Identify the soil type and explain what use the soil type is best for, if any.
0% Clay, 0% Sand, __% Silt
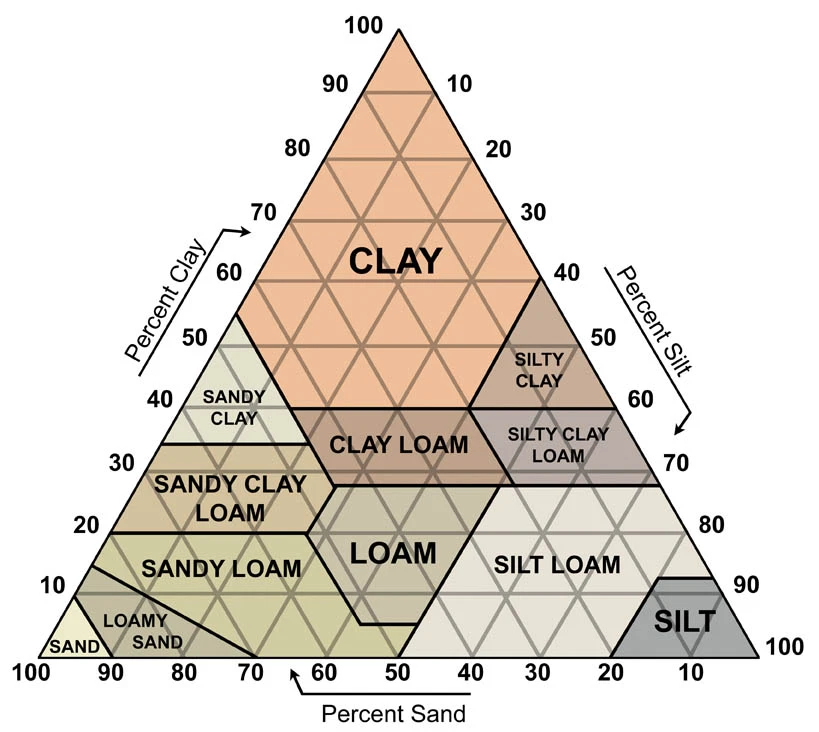
100% Silt
Soil Type: Silt
Silty soil is usually more fertile than other types of soil, meaning it is good for growing crops. Silt promotes water retention and air circulation. Too much clay can make soil too stiff for plants to thrive.
NOT ideal for building due to its prolonged ability to hold water.
What is the purpose of ribboning?
It is a technique that can help identify size of soil particles and basic composition of the topsoil, leading to land use implications.
What horizon is "topsoil"?
The A horizon which is composed of mineral and humus.
Navigate to the web soil survey and create an AOI of Huntingtown High School. Go to the soil map.
Find the map unit name of Huntingtown High School's sports field. Find the map unit name of the field in the legend to the left and click it. From the map unit description pop-up, find what information is under "Typical Profile."
AC - 0 to 2 inches: loam
C - 2 to 72 inches: gravelly loam
Alluvium vs. Colluvium
Alluvium accumulates in and adjacent to river channels, whereas colluvium is deposited by mass wasting processes acting on hill slopes.

Identify the soil type and explain what use the soil type is best for, if any.
60% Sand, 30% Clay, __% Silt
10% Silt
Sandy Clay Loam
Sandy clay loam soil is great for gardening because it contains a good mix of sand, silt, and clay. This type of soil is easy to work with and drains well.
If a soil feels largely "grainy" and doesn't hold a ribbon well, what soil type is most of its composition?
Sand
What soil horizons are represented by "Our Aunt Ethel Bakes Cookies Rapidly"?
Navigate to the web soil survey and create an AOI of Huntingtown High School. Go to the soil map.
Find the map unit name of ZBA that "rings" Huntingtown High's property to the right. What type of soil is this? What environmental feature is expected to be there based on the soil map unit description?
What is the best type of soil to sustain a basement?
Loam as it is a of majority sand and silt with some clay, allowing for even drainage which prevents flooding and holds to make a solid foundation.
Identify the soil type and explain what use the soil type is best for, if any.
50% Sand, 20% Clay, __% Silt
30% Silt
Soil Type: Loam
Loam is a mix of the soil particle types. It is ideal for agriculture except for sand-adapted plants such as tubers.
Loam soils generally contain more nutrients, moisture, and humus than sandy soils, have better drainage and infiltration of water and air than silt- and clay-rich soils, and are easier to till than clay soils.
It is great for growing a variety of vegetables. Some of the most common vegetables that do well in loamy soil are tomatoes, peppers, green beans, cucumbers, onions, and lettuce.
What is this tool and what is it used for?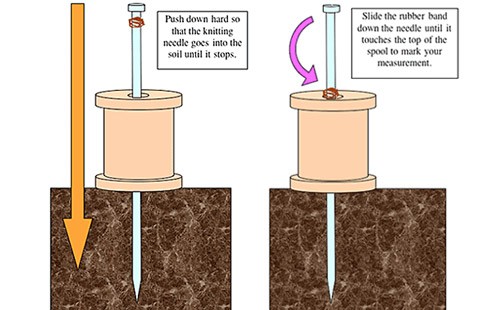

