Define: Syntax
the grammar rules that control how we put words together to make sentences.
- Word order: How words are placed in relation to each other.
- Grammatical relationships: How words relate to each other within a sentence (e.g., subject, verb, object).
- Sentence structure: How phrases and clauses are combined to form sentences.
Define: Parts of Speech
grammatical categories, are classifications of words based on their roles and functions within a sentence.
Nouns
Pronouns
Adjectives
Adverbs
Prepositions
Conjunctions
Interjections
Define: Etymology
the study of the history of words. It delves into how words originate, how their forms and meanings have changed over time, and how they have spread across different languages.
What are the 3 eras of English
Old, Middle, Modern
What is unique about The Lord's Prayer in terms of the language it is written in?
one of the few surviving texts across a range of eras
Look at what is written below. Is this a sentence, clause, or phrase?
"the big, red ball"
phrase
What is a noun?
A noun is a word that names something.
- People: (e.g., teacher, John, student)
- Places: (e.g., city, park, home)
- Things: (e.g., book, table, car)
- Ideas: (e.g., freedom, love, justice)
Explain language elevation in relation to the French influence on English
words of French origin often came to be associated with higher social status, formality, and prestige compared to their native Anglo-Saxon counterparts.
E.g.: Cow vs Beef
Who was in England before the Romans invaded?
Celts
What language was Beowulf written in?
Sample below:
Old English
What is the difference between an independent and dependent clause
Example: because it was raining (dependent)
What is a verb?
a word that expresses an action, an occurrence, or a state of being. In simpler terms, it tells you what the subject of a sentence is doing or what is happening to it.
What is a lexicon?
The vocabulary of a language, an individual speaker, or a subject or field of study.
What happened after the Romans invaded and before the French invaded?
- Anglos, Saxons, Jutes, Frisians
then
- The Vikings
What is a key difference between Old English and Middle English 
Syntax OE= more flexible word order (inflectional morphemes) ME = SVO order
Morphology = OE = cases and inflectional endings, ME = relied on syntax
Orthography: OE = Latin alphabet and some runic characters
Lexicon: OE was primarily Germanic, ME borrowed extensively
What's the difference between a clause and a phrase?
Phrase:
Definition:
- A phrase is a group of related words that does not contain both a subject and a verb.
- It functions as a single unit within a sentence.
- A phrase cannot stand alone as a complete sentence.
Definition: - A clause is a group of related words that does contain both a subject and a verb.
- A clause can be either independent or dependent.
- An independent clause can stand alone as a complete sentence.
- A dependent clause can not stand alone as a complete sentence.
What is the difference between an adjective and adverb?
The key difference between adjectives and adverbs lies in what they modify:
- Adjectives:
- Modify nouns or pronouns.
- They describe the qualities or characteristics of nouns or pronouns.
- They answer questions like "What kind?", "Which one?", or "How many?".
- Examples:
- "The red car." (describes the car)
- "She is beautiful." (describes she)
- "They ate five cookies." (describes cookies)
- Adverbs:
- Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
- They provide information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action is performed.
Which refers to semantics and which refers to pragmatics?
1. Focuses on the literal meaning of words, phrases, and sentences.
2. Focuses on the meaning of language in context.
Semantics: literal meaning
Pragmatics: meaning in context
What was the purpose of the Statute of Pleadings?
To change the language of law from French to English
Explain the cultural relevance of Latin in English texts
1. Historical Prestige (Romans, The Church)
2. Intellectual Presitge ( Academia, Science, Medicine, the Church)
3. Authoritive (Law, the Church)
4. Modern Cultural Symbolism (prestige, heritage, scholarly, ancient, traditional, reverent)
Identify a noun phrase in this sentence:
She enjoyed reading books about ancient history
books about ancient history
What is a preposition?
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence.
It essentially indicates location, direction, time, or other connections.
in, on, at, to, from, with, by, for, about, under, over, between, behind, through, during, before, after.
