This is something that changes the rate of the reaction of the chemical without being consumed by the reaction
Catalyst- a positive catalyst speeds up; a negative catalyst slows down
This stain will differentiate type l, type llA and type llB fibers. It also helps in separating myopathic from neuropathic processes
ATPase stain
Naphthol AS-D chloroacetate- granulocytes & mast cells
Bright red
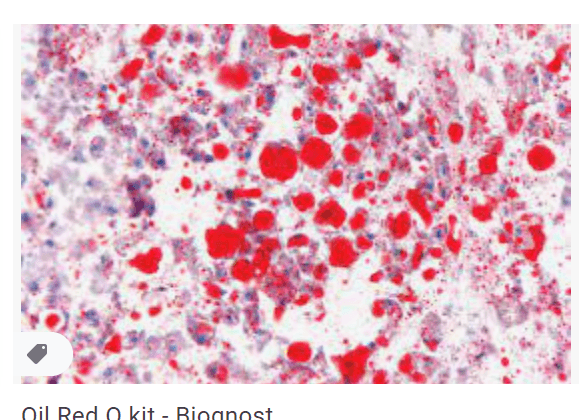
Oil red O
Chatter
Cold formalin, cold calcium formalin and cold acetone are used for enzymes for this purpose
Used to fix tissue for enzyme studies
This stain demonstrates abnormalities in mitochondria, Z-band material, and sarcoplasmic reticulum
NADH diaphorase
NADH diaphorase - site of enzyme activity & type l muscle fibers
