What is most effective way to reduce risk of disease transmission?
Proper handwashing
... and PPE compliance appropriate to the patient presentation.
What is the dose and administration route of Aspirin?
Dose: 324 mg (in 4x 81 mg non-enteric coated chewable tablets).
Route: PO (by mouth), chewed.

A friend of yours works at a woodworker shop on the side. While working with a automated saw, they accidentally sustained a laceration to their right forearm and now has bright red spurting blood present. Go ahead and manage that bleed!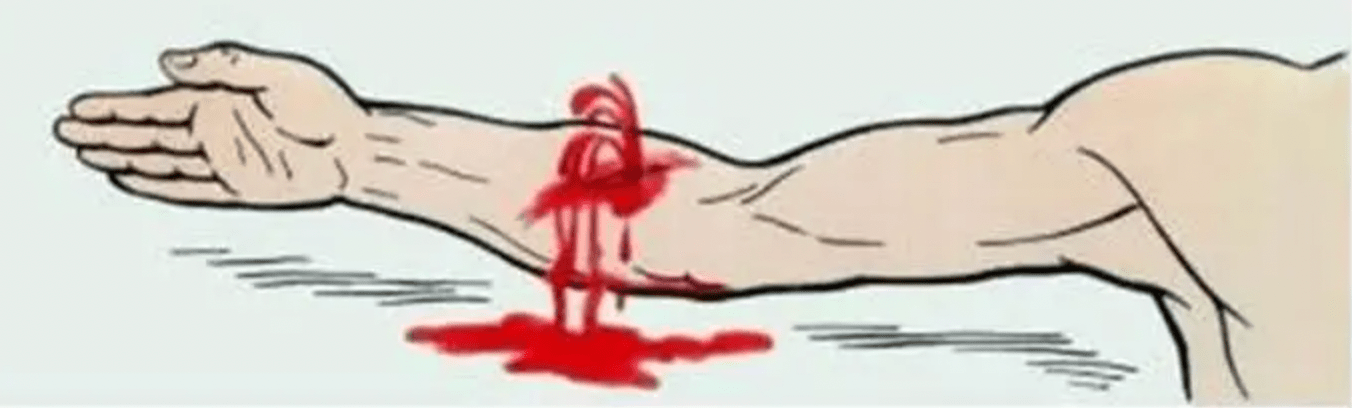
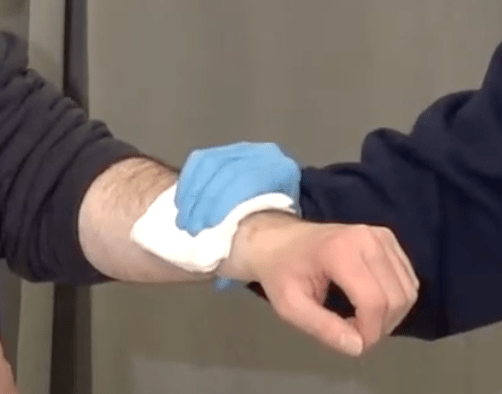
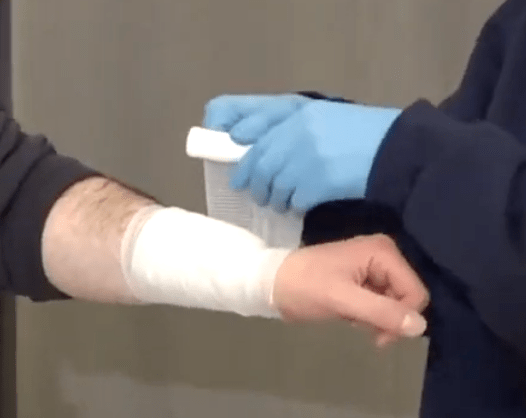
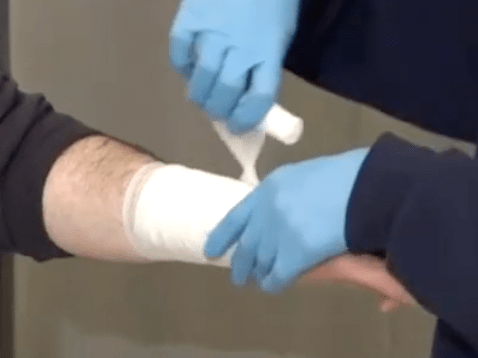
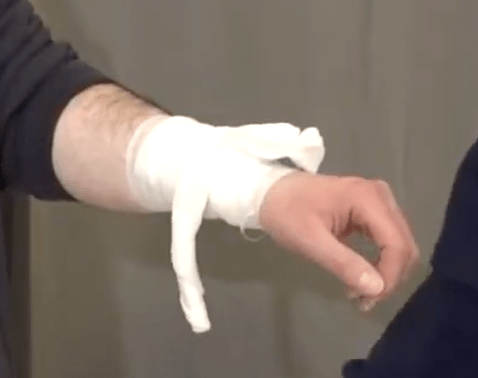
What type of shock is associated with a sudden reaction of the nervous system that leads to temporary vascular dilation which causes a syncopal episode?
Shock Type: Psychogenic
0:00 - 0:05
You are interviewing a patient who presents with what you believe is a cardiac-related chest pain. What is the acronym (and what does each letter mean) you can use to complete the interview regarding the history of the present illness (HPI)?
Onset - what were you doing when the chest pain began?
