Magnitude of charge and distance between electric charges
What is the units of an electric field?
Newtons/Coulombs
Name 2 examples of a conductor
Silver
Gold
Copper
Steel
Sea Water
Metals generally
What is the equation for the force of rotational motion?
F=mv^2/r
Like charges _____, opposite charges ______
attract, repel
Name the 4 fundamental forces
1. weak force
2. strong force
3. electromagnetic force
4. gravitational force
What is the electric flux if the field lines are parallel to the surface?
0 -> angle is 90, so cos(90)=0
Name 2 examples of an insulator
rubber
glass
oil
diamond
dry wood
Who discovered the 3 laws of motion?
Newton
What is the basic unit of charge? (A number)
1.6 x 10^-25 C
If the charges of two particles double and the distance stays the same, what happens to the force?
Multiplies by 4
Electricity is caused by...
The movement of electrons
A balloon is rubbed on a cloth and all the positive charges move to one side of the balloon and all the negative to the other side. Is the balloon a conductor or insulator?
Quarks!
What are the two principles of electric charge?
1. Charge is always conserved
2. Charge is always a multiple of the basic unit of electric charge
A charge of 2 X 10-7 C is acted upon by a force of 0.1N. Determine the distance to the other charge of 4.5 X 10-7 C.
Distance = 0.09 m
What is the electric field inside a conductor?
E=0
What is it called when an object is very conductive?
Superconductor!
Ultraviolet light has a wavelength of about 6 × 10-8 m. What is the frequency of this light? (remember the speed of light is 3*10^8 m/s)
A. 5 × 1015 Hz
B. 0.5 Hz
C. 2 Hz
D. 20 Hz
A
Which of the following best represents the lines of electric potential surrounding two identical positively charged spheres?
A. 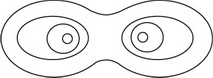
B. 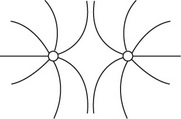
C. 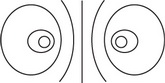
D. 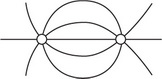
B
Which has the larger charge (in terms of magnitude, not sign) -- electron or proton?
Both have the same charge, different signs
In conductors, electrons can flow because their
- ions are free
- protons are free
- electrons are free
- negative ions are free
3
How much stronger is the electromotive force times gravity?
10^36