This term refers to the three components: embryoblast, fluid-filled cavity, and outer cell layer.
What is a... blastocyst
Conservatively by week 20 of fetal development, this is functional
What is....
rudimental hearing
any agent or factor that causes malformation of an embryo, as well as can also increase the risk for miscarriage, preterm labor, or stillbirth.
What is a...
teratogens
The membrane lying of the middle ear, Eustachian tube, liver, and pancreas, all develop from this disk germ layer.
What is a... Endoderm
By the 4th month these structures ossify, but only by the 8th month they are free of mesenchyme
What is the...
malleus, incus and stapes
Minor congenital anomalies or functional deficits to the auditory system and CNS are more likely to occur during this period of development
The fetal stage or weeks 10-20 (ear) weeks 20-40 (CNS
Theses external coverings are referred to as _______ and develop from _______________
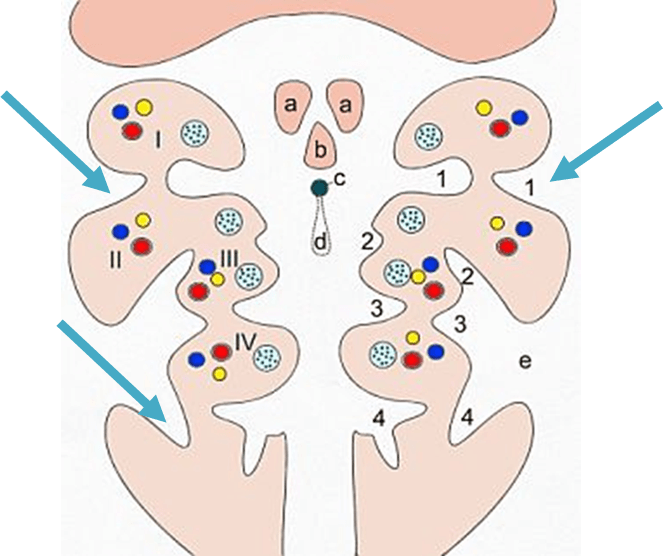
Branchial Grooves (develop from ectoderm)
Connective tissue around the tympanic membrane begins to harden and form bone, at approximately
What is...
Week 12
Many women share stories of their last night out [drinking] before they knew they were pregnant, ....this is why their babies don’t have Fetal alcohol syndrome
What is...
prior to week 3 of development, the pre-embryonic is not susceptible to teratogens
What three critical events in the development of auditory structures all begin in week 4?
What are:
•Branchia arches develop and swell --> OE
•Otic pit invagination (sink into mesoderm) --> IE
•Stereo acoustic ganglia apparent --> CN VIII
The stapes [most likley] developed from which develops from the __________ arch
What is....
2nd Branchial (pharyngeal) arch or Hyoid arch
This is a typical configuration of Mondini malformation.
What is...
Unilateral profound Seneorneural hearing loss
E represented the cochlear duct at week 8, but which weak is the duct completed coiling?
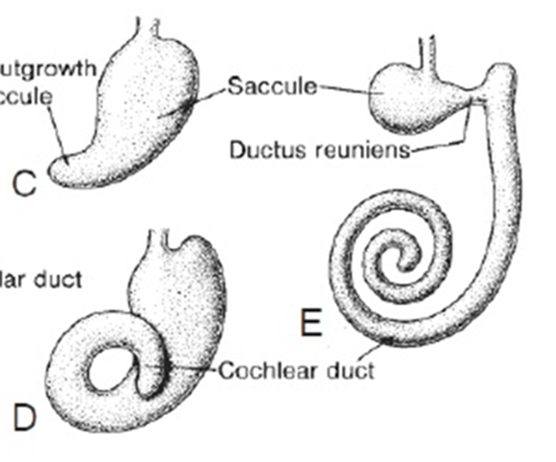
What is...
•Week 9 (according to Dr. Weaver)
Describe the process by which the tympanic membrane forms:
What is...
"the ectodermal epithelial lining at the bottom of the auditory meatus, the endodermal epithelial lining of the tympanic cavity, and an intermediate layer of connective tissue that forms the fibrous stratum.
Which cochlear malformation is most likely to occur at ~4th week
What is...
Common cavity
Formation of the three semicircular canals occurs around...
What is...
Week 6
The greatest period of [percent] change in the cerebrum weight occurs....
What/ when is...
Birth -3 years of age
When these defects are present:
1) aural atresia,
2) microtia,
3) ossicular (ear, face, palate) deformities
with normal inner ear a clinician should suspect this syndrome?
What is...
1st Arch Syndrome
Explain the process of gastrulation.
Being in at week 3, gestation, the bilaminar blastocyst structure tri-furcates into three germ layers. The Ectoderm (neural crest gives rise to CNS & PNS); mesoderm (bone and tissue --> middle ear), and Endoderm (gives rise to tissue lining and organs including the middle ear cavity).
While many aspects of the auditory system are mature at birth. The following will not be adult-like until someone provide 5 structures that are not adult-like until after birth
Daily Double
What is...
~3 months =Tympanic membrane
~5 months = CN VIII
~6 years = Midbrain (CANS)
~7 years = EAM, and ET
~8 years = Pons (CANS)
~9 year = Pinna,
~5 to 20 Years =cerebbelum
This congenital anomaly can act as a "port of entry" to the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord (cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF). Sometimes, individuals are not diagnosed with Mondini dysplasia before several episodes of what occurs.
What is...
recurrent meningitis