Provocation/Palliation - what makes the chest pain worse? What makes the chest pain better?
Quality - describe the chest pain, what does it feel like?
Radiation - Where is the chest pain located, and does the chest pain travel anywhere from that location?
Severity - On a scale from 0 to 10, 0 being no pain, 10 being the worst pain ever, what would you rate your pain at right now? Was that number ever lower or higher?
Time - How long have you been having chest pain?
While cleaning up the patient compartment after a call where you gave someone IM epinephrine and had paramedic backup...
You find a used 1 inch needle, a used lancet, a used glucometer strip, and a pair used gloves on the floor.
How do you dispose of each item?
Red bag (or normal trash at hospital)
- pair of gloves
- glucometer strip
Sharps container
- 1 inch needle
- lancet
What is the dose and route of nitroglycern?
How many times can you administer the dose?
Dose: 0.4mg
Route: sublingual, spray or tablet
Repeat: Up to 2 times (3 total doses)

What kind of injury is this?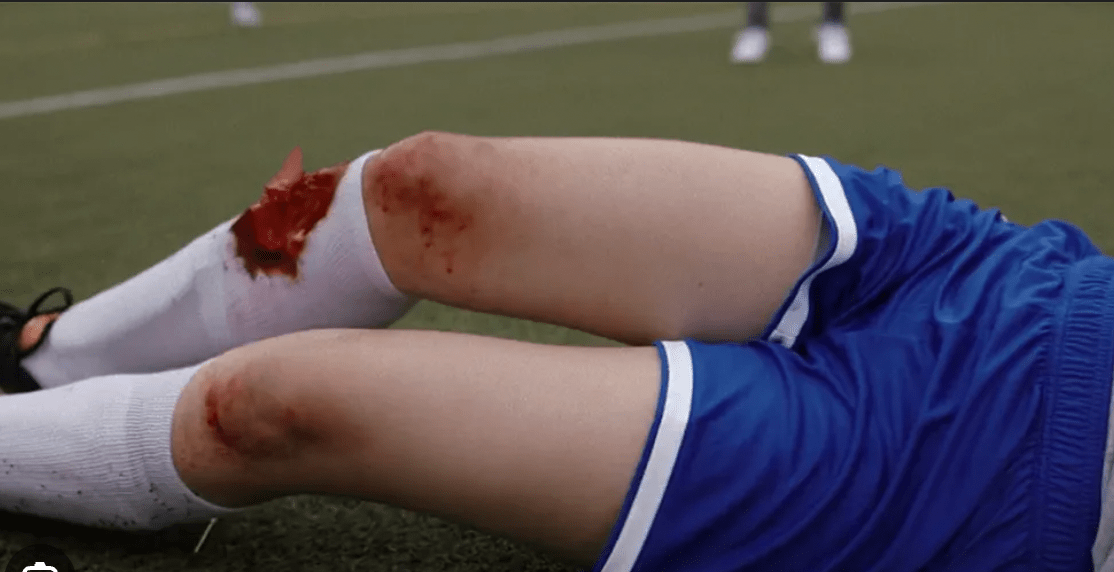
Bonus 100 points: demonstrate how you would immobilize this injury to the class
(100 points) Compound fracture to tibia/fibula
(100 points) Demonstrate how you would immobilize this injury!