Dark purple
Bielschowsky method
Water carryover in xylene
This occurs with the loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of elections
Reduction
This stain is useful in the diagnosis of McArdle disease, which has a single enzyme defect
Phosphorylase stain for muscle
Phosphorylase stain - phosphorylase activity
Varying shades of brow, blue and purple- no McArdle disease
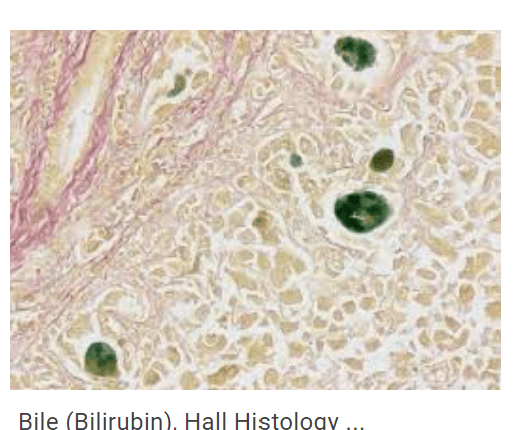
Bile stain
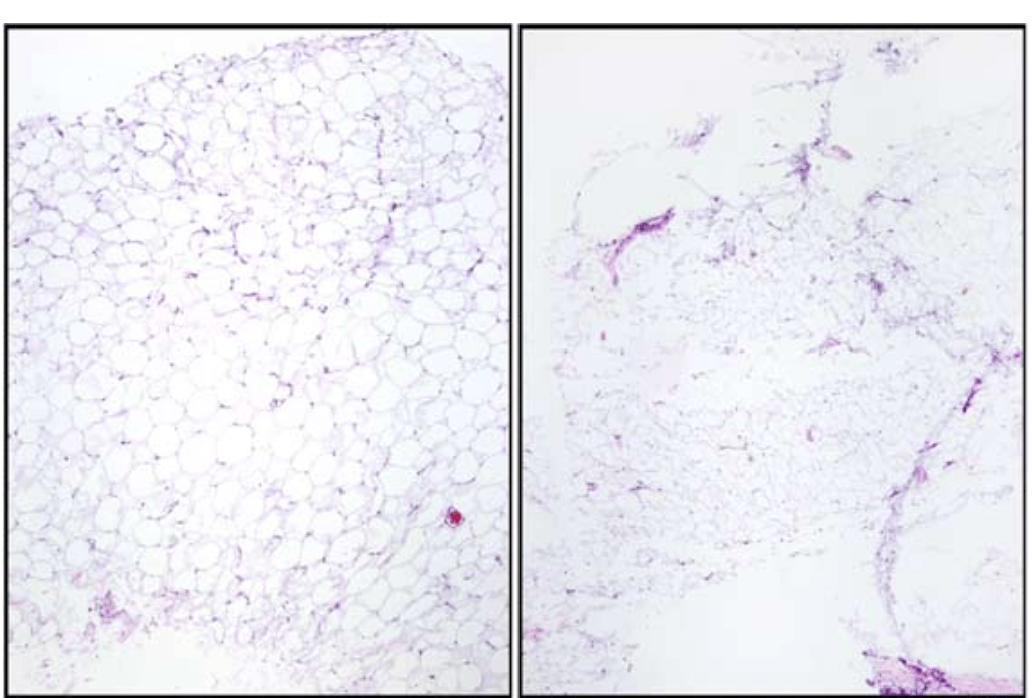
Non-compressed vs compressed tissue can result if tissue is underprocessed
This is the optimal pH for enzymes
pH 7.0
This stain differentiates between type 11 atrophy and neurogenic atrophy. Motor end-plates and lysosomes in inflammatory cells are also demonstrated