What is the connotation and denotation of:
"she is blue"
connotation = she is sad
denotation = she is blue (like a smurf)
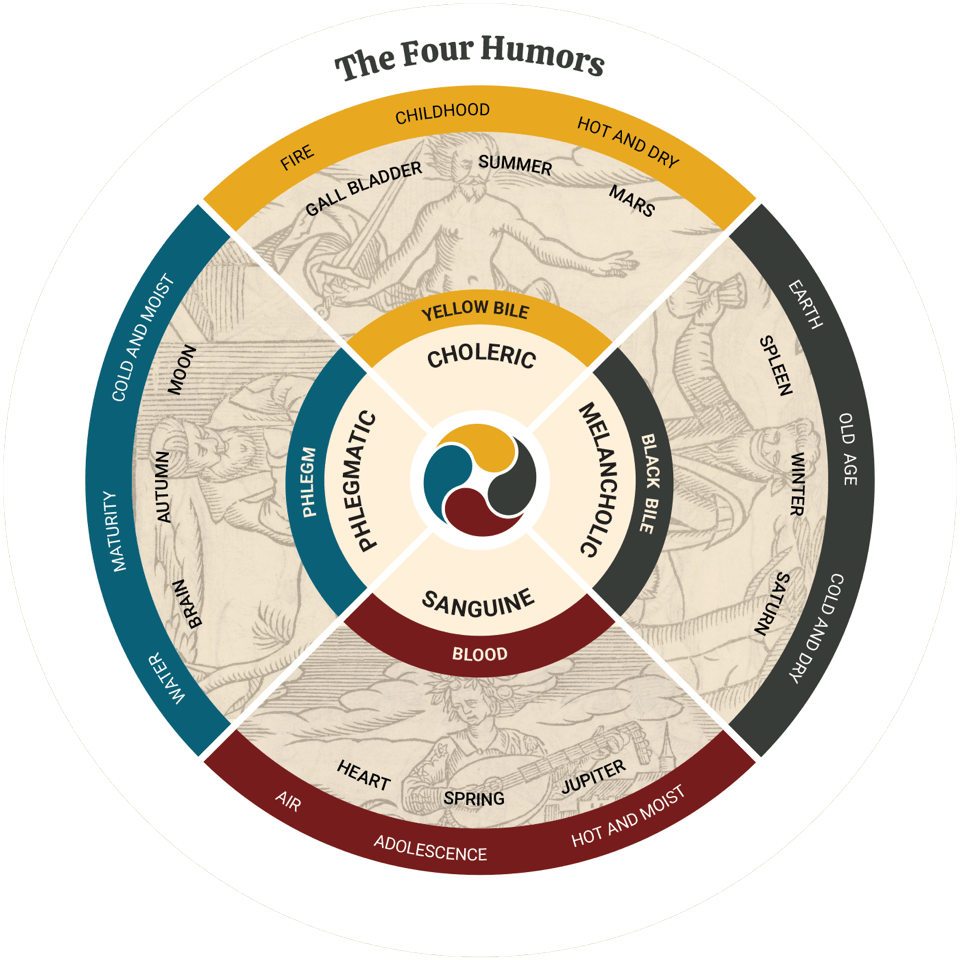
Explain the concept of the humours in medicine
The theory of humours suggested that the balance of four bodily fluids governed human health and temperament:
blood,
phlegm,
yellow bile,
and black bile.
Each humour was associated with specific qualities (warm/cold, moist/dry) and temperaments (sanguine, phlegmatic, choleric, melancholic).
Imbalances in these humours were believed to cause illness
Draw a parallel between these two images

Here Phlegm sits coughing on a marble seat, just like the money lenders in the city sit in front of their gold. His body is fat, not because he eats too much meat but because he has dropsy, so fluid has collected in his body. He keeps his lazy hand in his shirt as he drinks and spits and nods off to sleep by the chimney. A tortoise crawls beneath his feet, symbolizing his sloth, or laziness, because Phlegm hates working most of all, as his coarse clothing indicates. Nor does he like to study or put his mind to good use.