What type of shock is associated with toxins affecting body tissues throughout the circulatory system?
Bonus 100 points: what 3 other signs associated with this type of shock?
Shock Type: Septic Shock
Bonus: fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotension, chills, difficult or less frequent urination, unexpected or newly altered mental status, flushed skin, new rash, or mottling
You respond to a patient who reports they are pregnant and are experiencing contractions. What are you next questions to determine if a pelvic exam (assessment for crowning) is necessary?
Bonus 100 points: what is the only other time you should be exposing a patient down to the genitalia for an assessment?
Did your water break?
Do you feel the need to push?
How frequent are contractions?
How long do they last?
Bonus: The only other time to expose a patient entirely (ideally in the truck) is to assess for major hemorrhage -- which should be determined as necessary in the primary assessment during the C of your ABCs.
You are dispatched to a report of a 60 y/o Male in their second floor walk up residence who is potentially in cardiac arrest. What EQUIPMENT do you intend to bring on scene with you?
Tech Bag / Jump Bag
O2 tank (if separate from tech bag)
AED
Backboard
Portable Suction
What is the route and dose of Naloxone? Adult dose? Child dose? How many times can you give naloxone?
Route: Intranasal
Dose
Adult: 2mg, 1mg in each nostril
Pediatric: 1mg, 0.5mg in each nostril
Can repeat once.

One of your team members has sustained a mechanical fall, has not hit their head or passed out, and now presents with a painful and deformed right shoulder. You determine they are a lower priority patient and you decide to remain on scene to complete your secondary exam. This is their only injury at this time. Please demonstrate how you would effectively their right shoulder.
Describe the type of shock that is the result of loss of significant fluid or volume in the circulatory system. Provide an example of how one could sustain such type of shock.
Bonus (100 points): what are the two sub-categories of this type of shock?
Shock Type: Hypovolemic
Example:bleeding, extreme vomiting or diarrhea, dehydration
Bonus: hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic
You suspect a patient is experiencing an allergic reaction.
Give THREE appropriate focused history questions to ask them during the patient interview?
(Hint: these are not questions about the symptoms but rather the 'backstory' or events leading up to the chief complaint)
What do you think you were exposed to?
What route do you think you were exposed to it?
How much of it do you think you were exposed to?
How have your symptoms progressed since the exposure?
You are dispatched to a scene with multiple patients. What is the title of the person you and your partner should report to?
A. Crew Chief
B. Field Training Officer
C. Incident Command Officer
D. Conditions Boss
C. Incident Command Officer
What is the dose and route of epinephrine?
Adult Dose? Child Dose?
How many times can you repeat the dose?
Dose: Adult - 0.3mg; Pediatric - 0.15mg
Route: Intramuscular (IM)
Repeat: May repeat once, cumulative 2 doses.
