the charge of an electron
These are the 3 things (components) that a circuit needs
power (voltage) source, electrical conductors, resistor
The magnets below will ____________. (Explain what they will do and why)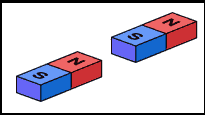
attract, because opposite poles attract
An electromagnet is a temporary magnet caused by running this through a solenoid, usually around something metal.
electric current
The unit to measure Voltage / Electric Potential
Volts
the charge of a proton
positive
This is the direction of conventional current
from positive to negative
This is what causes magnetism
motion of electric charges (electrons in each atom spinning in the same direction)
This is how you can reverse the poles of an electromagnet
A unit to measure Energy
Joules (J) or kiloWatt-hours (kWh)
This is how an object can become negatively charged
gain electrons
This type of circuit has multiple paths that current can flow through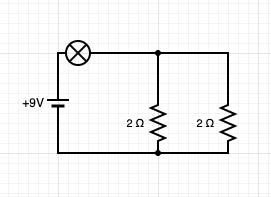
parallel circuit
the strength and direction of the magnetic force
Electromagnetic induction
The unit to measure Current
Amperes (Amps) (A)
this is how an object can become positively charged
lose electrons
The amount of current that will flow through a circuit connected to a 12V battery with three (3) lightbulbs each with a resistance of 1 Omega (Must include correct units!)
Ohm's Law: I = V/R
I = 12/ (1 + 1 + 1)
I = 12/3 = 4 Amps
This is the reason the Earth has a magnetic field around it
These 3 things can affect the amount of current produced by a moving magnetic field
speed, strength of the magnet, number of coils
The unit to measure Resistance
Ohms ( Omega )
amount of charge and distance between charges
You connect an ammeter to a simple series circuit powered by the hand crank generator with a 10 Omega resistor and find that the current is 2A. You are supplying this much voltage to the circuit with the hand-crank generator.
Ohm's Law:
V = IxR
V = 2x10
V = 20V
These are the 2 ways to make an electromagnet stronger.
Increase the number of coils (length of the solenoid) or increase the current (by adding more voltage / batteries)
These 2 devices use electromagnetic induction to help bring electricity into our homes
electric generator (creates the electric current), electric transformer (changes the voltage)
The unit to measure Charge
Coulombs (C)