A 25-year-old man presents after being pulled from a structure fire. He was combative and stridulous during transport and noted to be coughing up copious carbonaceous sputum. On arrival in the emergency department, he was intubated for airway protection. His vital signs on arrival are T 37.5°C, HR 45 bpm, BP 70/40 mm Hg, and oxygen saturations of 92% on 100% FiO₂. Co-oximetry shows a level of 20%. Point-of-care labs are notable for a lactic acid of 12 mmol/L. In addition to carbon monoxide poisoning, what additional diagnosis is made and what is the first line for treatment?
Cyanide Toxicity. Hydroxocobalamin.
(inhibits aerobic respiration, hence the high lactate)
unlike sodium thiosulfate, may be used in toxidrome with shock
nitrates (sodium nitrate, amyl nitrate) induce methemoglobinemia, which binds cyanide - but cannot be used in CO tox.
A 75-year-old man presents from the local nursing facility with severe lower extremity pain. His vital signs on arrival are T 39.3℃, HR 160 bpm, BP 72/40 mm Hg, and RR 40/min. Physical examination shows erythema and crepitus in the lower extremity. An X-ray of the extremity is shown above. Which of the following antibiotics is indicated for direct inhibition of toxin synthesis? 
CLINDAMYCIN
Necrotizing soft tissue infection
Typically polymicrobial (cover for GP, GN, anaerobes)
Needs EMERGENT surgical debridement.
What is the Parkland Formula for burn resuscitation?
Fluid Requirements = TBSA burned(%) × Wt (kg) × 4 mL
partial thickness/full thickness only in %
half first 8 hours, half next 16 hours
Give 3 findings associated with acute cholecystitis on ultrasound.
Give the toxic dose
7mg/kg
(4.5 mg/kg for 1% lido WITHOUT epi)
Antidote for tylenol overdose AND what 4 hour level would necessitate use.
NAC. > 150 on Rumack-Matthew nomogram.
20% may have anaphylacTOID reaction. Non-IgE mediated - flushing, urticaria, pruritis. Does NOT need to be paused unless severe.
Kings College criteria for liver transplant consideration.
What is the Diagnosis and Treatment:
A 16-year-old girl presents to your rural emergency department with a fever and a rash that began only 24 hours ago. She also reports headache, muscle pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. She has a temperature of 39.4°C, a heart rate of 140 bpm, and a blood pressure of 87/49 mm Hg. She has diffuse erythroderma with some skin peeling over her palms and mucous membrane redness. Intravenous access is obtained, and she is given two boluses of normal saline and antibiotics, after which her vital signs normalize.
Toxic Shock Syndrome / Antistaph Abx (PCN/Cephalosporin) + Clindamycin + Source Control
(exotoxin producing staph and strep)
Staph enterotoxin TSST-1 or GAS infection
What is this fracture?
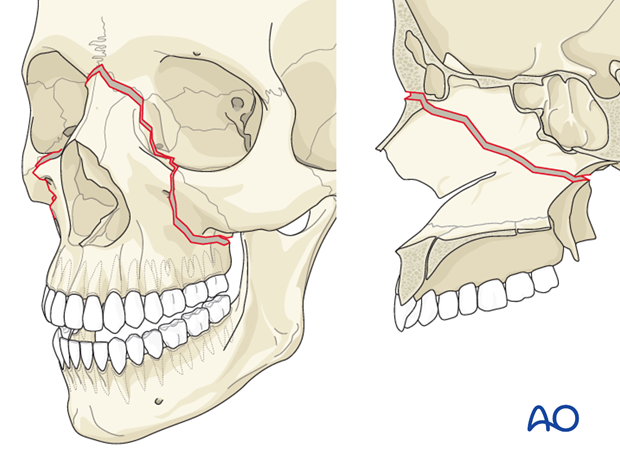
Le Fort II
Speak no evil, See no evil, Hear no evil
Maxilla, Nasal/Orbit, craniofacial dislocation/zygoma
Child's xray shown with button battery ingestion, < 5 hours since time of ingestion. They are asymptomatic. What is the management?