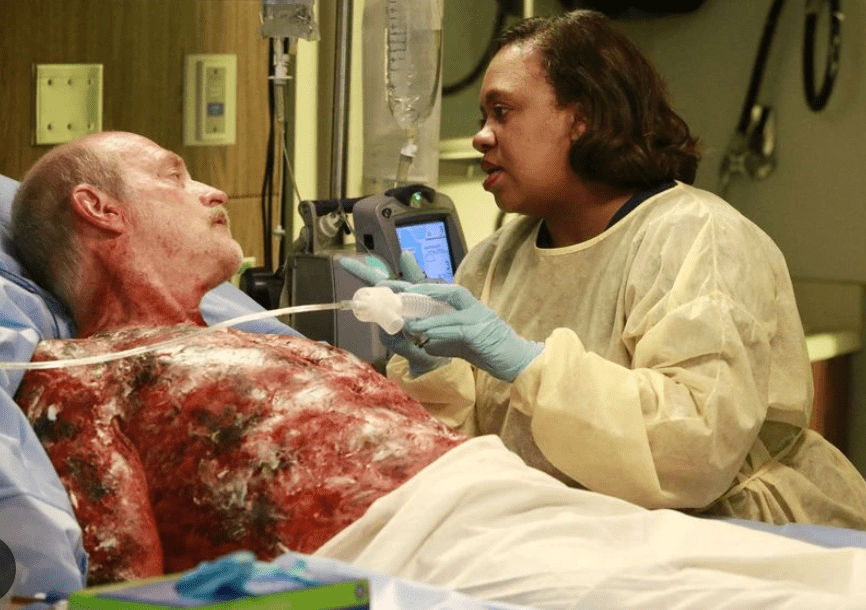


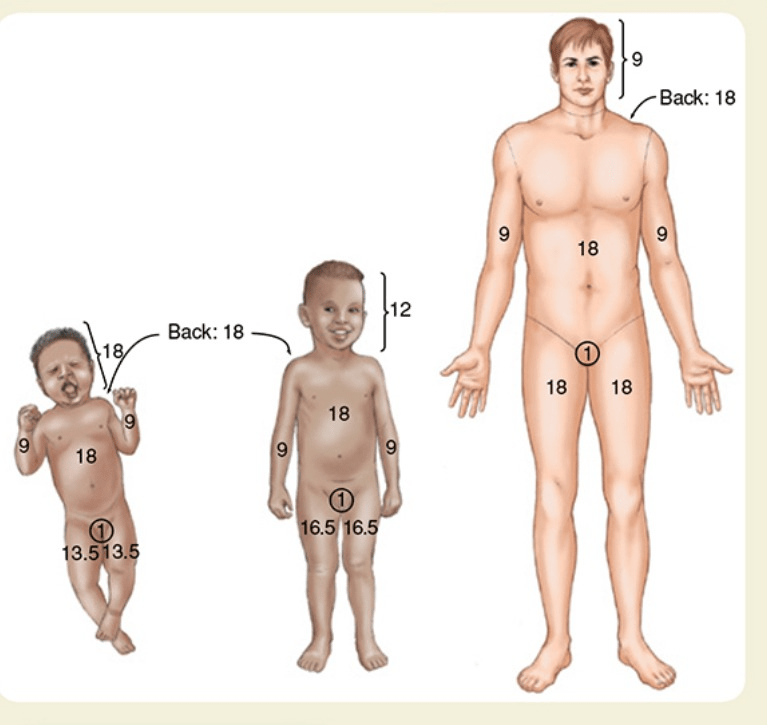
(1) Dr. Miranda Bailey is treating a patient of what type of injury? Be as specific as possible.
(2) What do we hope the EMTs had done (interventions) for this patient when they were first in their care?
(3) Let's say the injures cover the patient entirely from hips upwards (excluding the 1%). What would be their total body surface area (BSA) %?
