What is high blood pressure called?
Hypertension
What comes first in your arrival and assessment of patient?
SCENE SAFETY
What is the difference between anterior and posterior?
Anterior-front
Posterior-back
What is ATP?
When artificially ventilating an adult patient, how often do you ventilate?
once every 5-6 seconds
What does "OPQRST" stand for?
Onset, Provocation, Quality, Radiation, Severity, Time
When examining the throat of your patient what are two indicators of thoracic cavity trauma?
JVD and tracheal deviation
What does hyper- and hypo- mean?
high/over and low/below
What form of metabolism happens with oxygen?
aerobic
What is the most common thing blocking the airway of a patient?
the tongue
A pattern of vital signs is known as what?
Trending vitals signs
What is one of the first indicators that your patient is or is not having good perfusion?
Skin Signs
What does bilateral mean?
Both sides
What is found ion is found outside the cell?
Sodium(Na+)
How is an NPA measured for a patient?
tip of nose to tip of earlobe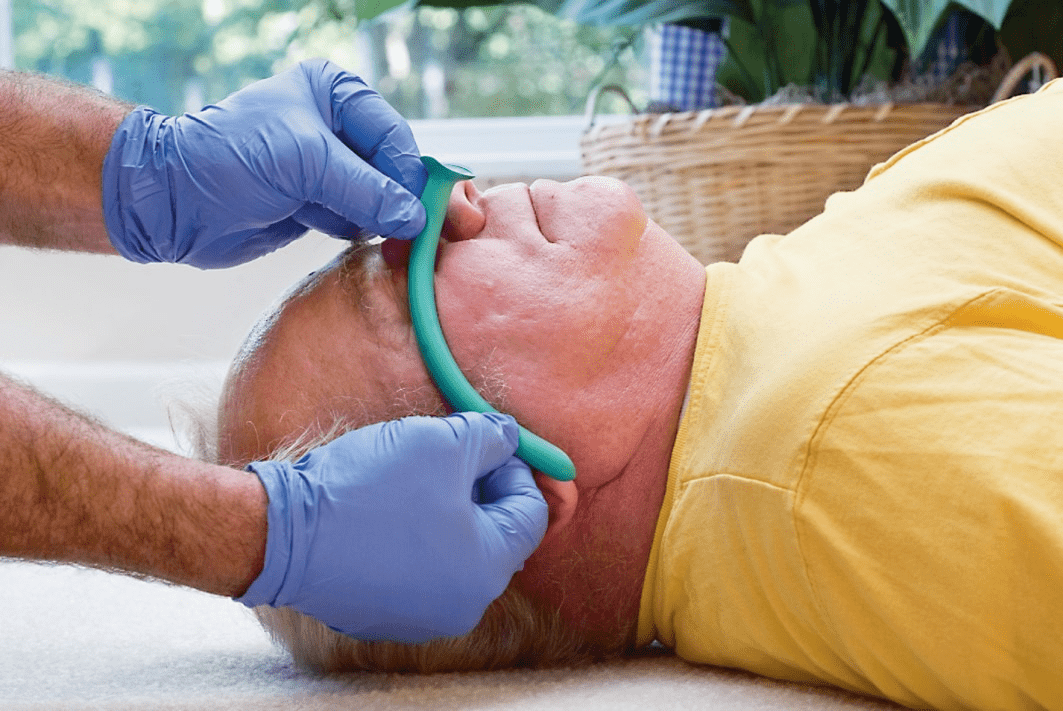
What is the medical term for "sweaty"?
*hint-its not clammy
Diaphoretic
What three things are checked on extremities during the trauma assessment and before and after splinting a limb?
Pulse, Movement, Sensation
What is the medical prefix used when referring to the heart?
cardio- cardi/o
What is required to complete the process of extracting energy from glucose and removing the wastes produced by the process?
Oxygen
What rhythm is the flatline on the monitor called?
asystole
If you take a blood pressure on a patient that is lying supine and then take another blood pressure when they are standing upright-what have you just conducted?
Orthostatic Vital signs
During what assessment would you manage life threats?
Primary Assessment
What is the medical prefix used when referring to the lungs?
pulmo- or pneumo-
The first portion of cellular metabolism that happens without oxygen(anaerobic) is called what?
glycolysis
What is our range for capnography?
35-45mmHg