The three main subatomic particles.
What are protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Discovered the electrons and came up with the Plum-Pudding model of the atom.
Who is J.J Thomson?
What is the main reason for electrostatics?
What is separation of charge?
What is Coulomb's Law?
F = (k*q1*q2)/r2
Arrows point towards the charge.
What is a negative charge?
What is a proton?
Experiment where alpha particles were shot at a thin sheet of gold.
What is the gold foil experiment?
Uses friction to create imbalance of charge.
What is the movement of electrons to and from neutral objects?
What is the relationship between force and distance?
Inversely related to the square
Where is the electric field weakest?
Furthest away from the charge.
What is fundamental charge?
Ernest Rutherford's conclusion from the gold foil experiment.
What is atoms are made up of mostly empty space with a small nucleus of protons?
Positive charged object.
What is the loss of electrons?
One charge of +43nC is 9 mm apart from a a charge of +76nC. What is the electrostatic force? k = 8.99x109
Force = 0.363 N
Draw two positive charges close to eachother and their electric field lines.
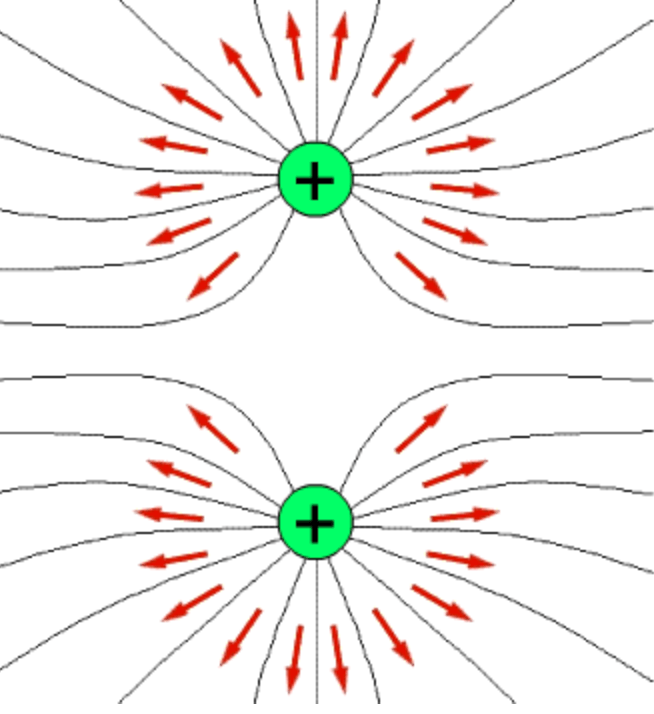
Has no charge.
What is a neutron?
Describes the planetary/Rutherford model.
What is a small dense nucleus of protons with electrons moving around it.
Two negatively charged particles will...
What is repel?
A force between a pair of .065 C charge is 15 N. What is the distance between them?
1,591.28 m
Draw a negative and positive charge and their electric field lines.
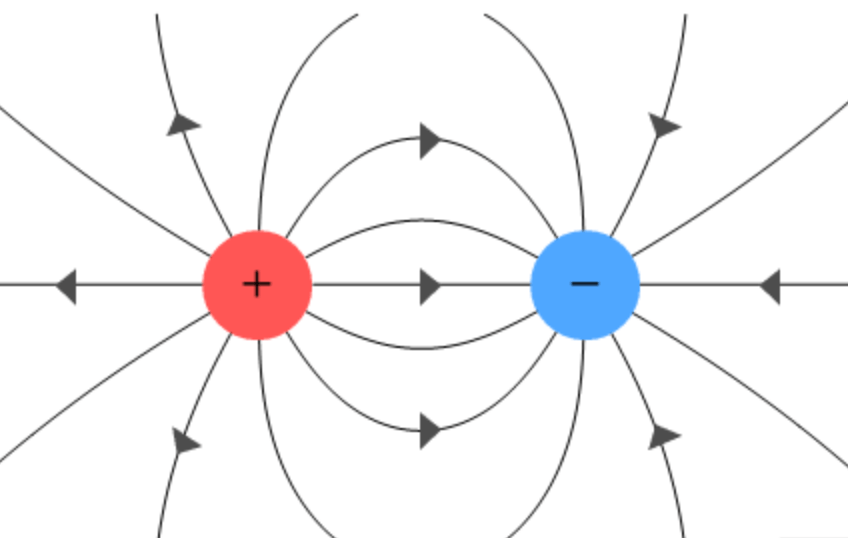
Subatomic particles that most easily moves between atoms.
What is electron?
JJ. Thompson's student.
Who was Ernest Rutherford?
The law of conservation of energy
What is that charge is not created or destroyed. It can be transferred.
A +10C charge is placed halfway between a +20C charge and a -30C charge that are 20cm apart. What is the net electrostatic force acting on the 6C charge?
1.79 x 1016 N
Name as many variables and their unit.
Coulomb's Constant = N*m2/C2
Charge - C
Distance of separation - m
Energy - Joules
Work - Joules
Power - Watts
Electric Field - Newtons/Coulomb