A 55-year-old woman is evaluated for hyperthyroidism.
The neck and corresponding thyroid scan are shown.
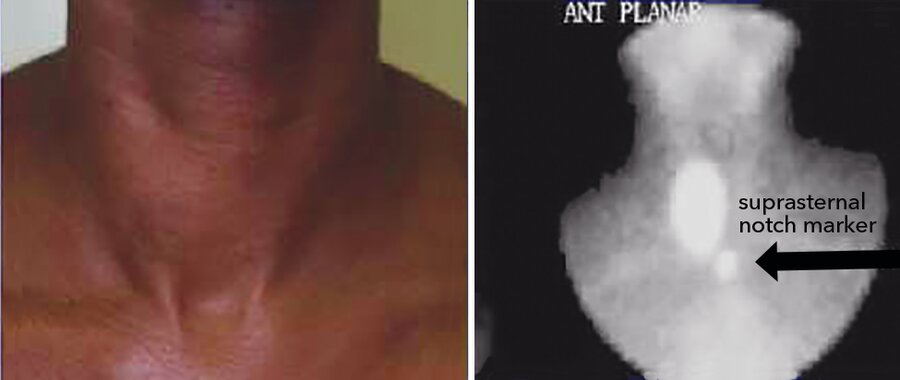
Exogenous intake of thyroid hormone
Graves disease
Multinodular goiter
Toxic adenoma
A 30-year-old transgender man is evaluated for ongoing management of gender-affirming hormone therapy. He began masculinizing therapy with weekly intramuscular testosterone cypionate 8 weeks ago. He is in good health and takes no other medications. He remains particularly concerned about when menses will cease, as this occurrence is very bothersome to him.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies:
Testosterone, total (measured midway between injections)
600 ng/dL (21 nmol/L) (target level, 400-700 ng/dL [13.9-24.3 nmol/L])
What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Decrease testosterone cypionate dose
Increase testosterone cypionate dose
Switch intramuscular testosterone cypionate to transdermal testosterone
Reassurance
An 85-year-old woman is evaluated at a follow-up visit for a right femur fracture that occurred 6 weeks ago and was treated with open reduction and internal fixation. The fracture occurred because of a ground-level fall. Medical history is significant for stage G4 chronic kidney disease, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and hypertension. Medications are amlodipine, lisinopril, and a vitamin D3 supplement.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. A healing surgical scar is noted on the right lateral hip. She reports no hip pain with passive range of motion. She bears weight without pain.
Laboratory studies:
Calcium
9.2 mg/dL (2.3 mmol/L)
Creatinine
1.6 mg/dL (141 μmol/L)
H
Creatinine clearance
28 mL/min (normal range, 88-128 mL/min)
L
Phosphorus
4.3 mg/dL (1.39 mmol/L)
Parathyroid hormone
75 pg/mL (75 ng/L)
H
25-Hydroxyvitamin D
32 ng/mL (80 nmol/L)
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Abaloparatide
Alendronate
Denosumab
Zoledronate
A 40-year-old man is evaluated for a painless foot ulcer (shown). He has diabetes mellitus.
