Two stones, one twice the mass of the other, are dropped from a cliff. Just before hitting the ground, what is the kinetic energy of the heavy stone compared to the light one?
twice as much
What is the spring energy equation?
Us=(1/2)kx2
What is the gravitational potential energy formula?
Ug=mgh
Mike performed 5 J of work in 10 secs. Joe did 3 J of work in 5 secs. Who produced the greater power?
Joe
By what factor does the kinetic energy of a car change when its speed is tripled?
factor of 9
What is the spring energy of a spring with a spring constant of 400 N/m and has been stretched 2cm?
0.08 J
Two paths lead to the top of a big hill. One is steep and direct, while the other is twice as long but less steep. How much more potential energy would you gain if you take the longer path?
Same amount
You lift a book with your hand in such a way that it moves up at constant speed While it is at constant constant speed, what is the total work done on the book?
Zero
Car #1 has twice the mass of car #2, but they both have the same kinetic energy. How do their speeds compare?
square root (2*v1) = v2
How does the work required to stretch a spring 2 cm compare with the work required to stretch it 1 cm?
4 times the work
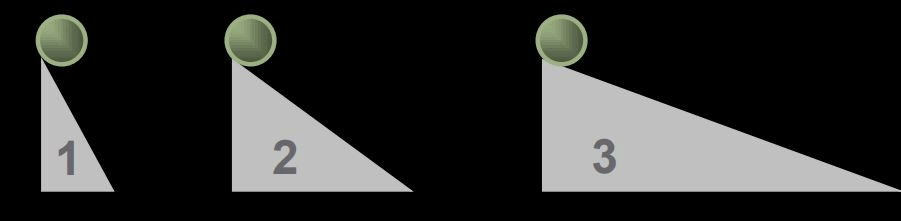 Three balls of equal mass start from rest and roll down different ramps. All ramps have the same height. Which ball has the greater speed at the bottom of its ramp?
Three balls of equal mass start from rest and roll down different ramps. All ramps have the same height. Which ball has the greater speed at the bottom of its ramp?
All the same
A box is being pulled up a rough incline by a rope connected to a pulley. How many forces are doing work on the box?
3 forces
Gravity
Tension
Friction
A car starts from rest and accelerates to 30 mph. Later, it gets on a highway and accelerates to 60 mph. Which takes more energy, the 0 to 30 mph, or the 30 to 60 mph?
30 to 60
A spring is placed horizontally on a frictionless table. The spring constant of the spring is 50 N/m, and it is compressed 0.1 m by a 2 kg block. When the spring expands back to its resting position, it pushes the block away. What is the speed of the block as a result of this force?
0.5 m/s
A 5kg ball is dropped from the top of a 100m tall tower. The ball lands in a pool of water. If the water provides a constant resistive force of 25N, how deep must the pool be to stop the ball?
196m
If a car traveling 60 km/hr can brake to a stop within 20 m, what is its stopping distance if it is traveling 120 km/hr? Assume that the braking force is the same in both cases.
80 m
Is it possible for the kinetic energy of an object to be negative?
No
A 1.00 kg mass is placed at the free end of a compressed spring. The force constant of the spring is 115 N/m. The spring has been compressed 0.200 m from it neutral position. It is now released. Neglecting the mass of the spring and assuming that the mass is sliding on a frictionless surface, how fast will the mass move as it leaves the spring?
2.14 m/s
Is it possible for the gravitational potential energy of an object to be negative?
Yes
A golfer making a putt gives the ball an initial velocity of v0 , but he has badly misjudged the putt, and the ball only travels one-quarter of the distance to the hole. If the resistance force due to the grass is constant, what speed should he have given the ball (from its original position) in order to make it into the hole?
2v0