The s block has how many lines and arrows when filled?
1 line, 2 arrows
What is the electron configuration of Lithium?
1s2 2s1
What element has the following electron configuration:
1s2 2s2 2p4
What is Oxygen
This is the name for the outermost electrons.
What is valence electrons
What element is found in period 3, group 2?
Magnesium
What is ionization energy?
It's the energy required to remove a valence electron.
Which element is bigger: Ca or Se?
Ca
The p block has how many lines and arrows when filled?
3 lines, 6 arrows
What is the electron configuration of Carbon?
1s2 2s2 2p2
What element has the following electron configuration:
[Ar] 4s2 3d9
What is Copper
What is the name of a negative ion?
What is an anion
What element is found in period 5, group 14?
Tin
What is atomic radius?
It is half the distance between two adjacent nuclei of atoms of the same element.
What's the difference between a group and a period?
Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table, periods are the horizontal rows.
The d block has how many lines and arrows when filled?
5 lines, 10 arrows
What is the noble gas electron configuration of Arsenic?
[Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p3
What element has the following electron configuration:
[Xe] 6s2 5d1 4f14 5d9 6p2
What is Lead
In the f-block, this is the top row.
What are the Lanthanides?
What is the name of the last column on the periodic table?
Noble Gases
What is electronegativity?
It's a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons.
Explain why we observe the periodic trends in atomic radius.
It increases from top to bottom within a group because energy levels are added, which increases the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus.
It decreases across a period, because nuclear charge increases without adding energy levels, so that increases the attraction for electrons which pulls them in and makes the atom smaller.
The f block has how many lines and arrows when filled?
7 lines, 14 arrows
What is the noble gas electron configuration of Titanium?
[Ar] 4s2 3d2
What element ends on the following electron configuration:
4s1
What is Potassium
This is the energy either lost or gained when acquiring an electron.
What is electron affinity?
What noble gas will be in the configuration for neptunium?
Radon
What is the periodic trend in atomic radius (both in groups and in periods)?
Atomic radius decreases from left to right within a period and increases from top to bottom within a group.
Explain why we observe the periodic trends in ionization energy.
It decreases from top to bottom within a group because energy levels are added, which increases the distance between the valence electrons and the nuclear pull. There are also more core electrons to shield the pull from the nucleus, which makes it easier to remove electrons, making ionization energy decrease.
It increases across a period, because nuclear charge increases without adding energy levels, so that increases the attraction for electrons and makes them harder to remove, which increases ionization energy.
Explain what's wrong the orbital diagram: 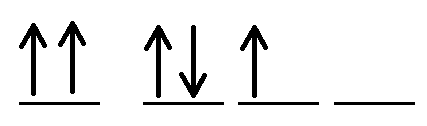
You are not allowed to have two arrows pointing in the same direction on the same line.
What is the noble gas electron configuration of Osmium (Os)?
[Xe] 6s24f145d6
What element ends on the following electron configuration:
5f7
What is Americium
This is the name of the configuration that all atoms wish to achieve, normally through ionization.
What is an octet?
How many valence electrons will arsenic have?
5
What is the periodic trend in ionization energy (both in groups and in periods)?
Ionization energy increases from left to right within a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
Explain why we observe the periodic trends in electronegativity.
It decreases from top to bottom within a group because energy levels are added, which increases the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus. This weakens the attraction for electrons.
It increases across a period, because nuclear charge increases without adding energy levels, so that increases the attraction for electrons.