Like charges _______ and opposite charges ________.
repel,
attract
Electrostatic force is ________ proportional to the amount of charge in the objects and _________ proportional to the distance between the objects. (directly or inversely)
directly, inversely
Aside from the strength, what is the biggest difference between gravitational force and electrostatic force?
gravitational force is only attractive. Electrostatic force can be attractive OR repulsive!
Identify the three methods of charging.
conduction
friction
induction
Field lines are always drawn to show what a ____ charge would do in the field.
positive (+)
Describe what happens to the charges in a neutral object when a negatively charged object is held nearby?
The electrons (- charges) in the neutral object move to the far side (away from the charged object).
Which of the following subatomic particles exist inside the atomic nucleus?
protons
electrons
neutrons
protons and neutrons
What happens to the electrostatic force between two objects if one of the charges is tripled (3x) and the other charge is doubled (2x)?
6x stronger force
What is Coulomb's Law? (write the equation)

In which of the three methods of charging do the two objects always end up with opposite charges?
friction and induction
To show a stronger electric field in a diagram, you would:
draw more field lines /
draw field lines closer together
Describe what happens to the charges in a neutral object when a positively charged object is held nearby?
The electrons (- charges) in the neutral object move to the near side (toward the charged object).
Two charged metal spheres are repelled from each other. Which answer must be true?
a. they are both positive
b. they are both negative
c. one is positive, one is negative
d. they have the same type of charge
d. they have the same type of charge
What happens to the electrostatic force between two objects if the distance between the charges is quadrupled (4x)?
the force is 1/16 as strong
A 3C charge and a -3C charge are 1m apart.
Calculate the electrostatic force between them.
-81x109 N
When charging by induction, you must touch one side of the neutral object with your finger. This step is known as ________.
grounding
What's wrong with the electric field line diagram drawn below?
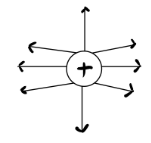
Field lines need to be drawn at 90-degree angles to the charge (and should be drawn evenly spaced).
A (+) charged object induces a polarization in a neutral object. The (+) object _________ the neutral object.
a. is attracted to
b. is repelled by
c. does nothing to
a. is attracted to
What are the units of electric charge?
Coulombs (C)
What happens to the electrostatic force between two objects if one of the charges is quadrupled (4x), the other charge is halved (1/2), and the distance between them is doubled (2x)?
force is halved (1/2)
A +6.4 x 10-3 C charge is a distance of 5.6 x 102 m away from a +2.3 x 10-4 C charge.
Calculate the electrostatic force on the charges.
4.22x10-2 N
When a (+) object is grounded:
a. electrons move from the ground into the object
b. electrons move from the object into the ground
c. protons move from the ground into the object
d. protons move from the object into the ground
a. electrons move from the ground into the object
Charge A is ___ and charge B is ____.
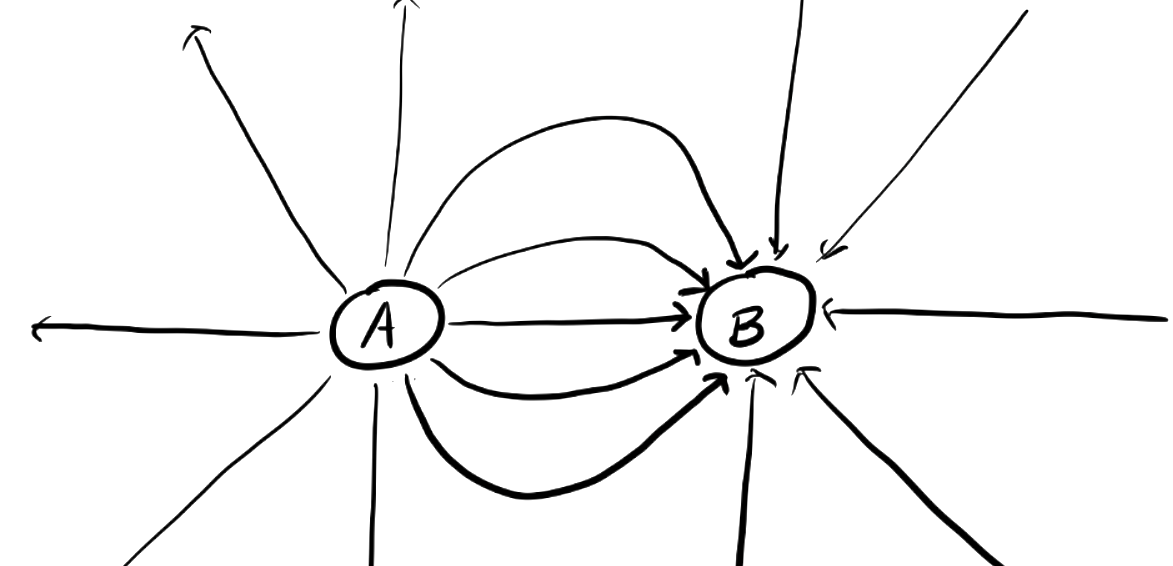
positive, negative
A (-) charged object induces a polarization in a neutral object. The (-) object _________ the neutral object.
a. is attracted to
b. is repelled by
c. does nothing to
a. is attracted to
What are the units of electrostatic force?
Newtons (N)
What happens to the electrostatic force between two objects if both charges are tripled (3x) and the distance between them is 1/3 of the original distance?
the force is 81x stronger!
How far apart must two charges (both 2.0x10-2 C) be if the force between them is 50N?
*Calculate d!
268.33 meters
A metal sphere has a charge of -12 C and charges an identical neutral sphere through conduction. What will be the charges of the two spheres after they touch?
-6 C
A negative charge placed at point C will move in what direction? (Up/Down/Left/Right)
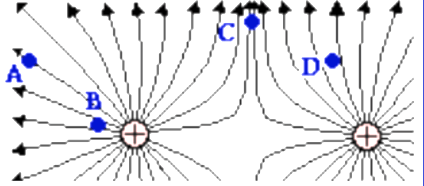
down (opposite direction that a + charge would move)
After the electrons move to the far side of a neutral object during induced polarization, the overall charge of the object is now _________.
still neutral!