a-naphthyl acetate esterase stain for muscle biopsies
Modified Gomori trichrome- myofibrils (muscle)
Bluish-green
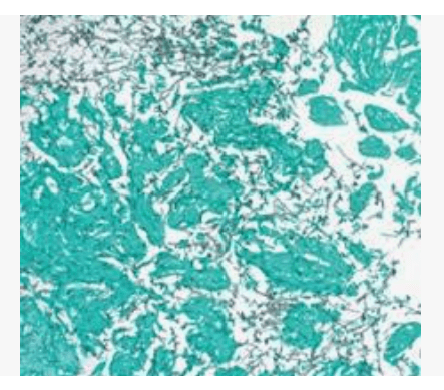
GMS stain
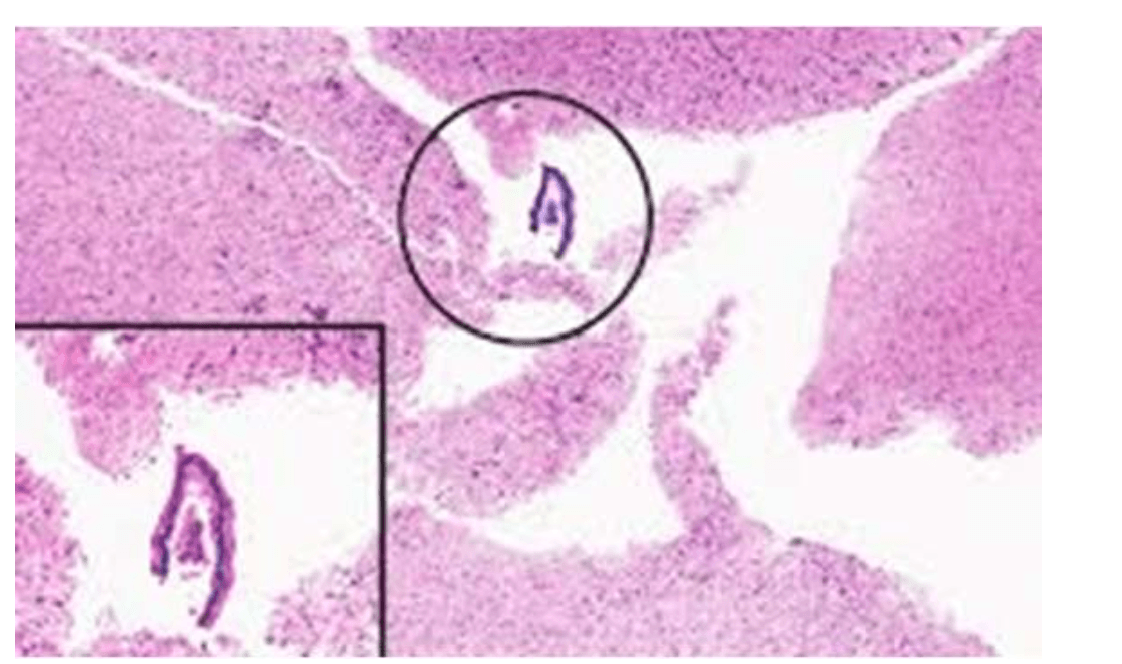
These type of fibers are considered "fast-twitch", which have an anaerobic metabolism
Type ll muscle fibers
This stain identifies granulocytes in the classification of leukemias or in chloromas
Naphthol AS-D chloroacetate esterase technique
ATPase stain - pH 9.4
Type ll fibers are dark and type 1 fibers are light to unstained
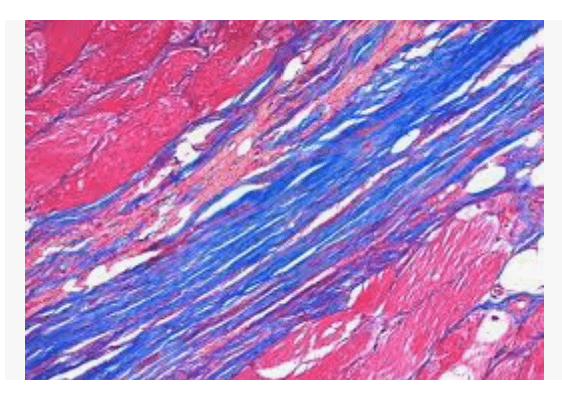
PTAH technique
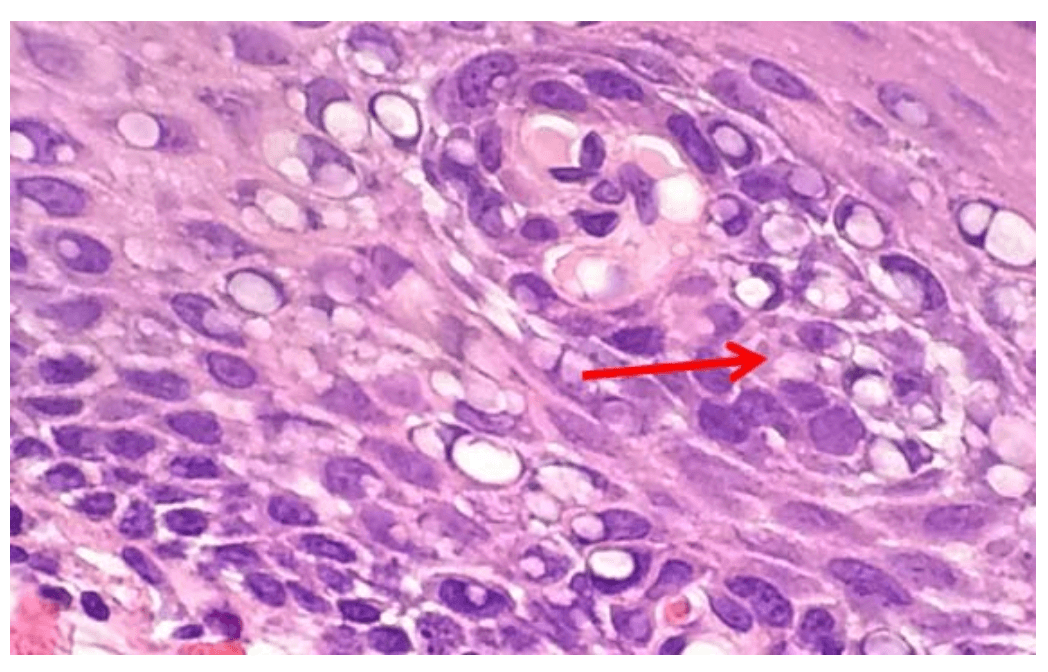
Nuclear bubbling- occurs when poorly fixed tissue is exposed to high levels of heat; high fixative pH