Please describe what domains and sub-domains are.
Domains are the major categories of childrens development. Sub-domains are specific skills within these categories.
How often must each of the essential learning domains be addressed in lesson plans?
a) Daily
b) Weekly
c) Monthly
b) Weekly
Lesson planning is done in weekly blocks. Each essential learning domain must be addressed at least once during the course of a week.
Remember, certain activities often address more than one learning domain at a time. Activities can be repeated and there is no rule that you must have a new or different activity for each day of the week. Children often thrive with repetition)
(Example: retelling the same story multiple days in a row in different formats, playing the same game multiple days in a row etc.)
When would a teacher mark off "Yes" next to a skill?
When a child consistently exhibits a skill on their own.
What is one advantage of performing Planned Observations?
•Teachers can target specific skills
•Information gathered is accurate and concise
•Physical documentation can be easily gathered (photos, notes etc.)
•Teachers can observe multiple children at once
TRUE or FALSE
Developmental domains never overlap and are not interrelated in any way.
FALSE
Although developmental milestones are
described within separate domains in the
guidelines in order to provide an organizational
scheme to the document, in practice child
development and learning across domains are
highly interrelated. (p.6 ELDGs)
TRUE or FALSE
You must have a new activity for every learning domain on your lesson plan for every day of the week.
FALSE
There is no lesson plan police! You can repeat the same activity multiple times depending on the interest level and progression of your classroom.
How soon after a child enrolls in your classroom should you perform an observation and assessment?
No later than 90 days (Colorado Shines)
What is a work sample and why are they helpful?
Work Samples: Visible work that educators can save for portfolios
•Work samples are records that children create
•Effective documentation strategy
•Collecting work samples over time is likely to show progress more effectively.
What are the four sub-domains of Creative Art & Expression for children aged 3-5?
(Hint: Page 105 in ELDG's)
1. Music
2. Creative Movement & Dance
3. Art
4. Drama & Theater Arts
You are an older Infant Room Teacher (9-18 months)
Use the ELDG's to come up with an activity to put on your lesson plan that supports Relationships with Peers.
(Hint: Look under suggested supports, p. 35)
*Roll the Ball Game*
"Engage older infants in simple games with one
another (e.g., rolling a ball with two or three
children and saying, “i’m rolling the ball to
Joey; Joey is rolling the ball to izzy.”
In this Observation, the child exhibited 6/11 indicators of Print and Alphabet Knowledge. Is this skill Emerging, Developing or Mastering?

Developing
6/11= 54%

What is ONE characteristic of a skilled observer?
Intentional
Knowledgeable
Inquisitive
Unbiased
In the Moment
For Infants and Toddlers, what domain is a precurser for emerging Math and Science skills in preschool (Hint: Look at the Wheel!)
Cognitive Development is a precursor to several developmental domains including Math, Science, Social Studies, Creative Arts and Logic/Reasoning.
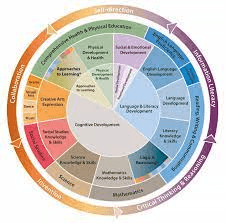
To help children build their emerging understanding of mathematics, it is important for caregivers to frequently use math-related concepts in their
interactions with babies and toddlers. These early ideas about number and size lay the foundation for the development of more advanced mathematical concepts. Learning to discriminate between objects based on their different attributes is important not only for learning mathematics—it is critical for developing logic and reasoning. Early developments underlying logical reasoning and other essential cognitive processes will not only contribute to children’s future mastery of school subjects, but will also help them in problem solving across a variety of contexts. (ELDG's, p. 9)
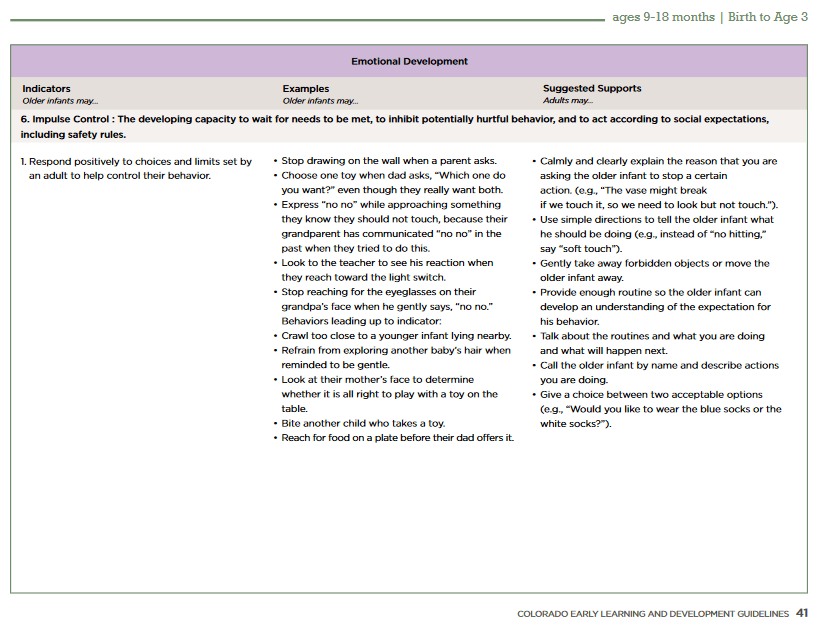
What page number could I find examples of typical behavior for a young infant or toddler (9-18 months) learning Impulse Control and ideas for how to support development of this skill?
(Hint: Emotional Development)
Page 41
Donna is Preschool teacher. Donna is completing her observation and assessment tool for a 5 year old named Lilly who recently enrolled in her class.
Lilly can count up to 50 and is able to recognize most printed numbers up to 20. But Donna hasn't yet observed if Lilly is able to write any numbers yet. Since Lilly is so good at counting and reading numbers, Donna checks "Yes" next to that skill because it is safe to assume that Lilly is very likely to be able to write at least some numerals from 0-10.
Is Donna making the right choice? Why or Why Not? What do you think Donna should do?This is not best practice.
Remember, a skilled observer is inquisitive and does not make assumptions about children. Donna should plan an activity where she can observe Lilly to assess Lilly's abilities. She may keep work samples or take photos or a video of Lilly doing the activity to reference later and add into her portfolio.
Is this an example of a subjective or objective observation?
"Jaylen hates doing art, he never wants to participate"
This is a subjective observation. This is an assumption, hates and never are subjective words.
What are the facts? Be inquisitive, investigate and observe further.
"Jaylen chose not to do the painting activity today. Teachers encouraged him to join. Jaylen wanted to count coins in the cash register instead"