A physical barrier such as a canyon forming separating members of the same species is an example of
geographic isolation
Populations that grow exponentially are called this type of curve.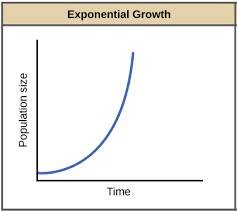
J curve
A population that levels off at the carrying capacity with have a population graph that resembles the letter _
S
These type of strategists reproduce slowly and have high parental care
K strategists
Different snail species have different shaped shells preventing them from reproducing with one another.
mechanical isolation
The rate at which a species increases is called its biotic potential and is based on its habitat requirements and _________ rates
reproductive
Death rate
Mortality
These type of strategists reproduce quickly, low parental care, and high mortality
R strategists
The Eastern and Western Spotted Skunks live in overlapping areas, but breed at different times of the year.
Temporal Isolation
Limiting factors prevent a species from increasing forever. These factors may cause a species to _____ or ______
die or move out of an area
Number of offspring produced
fertility
A population ________ shows a snapshot of a current population
pyramid
Speciation occurs when the gene pool of two populations is separated and cannot be shared through reproduction a new ___________ may develop.
species
The number of organisms the environment can sustain / support over a long period of time
carrying capacity
The ability to reproduce
fecundity
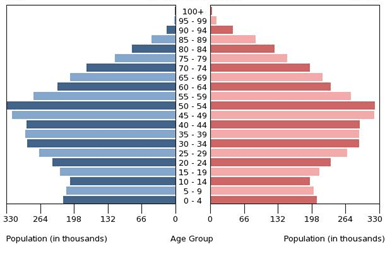
What does this population pyramid show the population doing?
decreasing
interspecific competition
Predators and disease are examples of ______ factors that can affect the carrying capacity of a population
Birth
natality
The main difference between s and j curves is that s curves have a ____________ capacity
carrying