The energy an object has due to its motion.
What is kinetic energy?
Energy stored in an object due to its position.
What is potential energy?
The kinetic energy of a 2 kg ball moving 3 m/s.
What is 9 J?
The gravitational potential energy of a 5 kg object lifted to a height of 4 m.
What is 196 J?
The energy supplied to a system.
What is input energy?
The useful energy produced by a system.
What is output energy?
The Law of Conservation of Energy.
What is energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can change forms?
The sum of potential and kinetic energy.
What is mechanical energy?
Energy stored in food or fuel.
What is chemical energy?
The kinetic energy of a 54 kg object moving 15 m/s.
What is 6,075 J?
The gravitational potential energy of a 75 kg object lifted to a height of 5 m.
What is 3,675 J?
Energy produced by a system, but not used for the intended purpose of the system.
What is wasted output energy/
The input and output energy of a toaster.
What is electrical and heat?
The point on this pendulum where potential energy would be the least.
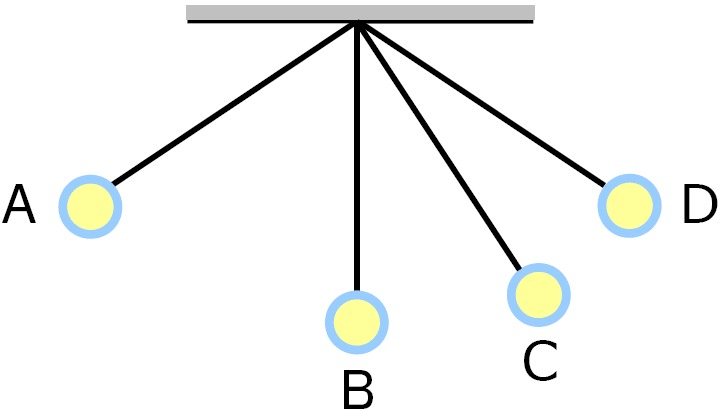
What is B?
The energy stored in an object when it is stretched or compressed.
What is elastic potential energy?
Energy of particles moving through a wire.
What is electrical energy?
The reason a stationary object has 0 kinetic energy.
What is the lack of motion, as kinetic energy depends on motion/
The two factors (other than gravity) that affect an object's gravitational potential energy.
What are mass and height?
Two most common forms of wasted output energy.
What are heat and sound?
The input and output energy in an electric lamp.
What is electrical and light energy?
The point on this pendulum where the values of potential and kinetic energy would be the closest.
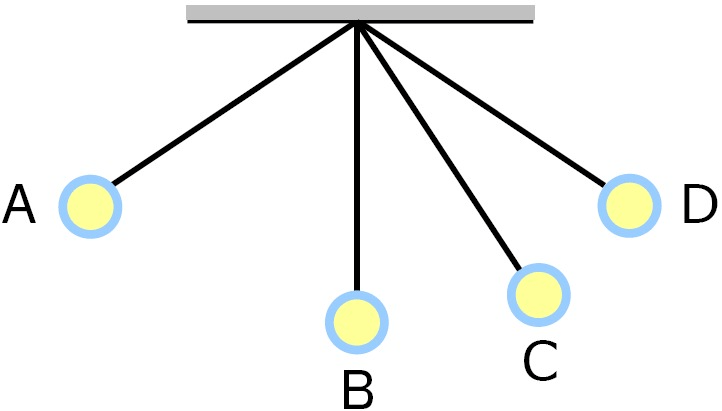
What is C?
The magnitude of acceleration due to gravity.
What is 9.8 m/s?
Energy of electromagnetic waves, such as UV or X-rays.
What is radiant energy?
The mass of an object with 4,500 J of kinetic energy moving at a rate of 5 m/s.
What is 360 kg?
How potential energy changes as an object falls.
What is decreases as it is converted to kinetic energy?
The reason a bouncing ball does not always return to its original height.
What is energy lost due to friction and air resistance?
The input and output energy of photosynthesis.
What is light and chemical energy?
This can be said about the mechanical energy of a pendulum if friction and air resistance are not taken into consideration.
What is remaining constant?
The formula for Gravitational Potential Energy.
G.P.E. = m x g x h
The formula for kinetic energy.
What is 0.5mv2?
The velocity of a 10 kg object with a kinetic energy of 950 J.
What is 13.78 m/s?
The mass of an object dropped from 9 m with a potential energy of 700 J.
What is 7.93 kg?
The input, output, and wasted output energy of a person ringing a bell.
What is chemical, sound, and mechanical/kinetic?
The energy transformations occurring in a hand-cranked flashlight.
What is mechanical - electrical - heat/light?
The reason it is highly unlikely for a machine to have 100% efficiency.
What is due to the loss of energy to factors such as friction and air resistance?