(1) Burn injury, 2nd and 3rd degree burns
(2) > 9% BSA = dry sterile burn dressing/sheet (non-adherent) applied to all areas of burn
(3) torso anterior (18) + torso posterior (18) + R arm (9) + L arm (9) + Head (9) = 63%
What is the type of shock associated with a heart's inability to maintain sufficient cardiac output to meet the demands of the rest of the body? Provide at least one example of what can cause this type of shock.
Shock Type: Cardiogenic
Example: Secondary to a myocardial infarction or pulmonary edema
You are on the scene of a workplace where the 911 caller is requesting their colleague to be evaluated. The 911 caller states the patient has been appearing more dissociated, less sociable, noted weight loss in the last month, and was found in the bathroom on their own with a razor. The colleague (your patient) has a flat affect but is cooperative to your assessment.
List 3 appropriate questions to ask this patient.
(100 points) How do you feel?
(100 points) Do you have any thoughts of wanting to hurt yourself?
(100 points) Do you have any thoughts of wanting to hurt anyone else?
BSI, your scene is safe. You arrive on scene to an explosion at a paint store.
What are your next immediate steps in rendering care? (think broader than your assessment formula)
Where is your crew to locate themselves in relation to the incident?
- (100 points) Determine the number of patients.
- (100 points) Make contact with all 6 patients to complete triage and request appropriate resources
- (100 points) What could the request for additional resources sound like on the radio?
- (100 points) Clarify a proper staging area for the patients - consider removal of any and all patients possible to treat in the ambulance / not in the roadway
- (100 points) the staging area qualifies as the green/cool zone of an incident - where your patients, your crew, and your equipment should be located
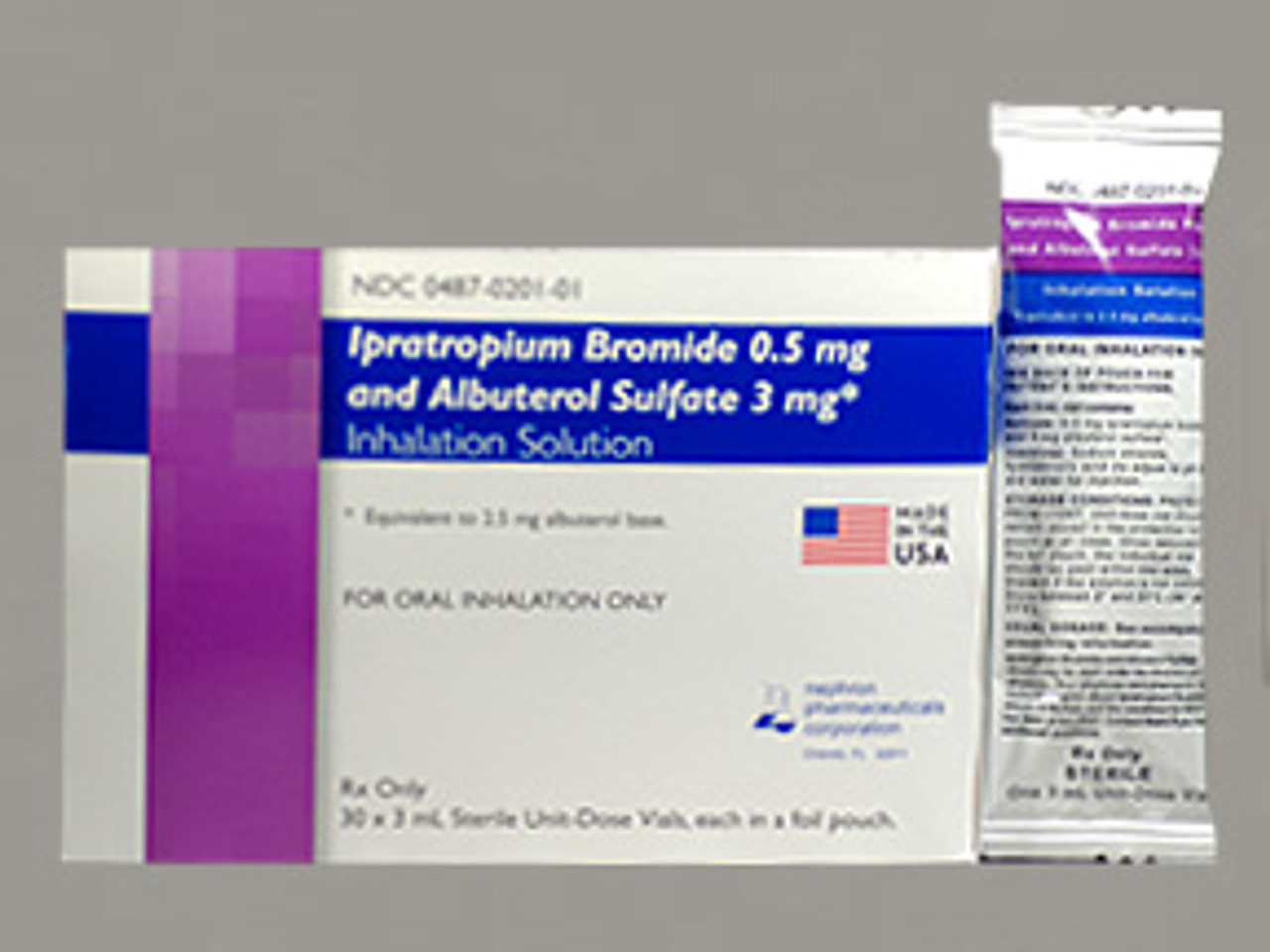
What is the route and dose of Albuterol Sulfate?
What mask and flow rate is the medication delivered in?
Bonus: what's the NYC protocol medication also to be given for the same indications? (extra 100 points!)
Dose (100 points): 2.5 mg in 3 mL
Route (100 points): Inhalation
