Definition of energy.
What is the ability to do work or cause change.
Finish the following sentence with the word “repel” or “attract” … Like charges _________.
What is REPEL.
The movement of _______ ________ creates an electric current.
What is electric charge.
Draw the Ohm’s Law triangle.
This is the symbol for what?

What is a Light Bulb.
These bar magnets are repelling one another. The red circle is best described as being.
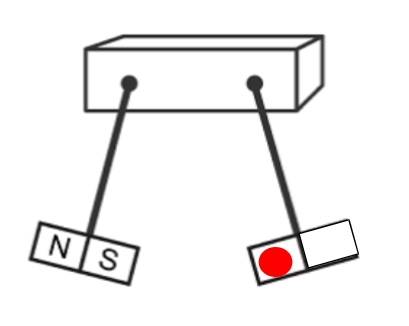
What is the South Pole.
The two basic kinds of energy.
What are potential and kinetic energy.
What is the definition of the term “static electricity”?
What is the buildup of electric charges on an object.
_____________ is the tendency of a material to oppose the flow of electrons.
What is Resistance.
What does the V stand for?
What does the R stand for?
What does the I stand for?
What are Voltage, Resistance, Current.
Is this a closed or an open circuit?
What is open.
What is this a picture of?
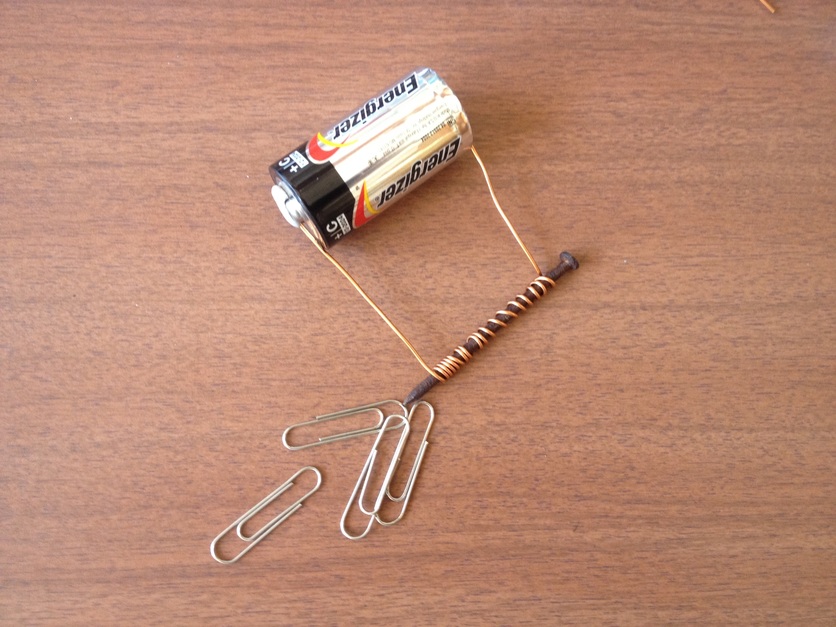

What is an electromagnet.
A generator converts _________ energy to __________ energy.
Mr. Gaines rubs a PVC pipe with fabric… explain WHY an aluminum can starts to move toward the pipe when he puts the puts the pipe near it.
By rubbing the pipe with the fur fabric, Mr. Gaines created a buildup of negative charges on the pipe. When the pipe comes near the can, the can moves towards the pipe because they are opposite charges (opposite charges attract).
Explain the difference between a conductor and an insulator. Give one example of each.
Conductor - a material that allows electricity to easily move through it (metals - copper/silver, wires)
Insulator - a material that allows little electricity to move through it (glass, paper, rubber, plastic)
Finish the following equations…
V =
R =
I =

Label the circuit diagrams below as Parallel or Series.
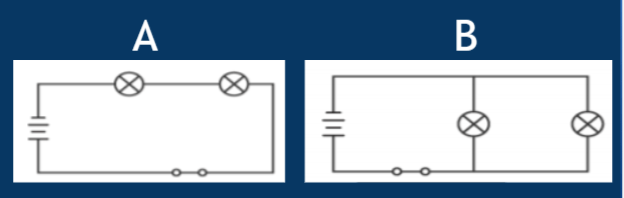
What is...
A = Series
B = Parallel
True or False: Current traveling through an electrical wire creates a magnetic field.
What is true.
State the Law of Conservation of Energy.
What is energy is neither created nor destroyed... it can only change form.
Two spheres, A and B, are held together as shown below. They are then released and move away from each other. What are the electrical charges of spheres A and B?
What is A and B are both + OR A and B are both -
Voltage: What effect does increasing the potential difference have on current?
What is... the greater the potential difference, the stronger the current.
What are the units for voltage, resistance, and current?
What are Voltage = Volts (V), Resistance = Ohms (Ω), Current = Amperes (A)
Give one advantage of a series circuit.
What is..
- Simple to design and build
- Each added source of current adds more current to the circuit
Explain where Earth's geographic North and South Poles are and where Earth's magnetic north and south poles are.
Geographic North Pole = Magnetic South Pole
Geographic South Pole = Magnetic North Pole.
Give an example of potential and kinetic energy.
Answers will vary.
Example - Kinetic... what is a moving roller coaster, Potential... what is a roller coaster at the top of the hill, unmoving.
Draw the electric field lines between a negatively charged particle and a positively charged particle.
How is current electricity different than static electricity?
What is current electricity flows through wires and electrons flow in a definite path.
Finish the following sentences…
When voltage increases, current __________.
When resistance increases, current __________.
What is increases, decreases.
When one light goes out in this classroom, the other lights stay lit. Are the lights in the room in a parallel circuit or a series circuit? Explain how you know.
What is in a Parallel Circuit - multiple pathways to each light bulb...when one goes out, the others still have electric current flowing through.
Explain one way you can make an electromagnet stronger.
What is...
- Increasing the current
- Adding iron to the middle
- Increasing the # of coils
- Tightening the coils