What is the chemical symbol for oxygen?
O

Is salt water a mixture or a compound?
A mixture.
How many grams are in 1 kilogram?
1,000 g
What does the Law of Conservation of Mass state?
Matter cannot be created or destroyed.
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, how do particles in a gas move?
They move quickly and in random, straight lines.
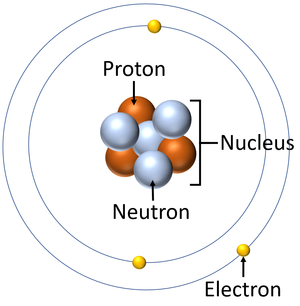
What is the center of an atom called?
Nucleus
What is the main difference between a compound and a mixture?
A compound is chemically combined; a mixture is physically combined.

Convert 2500 milligrams to grams.
2.5 g
In a closed system, you have 10g of reactants. How much product will be formed?
REACTANTS = PRODUCT
What happens to the motion of particles when the temperature increases?
The particles move faster.
Particles go crazy!!!
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
An element is made of only one type of atom; a compound is made of two or more elements chemically bonded together.

Is air a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture?
Homogeneous. It is distributed evenly.

In the metric system staircase when we go down the decimal point moves to the ______. When we go up the staircase we move the decimal point to the ______.

right, left
In a closed system, 10 grams of hydrogen react with 80 grams of oxygen. According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, how much water is produced?
90 grams
Mass of products = Mass of reactants
Using Kinetic Molecular Theory, explain why a solid has a definite shape and volume.
Because the particles in a solid are tightly packed and vibrate in place, they don’t move freely.
Give two examples of a compound.
H2O - water
CO2 - carbon dioxide
Why is saltwater considered a homogeneous mixture even though it contains more than one substance?
Because the salt is evenly dissolved and the mixture looks the same throughout.
A pencil has a mass of 3,200 milligrams. Convert this to kilograms
0.0032 kg
A chemical reaction takes place in an open container. After the reaction, the total mass appears to be less than before. Explain how this can still follow the Law of Conservation of Mass.
Some gas may have escaped into the air, but the total mass is still conserved if all products and reactants are accounted for.
Why does a balloon expand when heated, based on Kinetic Molecular Theory?
Heating increases particle speed, causing gas particles to collide more and push outward, expanding the balloon.
Why can’t elements be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means?
Because elements are the simplest form of matter made of only one type of atom.
Classify the following mixtures as homogeneous or heterogeneous:
a)Tea
b) Oil and water
c) Vinegar
d) Sand and iron filings
a) Homogeneous
b) Heterogeneous
c) Homogeneous
d) Heterogeneous
A car weighs 1.2 × 10⁶ milligrams. What is its weight in kilograms?
1.2 kilograms
1,000,000 mg = 1 kg; move 6 steps up the metric staircase: milli → kilo = ÷1,000,000
In a sealed container, magnesium is burned in oxygen, forming magnesium oxide. The total mass before the reaction is 40 grams. After the reaction, the product weighs 40 grams. Explain why this supports the Law of Conservation of Mass and what would happen if the container were left open.
The total mass remains the same in the sealed container because no matter escapes. Mass is conserved. If the container were open, gases like oxygen could enter or leave, and the measured mass might appear to change, but the actual total mass of all particles would still be conserved.
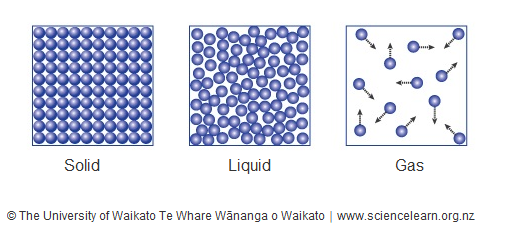
Compare the motion and spacing of particles in solids, liquids, and gases using Kinetic Molecular Theory.
Solids: Particles vibrate in fixed positions; tightly packed.
Liquids: Particles move around each other; more spaced than solids.
Gases: Particles move fast and freely; far apart with almost no attraction.