Close observation
Endoscopy emergent if esophageal, > 48 hours in stomach. Specialty consultation if symptomatic.
Name the sign, what's the diagnosis?
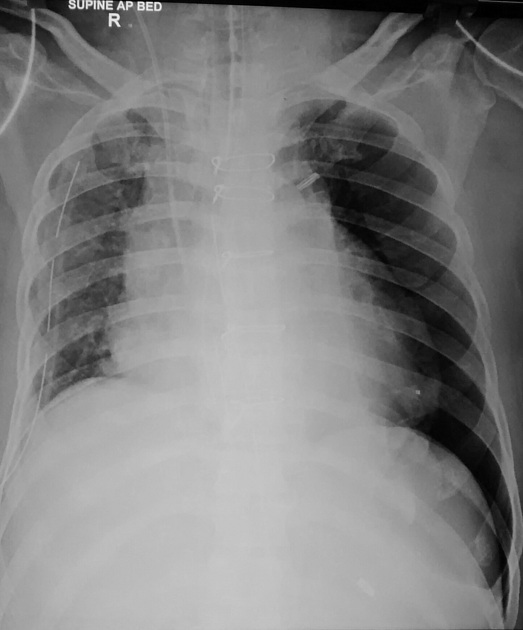
Deep Sulcus Sign on Patient's LEFT
Consistent with PTX in supine film
Hydrocarbon ingestion is known for what pulmonary complication AND why?
Pulmonary aspiration, low surface tension and viscosity.
Obs for 6 hours for pneumonitis.
Name of rash and treatment of choice.
Erythema migrans, Doxycycline 14-21 days.
Tick-borne
Borrelia burgdorferi > Lyme Disease
Doxy OK in kids if used < 21 days
This criteria prompts consideration of CT angiography to rule out blunt cerebrovascular injury (BCVI)
DENVER CRITERIA
Diagnosis and Med to AVOID:
Seafood, diarrhea, neurologic symptoms
Ciguatera and Imodium (toxin retention)
Hot/Cold reversal
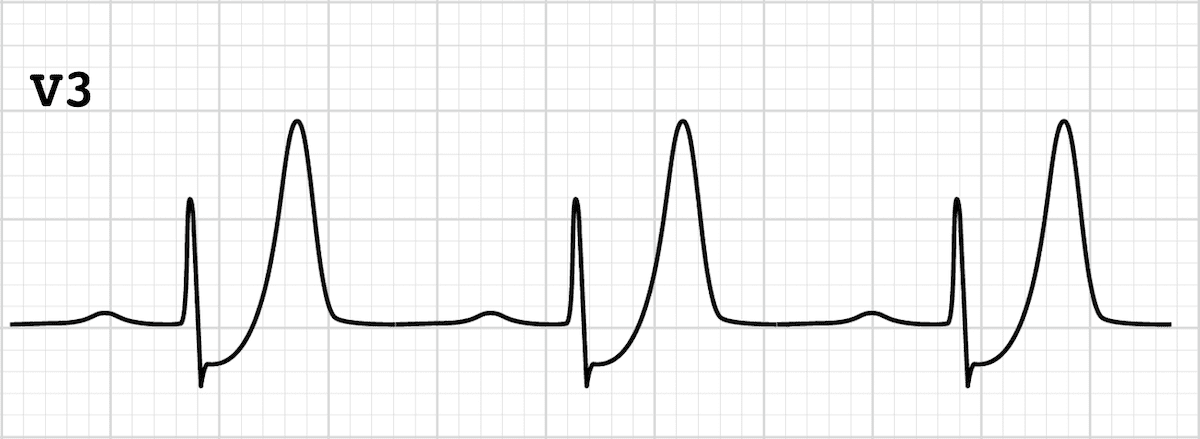 ECG finding and diagnosis.
