What is the normal compression to ventilation ratio for CPR?
30:2
What is the normal blood sugar range?
80-120
How can you tell the difference between AMI and AAA?
- Onset of pain
- Location of pain
- Description of pain
- Provoking factors of pain
- Level of pain
What are the signs and symptoms of opiod overdose and what medication reverses it?
–Slow/shallow/no breathing, pinpoint pupils, weak pulse, low blood pressure.
- Narcan.
What is the primary treatment for diving injuries?
Hyperbaric chamber
What is the difference between AMI and cardiac arrest
AMI: Plumbing problem
Cardiac Arrest: Electrical problem
Describe the three types of strokes
1. Ischemic stroke: clot
2. Hemorrhagic stroke: Bleed
3. TIA: "mini-stroke" is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain that resolves in 24 hours.
3 P's of hyperglycemia
- Polyuria: Frequent urination due to excessive glucose in the urine.
- Polydipsia: Increased thirst caused by dehydration from polyuria.
- Polyphagia: Excessive hunger, as the body cannot use glucose properly
Severe symptoms like agitation, aggression, confusion, trembling, hallucinations, sweating and tachycardia from alcohol withdrawal is called:
Delirium tremens
What is reverse triage and when do we use it?
Reverse triage means prioritizing care for those who appear dead or unresponsive, even if they are not breathing or have a pulse. Can be used during lightning injuries because lightning can cause temporary cardiac arrest, but with proper resuscitation efforts, a high percentage of these victims can be successfully revived
What is the compression to ventilation ratio for infant 2 rescuer CPR? Why
15:2. Cardiac arrest in children is usually secondary to respiratory arrest, so the breaths are more important than they are in adults
What are the mechanisms of Aspirin and Nitro?
Aspirin: Blood thinner
Nitro: Vasodilator
What are the three parts of the Cincinnati stroke scale?
Why do we give activated charcoal? What is the dose and what are some contraindications?
Binds to ingested poisons
1g/kg
decreased levels of consciousness, ingestion of acids/alkalis or petroleum products.
At what elevation in feet is acute mountain sickness most likely to occur?
8,000 feet
What are the two shockable rhythms?
V-Fib
Pulseless V-tach
What are the three types of seizures?
Generalized seizure: loss of consciousness, muscle stiffening, and jerking movements.
Febrile seizure: occurs in children with a fever, typically between 6 months and 5 years old
Absence seizures: a brief, sudden lapse in awareness characterized by a blank stare and unresponsiveness
What are the rules for giving nitroglycerin?
•Systolic BP is over 100
•No head injury
•No recent use of ED drugs
What are the signs and symptoms of nerve agent poisoning?

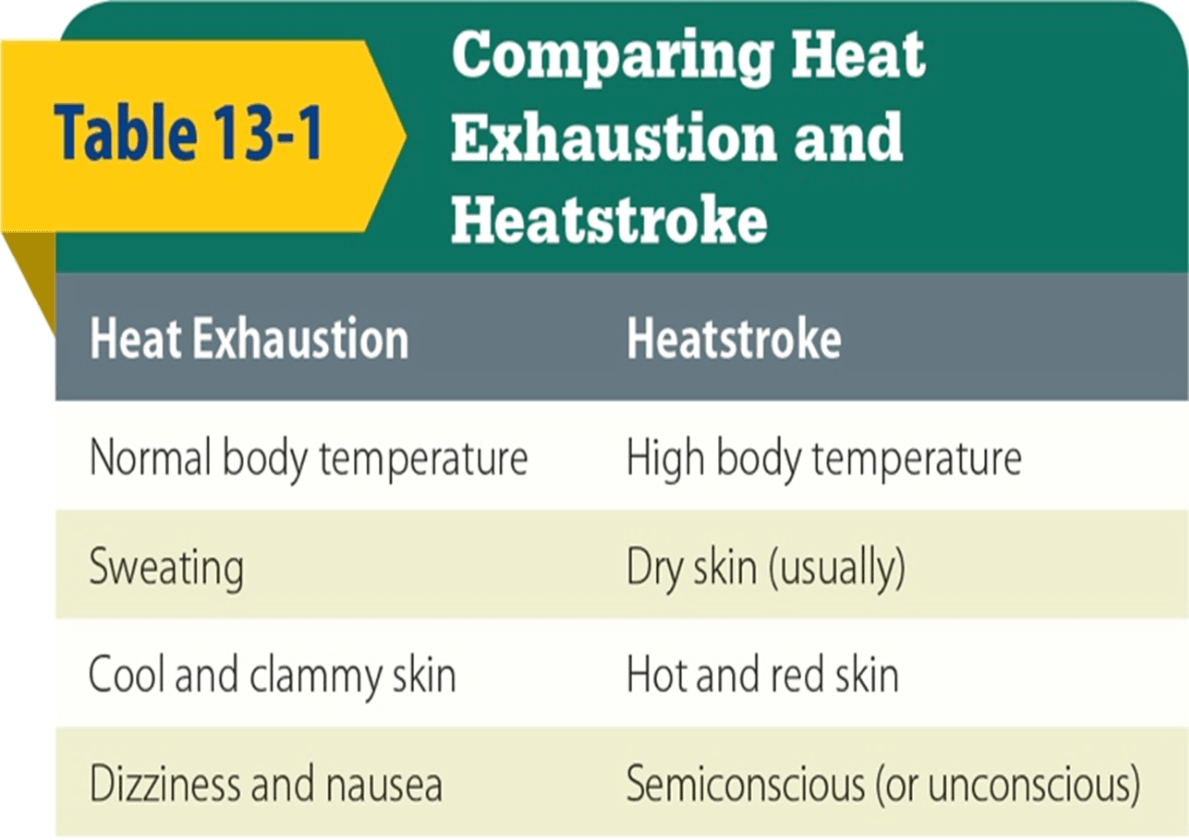
Explain the difference in symptoms between heat exhaustion and heat stroke
Name at least 2 H's and T's of reversible causes of cardiac arrest.