On the Envirothon test, soil compaction is measured by pushing a pin flag into the topsoil.
Soil compaction determines root limitation. The more compact the soil, the more limited the root growth and more laterally they grow.
How can you tell the B horizon from other horizons?
Accumulation of clay, sesquioxides, humus, or some combination of blocky structure, redder or stronger color than the A horizon. In well drained soils, the B horizon is typically a yellowish brown to strong brown color and is commonly referred to as the subsoil. B - horizons have material (usually iron but also humus, clay, carbonates, etc.)
Using your resources, define the three qualities of prime farmland.
(Example: Mark SUBCLASS
1. slope of 3% or more, or
2. sandy or moderately sandy surface texture.
Mark SUBCLASS
1. 40 inches or less to any limiting layer, or
2. surface texture or subsoil texture that is sandy or moderately sandy.
Mark SUBCLASS
1. poorly or somewhat poorly drained, or
2. on floodplain or filled depression landforms.)
Mark Prime Farmland
1. moderately sandy or finer subsoil texture, and
2. more than 20 inches to bedrock or coarse sand and gravel limiting layer (how deep the roots can grow), and
3. The slope is 6% or less.
Resource: https://www.agry.purdue.edu/soils_judging/new_manual/ch3-capability.html#sub3
What are the three ways that can define a place as a wetland?
Generally, wetland soils can be classified into three categories:
1. Soils permanently inundated with water above the soil surface
2. Saturated soils with the water table at or just below the soil surface
3. Soils where the water table depth is always below the surface
Identify the soil type and explain what use the soil type is best for, if any.
30% Sand, 60% Clay, __% Silt
10% Silt
Soil Type: Clay
Clay particles are so small that they have slight electrical charges. These charges hold on to plant nutrients, far better than sand. Clay soils also store large amounts of water in the very fine spaces between their particles. This ability contributes to their stickiness and plasticity.
Clay soil retains most nutrients very well because of its negative charge and high surface area, so clays usually are very fertile. Soils that contain more clay have higher nutrient amounts, but are not as easy to work in agriculture.
Ideal for water-holding, such as a wetland.
NOT ideal for building since clay tends to move due to its water holding capability. To build on clay, the clay foundation needs to be very deep in order to increase stability.
NOT ideal for a sewer system as clay's higher compaction can lead to drain failure.
Match topsoil structure with soil health.
A) Granular, soft & crumbly 1) Poor
B) Single plate, massive grain 2) Fair
C) Soil is a block & firm 3) Good
A - Good
B - Poor
C - Fair
How can you tell the E layer from other horizons?
The E horizon occurs when there is more precipitation than evaporation.
The E horizon appears lighter in color than an associated A horizon (above) or B horizon (below). An E horizon has a lower clay content than an underlying B horizon, and often has a lower clay content than an overlying A horizon, if an A is present. E horizons are more common in forested areas because forests are in regions with higher precipitation and forest litter is acidic. However, landscape hydrology, such as perched water tables, can result in the formation of an E horizon in the lower precipitation grasslands, as seen in the profile below. The dominant processes of an E horizon are losses.

Navigate to the web soil survey and create an AOI of Huntingtown High School. Go to the soil map.
Find the map unit name of ZBA that "rings" Huntingtown High's property to the right. Find what type of soil this is. Scroll to "Minor Components" in the map unit description. Under "Fallsington", what is the landform type?
Depressions, drainageways, swales
Use the soil books to summarize the difference between the main soil classifications present in the photo and their land use abilities.

Overall, the higher elevation soils have more limitations than the lower elevation soils but restrictions on land use are few or none.
(The higher the classification number, the more limited in soil use it is.)

Identify the soil type and explain what use the soil type is best for, if any.
80% Sand, 5% Clay, __% Silt
15% Silt
Soil Type: Loamy Sand
Loam is a mix of all soil particle types.
Loam soils generally contain more nutrients, moisture, and humus than sandy soils, have better drainage and infiltration of water and air than silt-and clay-rich soils, and are easier to till than clay soils.
What tool is this and what is its use?

The soil sample probe shows the different soil horizons.
What do letter designations of soil slope A - F mean?
The later the letter, the higher the slope and more steep, and limited in use, the soil is. Steepness in the coastal plain (Southern Maryland region) is classified more harshly than in the Piedmont or Appalachian. A 10% or below slope in the coastal plain is considered moderately steep or less.
(Page 4 of University of Maryland's Guide to Land Judging pdf has a table with the exact slope values and classifications.)
On the web soil survey, go to: Gabriels Way, Sunderland, MD, 20689
Zoom in on the house at the end of the road, some distance from the coldesac. It has a pool behind it. Make an AOI around the house.
What type of soil is the house mainly built on? Is the slope too high for building here to be reasonable?
The soil under the house is mainly dodon and marr. The slope is mainly 5 - 10%, meaning that while slightly steep, building is not very limited. So yes, a house here according to slope is fine.
(Soil description tip: If a soil is labeled like this: Name - name, then that means that those soils could be separated individually but it would be pointless to do so. If a soil is labeled like this: Name and name, then that means that those soils CANNOT be separated individually. The soil name that comes first is the more dominant in the soil profile.)
What are the fice Maryland Envirothon landscape positions and what are they?
Upland, Depression, Terrace, Floodplain
Upland - Higher terrain
Depression - A dip in the terrain
Terrace - A flat section of the terrain, typically is the level between a floodplain and upland
Drainageway - A path of weathering that water flows and erodes, especially after every rainstorm. Trails that are just soil at the top with revealed roots are likely drainageways.
Floodplain - Land bordering a body of water that often is flooded
Resource: https://mdenvirothon.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/soil-study-guide_revised_2017.pdf