ECG finding and diagnosis.
DeWinter's T wave suggestive of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Anterior STEMI equivalent.
A 19-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by staff at his group home. They report escalating confusion, hypertonia, and diarrhea. Vital signs include a heart rate of 121 bpm, blood pressure of 171/100 mm Hg, respiratory rate of 22/min, and oxygen saturation of 99% on room air. His examination displays diaphoresis, diffuse tremulousness, hamstring muscle hypertonicity, 3+ patellar reflexes, and marked ankle clonus. His confusion precludes him from providing any reliable history. However, a review of his group home records reveals he was recently started on citalopram for difficult-to-manage behavior. His medication list also includes fluoxetine, trazodone, and lorazepam. His ECG, CBC, and electrolyte panel are normal. However, his creatine phosphokinase is 2,875 U/L. His condition does not respond to oral and intravenous diazepam. What is the most appropriate treatment at this time?
Cyproheptadine for Serotonin Syndrome.
Name the organism and treatment of choice:
HA, fever, petechia.
Thrombocytopenia, Hyponatemia, Transaminitis.
Rickettsia rickettsia
RMSF
Doxy in adults and kids.
MOST COMMON NERVE INJURY...

AXILLARY NERVE
After paracentesis, what lab value is concerning for SBP?
Paracentesis positive if: total WBC > 500, PMN (neutrophils) > 250, pH < 7.34, low glucose, (+) gram stain/culture
If Peritoneal Dialysis: Cell count >100/mm with >50% neutrophils most consistent with infection
femoral, obturator, genitofemoral, and lateral femoral cutaneous nerves
A 74-year-old man presents with altered mental status and hypotension. He has a history of atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes mellitus. His medications include glipizide, atorvastatin, digoxin, and metoprolol. Upon arrival, you place him on the monitor and quickly recognize the rhythm noted above. What is the best next step in management?

Digoxin immune fab (digibind)
ECG: bidirectional ventricular tachycardia seen with severe toxicity
Hyperkalemia correlates with disease severity.
May be instigated by renal insufficiency/failure on therapeutic doses.
NKATPase inhibitor: inc. Na and Ca inside cells, inc. K outside of cells. Stone heart is a myth. K typically improves with digibind, though.
Hutchinson sign is diagnostic of what condition AND what branch of the trigeminal is affected AND what other organ is at risk?

Varicella Zoster Reactivation
Nasociliary Branch of CN V1
The globe: full ocular examination - sight threatening. Corneal pseudodendrites (no terminal bulbs), punctate keratitis, episcleritis.
Name the type of fracture. Stable or unstable.
Type III Odontoid Fracture
Unstable
Type I: avulsion injury, typically stable
Type II: highest non union risk.
Name the signs and 2 NON TRAUMATIC causes.
Cullen's and Grey-Turner Signs
Hemorrhagic Pancreatitis
Ectopic Pregnancy Rupture
AAA Rupture
Trauma and Iatrogenic (femoral cath with retroperitoneal hemorrhage) are also causes.
Name the CT finding. What is the diagnosis?
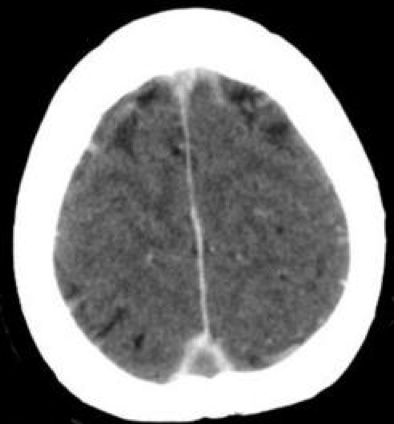
Empty Sella Sign. Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST)
Treatment: anticoagulation is first line therapy if no sig. bleeding risk.
