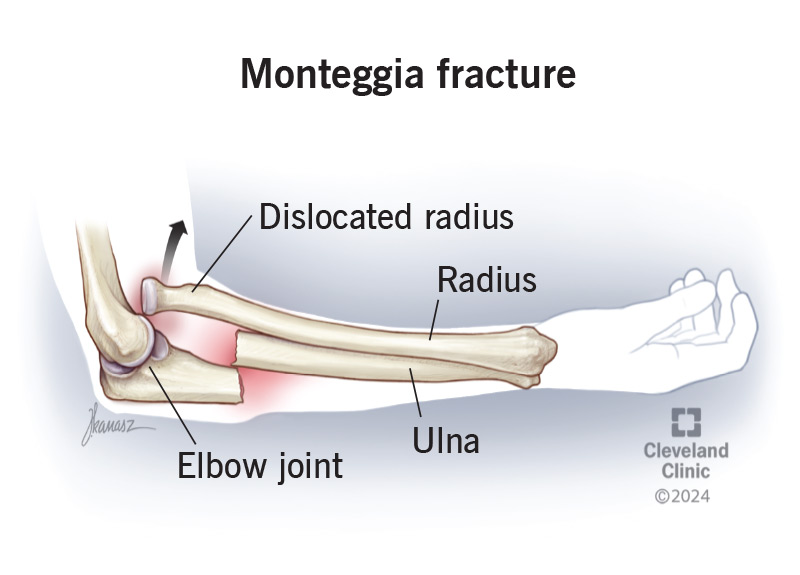
A direct blow to the forearm that causes a proximal ulna fracture with dislocation of the radial head
What is a Monteggia fracture?
A direct blow to the forearm that results in a fracture of the distal radius that causes dislocation of the ulna
What is Galeazzi fracture?

MUgGeR
Monteggia= Ulnar fx ----Galeazzi= Radial fx
M is more proximal in the alphabet, Z is most distal
This is informally called Panner's Disease and is believes to be caused by changes to blood supply in the elbow leading to resorption of the ossification center followed by repair/replacement. Symptoms are worse with use, assoc. w/tenderness at the lateral elbow, and seen in young men
What is Osteochondrosis of the elbow (which is an epiphysial aseptic necrosis of the capitellum)?

The short head of the biceps and the long head of the biceps have different insertions. Name the origin and insertion across the elbow
Origin:
Short head- coracoid process of the scapula
Long head- supraglenoid tubercle (and superior glenoid labrum of the scapula)
Insertion:
Radial tuberosity of the radius

This condition is caused by tensile stress in the medial elbow and lateral shear stress in the posterior aspect of the elbow that causes an olecranon osteophytosis and loose body formation secondary to repetitive abutment of the olecranon against the olecranon fossa. Patients have elbow pain, catching or locking at the elbow.
What is valgus extension overload (VEO)?

Hooray! Your patient has tennis elbow, they've been treated.
Oh no! They want to return to play.
You recommend at least one of the two changes to equipment
What is decrease string tension below 55 lbs or increase grip size?
This is the ancient word for the foundation of the word pound, often denoted as "lbs."
What is the libra?