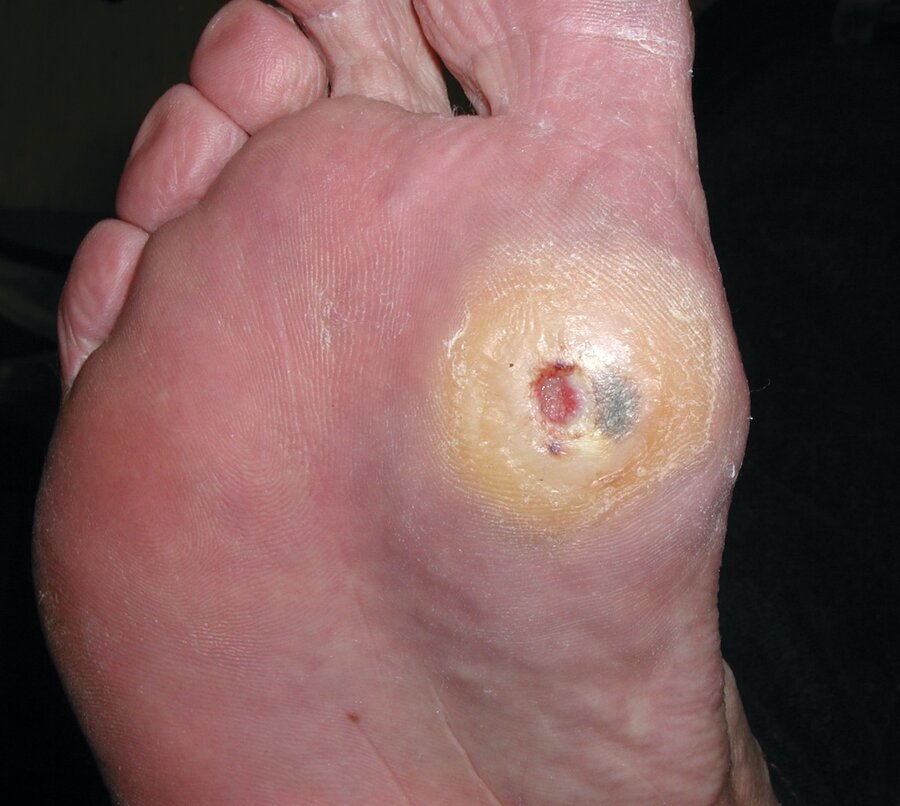
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Arterial ulcer
Neuropathic ulcer
Pressure ulcer
Venous ulcer
A 27-year-old man is evaluated for a pituitary tumor, which was discovered during an ongoing evaluation for a 6-month history of fatigue and decreased libido. He has no other medical conditions and takes no medications.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies:
8 am cortisol
18 µg/dL (496.8 nmol/L)
Follicle-stimulating hormone
3 mU/mL (3 U/L)
L
Luteinizing hormone
2 mU/mL (2 U/L)
L
Prolactin
14 ng/mL (14 μg/L)
Testosterone
140 ng/dL (4.9 nmol/L)
L
2 weeks ago
130 ng/dL (4.5 nmol/L)
L
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
1.5 µU/mL (1.5 mU/L)
Insulin-like growth factor-1 and late-night salivary cortisol levels are normal.
MRI shows a 1.5-cm pituitary macroadenoma without compression of the optic chiasm.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Measure free thyroxine level
Measure growth hormone level
Repeat MRI in 1 year
Start cabergoline
A 22-year-old man is evaluated in the hospital for newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus after being admitted 2 days ago for severe hyperglycemia associated with diabetic ketoacidosis. Over the course of the past month, he experienced an unintentional 5-kg (11.0 lb) weight loss and new-onset polyuria and polydipsia. During the 2 days before admission, he developed nausea, vomiting, and malaise. Treatment with intravenous fluids, insulin, and potassium was initiated. Today, the patient has improved.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 23. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Which of the following is the most appropriate confirmatory diagnostic test?
Fasting C-peptide
Fasting plasma glucose
Glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody
Hemoglobin A1c
A 51-year-old woman is evaluated after a 2.5-cm right adrenal mass with a density of 6 Hounsfield units was found incidentally on an abdominal CT scan. She has experienced intermittent sweating and hot flushes for the past 3 months. Medical history is relevant for hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide and doxazosin.
Blood pressure is 142/90 mm Hg. No supraclavicular fat pads or abdominal striae are seen.
Laboratory studies:
Overnight low-dose (1-mg) dexamethasone suppression test (LDST)
8 am cortisol, total
8 µg/dL (221 nmol/L)
Free metanephrine
15 pg/mL (0.078 nmol/L)
Free normetanephrine
17 pg/mL (0.0952 nmol/L)
Plasma aldosterone concentration/plasma renin activity ratio
13 (normal range, ≤20)
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Mild autonomous cortisol secretion (previously termed subclinical Cushing syndrome)
Non–hormone–secreting adrenal adenoma
Pheochromocytoma
Primary aldosteronism
A 59-year-old man undergoes a comprehensive ophthalmologic examination after a recent diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Funduscopic findings are shown.
