Chemical potential energy
Most important type of energy in Biology. Always a net gain or loss of ions. Energy potential is in the bonds.
page 101
Process of "sugar breaking" that happens in the cytoplasm.
What is Glycolysis?
page 106
Aerobic Respiration
What is respiration in the presence of oxygen?
A form of pure massless energy
What is Electromagnetic energy?
page 118
The Krebs cycle takes place here.
What is in the mitochondria?
page 107
Every reaction in the body requires this cofactor in order to proceed.
What is an enzyme?
page 104
Catabolism
The breakdown of macromolecules into usable building blocks.
page 105
Produces either lactate in the muscles or ethanol.
What is fermentation?
Plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use this process to store sugars that powers all life on earth.
What is photosynthesis?
Proceeds in the absence of oxygen.
What is Glycolysis?
Electrons are transferred from one reactant to another to form new products
Redox or oxidation-reduction reaction
page 101
Occurs across the mitochondrial membrane.
What is Oxidative Phosphorylation?
page 112
Fermentation takes place in
What is Glycolysis?
Products of photosynthesis in a chloroplast
What is glucose and oxygen?
page 117
How many ATP's are produced through oxidative phosphorylation?
What is approximately 26-28 ATP's?
The law of conservation of energy states
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed, only changed in form.
page 100
In Oxidation of pyruvate, pyruvate is acid is converted into Acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA). Acetyl CoA is a
Coenzyme (a type of cofactor) must be present with an enzyme in order to catalyze a particular reaction.
page 107
Aerobic exercise enables muscles to work harder by
What is by increasing the heart rate and respiratory rate to deliver more O2 to the muscles.
page 115
A knife that damages subatomic particles.
"Gamma knife" A very tiny gamma ray smaller than an atom used to deliver maximum damage to cancer cells.
Transpiration uses stomata's to do what?
What is to allow environmental CO2 to enter and H2O molecules to escape in plant leaves.
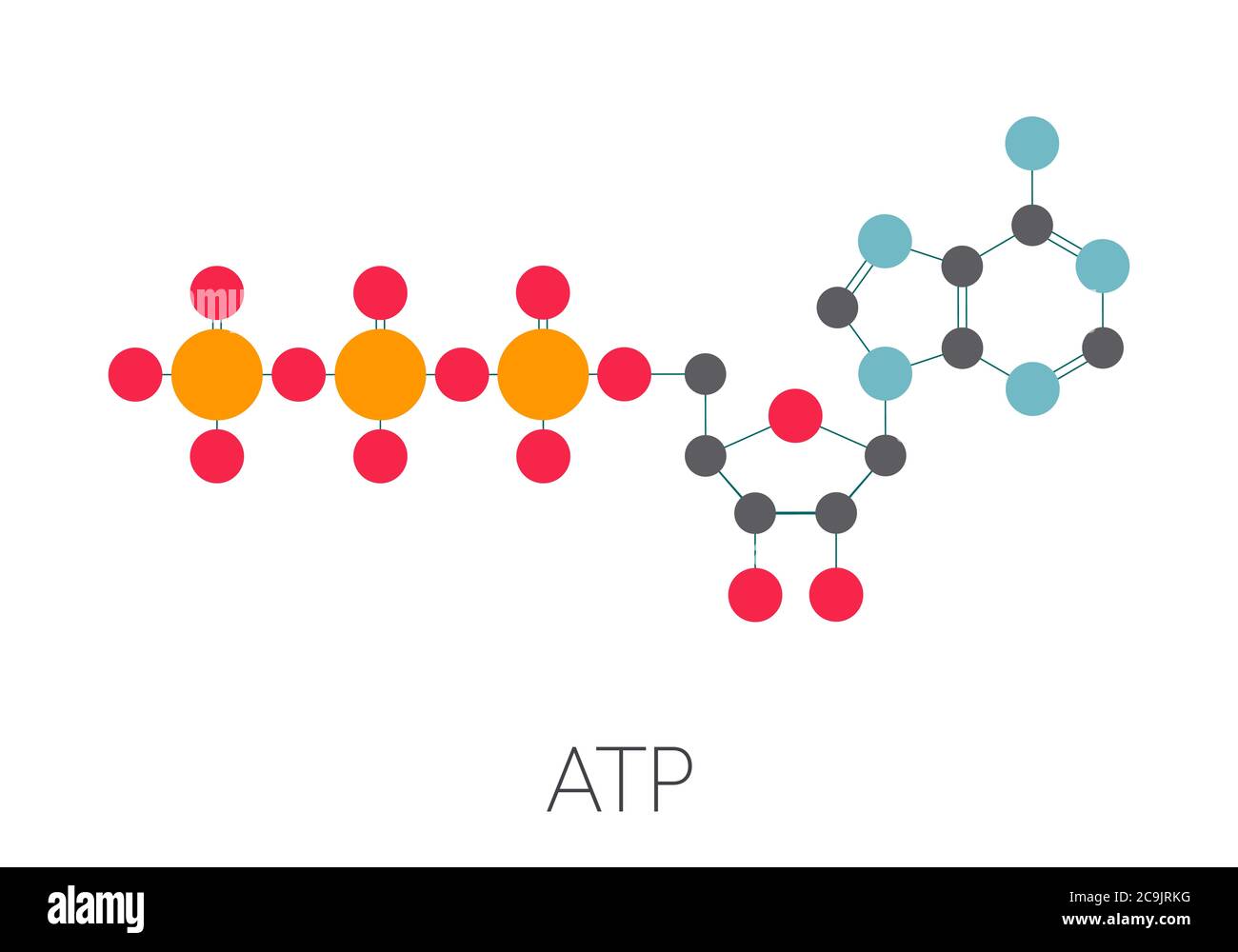
Draw the ATP molecule on the white board
The Krebs Cycle take place here and in a double-cycle outputs are
What is the Mitochondria matrix and 2 ATP, 6 FADH, 4 CO2
Besides fermentation, microorganisms living in environments where there is no oxygen produce ATP in this way.
Anerobic respiration, they use a different molecule (instead of O2) for the final acceptor in their ETC. Like sulfate (SO4).
page 116
The purpose of the Calvin Cycle
What is to synthesize sugars out of CO2 using energy supplied by ATP an NADPH from the light-dependent phase of photosynthesis.
This is how does oxygen get to the cell.
O2 is breathed in through the lungs where it diffuses across the membrane in the lungs to the red blood cells where hemoglobin picks it up and carries it to every cell.
page 106