- Hypovolemia
- Hypoxia
- Hydrogen ion excess (acidosis)
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypothermia
- Tension pneumothorax
- Tamponade – Cardiac
- Toxins
- Thrombosis (pulmonary embolus)
- Thrombosis (myocardial infarction)
Why do diabetes in DKA have kussmaul respirations?
When the body lacks sufficient insulin, it starts burning fat for energy, producing ketones as a byproduct. This leads to metabolic acidosis, triggering Kussmaul respirations. These are deep, labored breaths that the body uses to compensate for the high acidity by expelling more carbon dioxide.
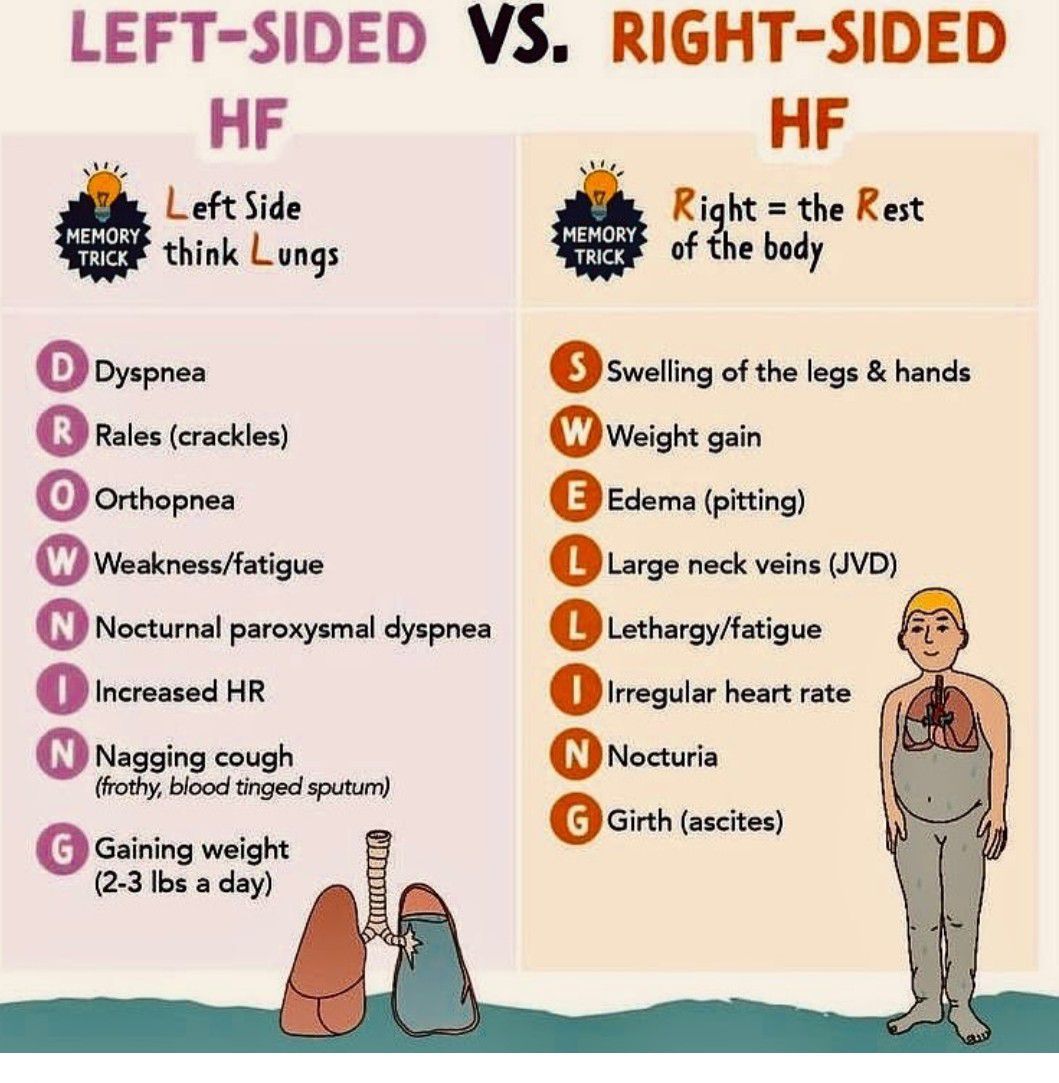
Explain the difference between left sided and right sides heart failure.
What is the concentration of IV or IM epinephrine?
IV: 1: 10,000
IM: 1: 1,000
Explain the difference in onset of symptoms between and air embolism and decompression sickness found in diving injuries.
–Air embolism generally occurs immediately on return to the surface.
–Symptoms of decompression sickness may not occur for several hours.