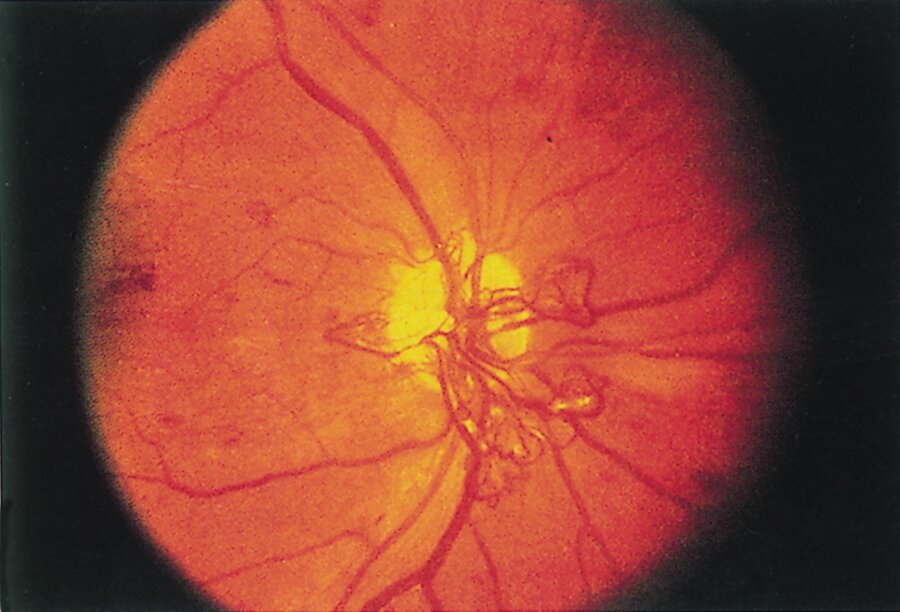
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Age-related macular degeneration
Glaucoma
Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
A 27-year-old woman is evaluated during a follow-up visit for prediabetes. She exercises at least 150 minutes/week and follows recommended dietary interventions but has only lost 2 kg (4.4 lb) in the past 6 months. She has no other medical conditions and takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 36. Examination of the posterior neck reveals velvety brown thickening of the skin.
Laboratory studies:
Hemoglobin A1c
6.2%
H
She is concerned about her risk for progressing to type 2 diabetes mellitus and is interested in additional interventions.
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Acarbose
Metformin
Orlistat
Pioglitazone
A 39-year-old man is evaluated because he is concerned about growth hormone deficiency because of feelings of fatigue and reduced muscle mass over the past few months. He has no history of head trauma, pituitary radiation therapy, or surgery. He has no other medical problems and takes no medications.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal. Muscle mass and strength are normal.
Laboratory studies:
Testosterone
550 ng/dL (19 nmol/L)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
1.8 µU/mL (1.8 mU/L)
Which of the following is the most appropriate screening test to perform next?
Glucagon stimulation test
Growth hormone measurement
Insulin-like growth factor-1 measurement
No further testing
A 72-year-old man is evaluated for ongoing management of subclinical hypothyroidism. He feels well. He has had no recent illnesses, hospitalizations, or exposures to iodinated contrast. Medical history is remarkable for coronary artery disease treated with percutaneous stent placement at age 65 years, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension. Medications are aspirin, atorvastatin, and lisinopril.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies:
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
12.1 μU/mL (12.1 mU/L)
H
Free thyroxine
1.1 ng/dL (14 pmol/L)
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Measure thyroid peroxidase antibodies
Repeat thyroid function testing in 3 to 6 months
Start levothyroxine
Start liothyronine
A 53-year-old man recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoes a comprehensive foot examination.
Physical examination findings are shown.
