An equilateral quadrilateral
Rhombus
Opposite angles in all parallelograms are this
Congruent
The ratio of the leg adjacent to an acute angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse
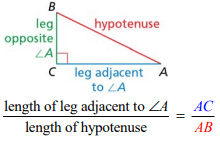
Cosine
This is the name of the formula I would use to find the midpoint of a segment in the coordinate plane.
The Midpoint Formula
A polygon in which all sides are congruent.
Equilateral polygon
An equiangular quadrilateral
Rectangle
Diagonals of all rectangles are this
Congruent
The ratio of the leg opposite an acute angle of a right triangle to the leg adjacent to that angle
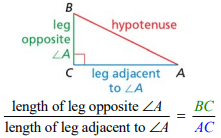
Tangent
This is the name of the formula I use to find the length of a segment in the coordinate plane.
The distance formula
A polygon in which all angles are congruent.
Equiangular polygon
A rectangle that is also a rhombus
Square
This is the formula for the area of a trapezoid
A=(b_1+b_2)/2*h
The ratio of the leg opposite an acute angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse
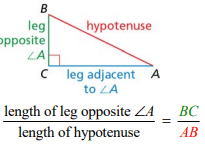
Sine
This is the name of the following formula:
m=(y_2-y_1)/(x_2-x_1)
The slope formula
A convex polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular.
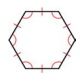
Regular polygon
A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides
Trapezoid
A quadrilateral with one set of parallel sides and one set of congruent, non-parallel sides
Isosceles trapezoid
An angle formed by a horizontal line and a line of sight up to an object
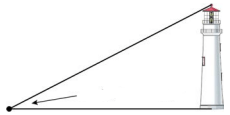
Angle of elevation
This is the name of the theorem from which the distance formula is derived.
The Pythagorean Theorem
A segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon
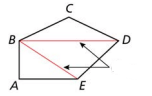
Diagonal
A quadrilateral taht has two pairs of consecutive congruent sides, but opposite sides that are not congruent
Kite
Diagonals of all rhombuses are this
Perpendicular
An angle formed by a horizontal line and a line of sight down to an object
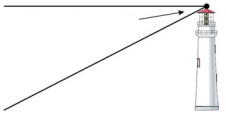
Angle of depression
This is the standard form of the equation of a circle.
(x-h)^2+(y-k)^2=r^2
The distance from the center to any side of a regular polygon
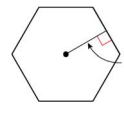
Apothem