Mask/Flow Rate (100 points): Nebulizer, 6-8LPM
Bonus (200 points): Ipratropium Bromide - 0.5mg in 2.5 mL
Help! Your best friend accidentally cut off one of their fingers while working at the local deli shop! The knew you are in an EMT class and called you urgently to assist them with what to do while they await EMS. How would you advise them to manage their amputation injury?
Stump (100): Elevate and wrap with moist sterile dressings and cover with dry bandage
Amputated part (100): Moistened sterile dressings to wrap the amputated part
(100): Place wrapped amputated part into a water-tight container (sealed plastic bag)
(100): Place sealed plastic bag with wrapped amputated part onto ice (being careful not to freeze part)
(100): Never wait for locating the amputated part -- treat the patient :)
What type of shock is a result of a rapid reaction to an exposure and quickly leads to decompensated shock phase in a matter of minutes?
Bonus:
+ (100) Note how the respiratory and cardiac system reacts (dilation or constriction to each)
+ (200) What life saving medication can assist in the treatment of this type of shock, and how does it impact the dilation or constriction of the respiratory and cardiac system? Include dose and route!
Type of Shock (100): Anaphylactic Shock
Bonus +100: Bronchoconstriction and Vasodilation
Bonus +300: Epinephine, IntraMuscular (IM),,
0.3mg for an adult (> 30kg) or 0.15mg for a pediatric (<30kg)
You are treating a patient who you determine is presenting with an altered mental status (AMS). You are now in your focused assessment. List 3 relevant questions to ask in your interview.
BONUS: List 5 different things you can look for that would be relevant to assess for in an AMS patient.
Questions:
- Describe the Episode
- How long as the episode been occurring
- How has the episode progressed
- When was the patient last known to be well (their baseline behavior)
Bonus:
- Blood glucose level (rule out hypoglycemia)
- Cincinnati Stroke assessment (rule out acute signs of a stroke)
- Evidence of alcohol or drug use (rule out drug use/misuse/abuse cause)
- Evidence of trauma
- Pulse Oximeter/Skin assessment/Respiratory effort (rule out hypoxia cause)