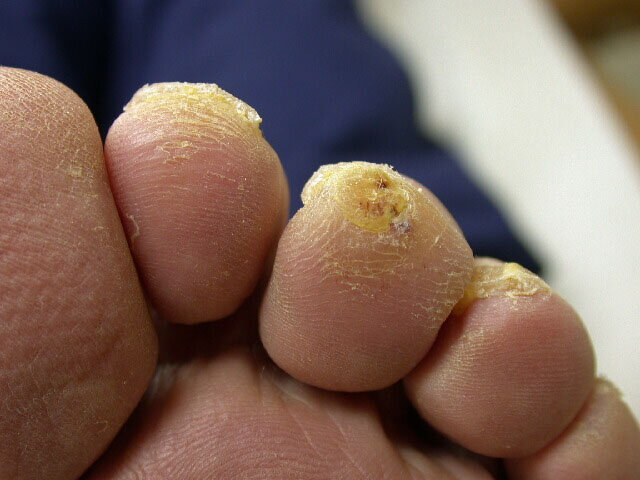
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cellulitis
Onychomycosis
Pre-ulcer with callus formation
Venous insufficiency
A 64-year-old man is evaluated for a routine physical examination. He is asymptomatic. He walks about 10 minutes per day. Medical history is unremarkable, and he takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 27. Waist circumference is 104 cm (41 in).
Laboratory studies:
Glucose
108 mg/dL (6 mmol/L)
H
Triglycerides
210 mg/dL (2.37 mmol/L)
H
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Increase daily physical activity
Reduce calorie intake to less than 800 kcal/d
Start metformin
Start orlistat
A 67-year-old man is evaluated for a 6-month history of myalgia and fatigue. Medical history is relevant for Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery for obesity 2 years ago. He was prescribed a once-daily multivitamin and monthly vitamin B12 injections but stopped both 6 months ago because of constipation.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies:
Hemoglobin
14 g/dL (140 g/L)
Albumin
3.8 g/L (38 g/L)
Calcium
8.8 mg/dL (2.2 mmol/L)
Creatinine
0.9 mg/dL (79.6 μmol/L)
Parathyroid hormone
89 pg/mL (89 ng/L)
H
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
Bone mineral density measurement
Parathyroid sestamibi scan
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D measurement
24-Hour urine calcium measurement
A 68-year-old man is evaluated for abnormal thyroid function test results. Over the past 2 months, he has had decreased appetite, a 9.1-kg (20.0 lb) weight loss, loss of interest, and fatigue. Medical history is significant for chronic persistent atrial fibrillation, diagnosed 3 years ago, and hypertension. Medications are apixaban, metoprolol, amiodarone, and lisinopril.
On physical examination, pulse rate is 101/min and irregular; remaining vital signs are normal. BMI is 19. No exophthalmos is noted. The thyroid gland is palpable, nontender, and has no nodules. The patient exhibits bilateral hand tremors. Mood is depressed.
Laboratory studies:
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
0.01 μU/mL (0.01 mU/L)
L
Free thyroxine
3.9 ng/dL (50 pmol/L)
H
Total triiodothyronine
225 ng/dL (3.5 nmol/L)
H
Thyrotropin receptor antibody
Negative
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Methimazole
Prednisone
Thyroid Doppler ultrasonography
Thyroid peroxidase antibody measurement
Thyroid scintigraphy with radioactive iodine uptake
A 20-year-old woman is evaluated for amenorrhea. She underwent menarche at age 12 years and had regular monthly menses until 12 months ago, when menses became irregular. Menses ceased completely 6 months ago. She also reports hot flashes and vaginal dryness. She has a history of overweight but has lost 27.2 kg (60.0 lb) in the past year through running and diet changes. She is not sexually active. She takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 17. Physical examination is otherwise unremarkable.
Laboratory studies:
Estradiol
0.5 pg/mL (2 pmol/L)
L
Follicle-stimulating hormone
4 mU/mL (4 U/L)
L
Prolactin
10 ng/mL (10 μg/L)
Testosterone, total
18 ng/dL (0.6 nmol/L)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
1.2 μU/mL (1.2 mU/L)
β-Human chorionic gonadotropin
Negative
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Primary ovarian insufficiency
Turner syndrome