What are the two forces/impacts when a horse's foot lands on the ground?
1. Impact from the ground hitting the foot. Force transmitted to leg when foot strikes the ground.
2. Impact of the horse's weight. Body weight forces down through the leg at point of contact with the ground.
What is a major factor in the physical soundness of a horse?
Conformation
What are the main bones that we look at when analyzing the conformation/angle of the hoof?
Long pastern
Short pastern
Coffin bone
Describe the ideal shoulder
A straight line should be able to be drawn from the center of the scapula through the front edge of the knee and bisect the hoof.
Describe the ideal conformation when observing the horse's legs from the rear
-Should be able to draw a straight line from the horse's point of buttock through both its hock and fetlock
-Hooves on the back leg will not be as straight as the front hooves; it is normal for hind feet to be slightly toed outDefine Interference
One limb contacting another limb during some phase of a horse's stride.
It can be a sign of an underlying problem and in itself can also cause limb injuries.
What are three factors that affect the concussive force on the horse's leg?
-Ground
-Horse's overall fitness
-Horse's conformation
Inward swinging of the leg, may be associated with a toe-out conformation
Winging-in/Dishing
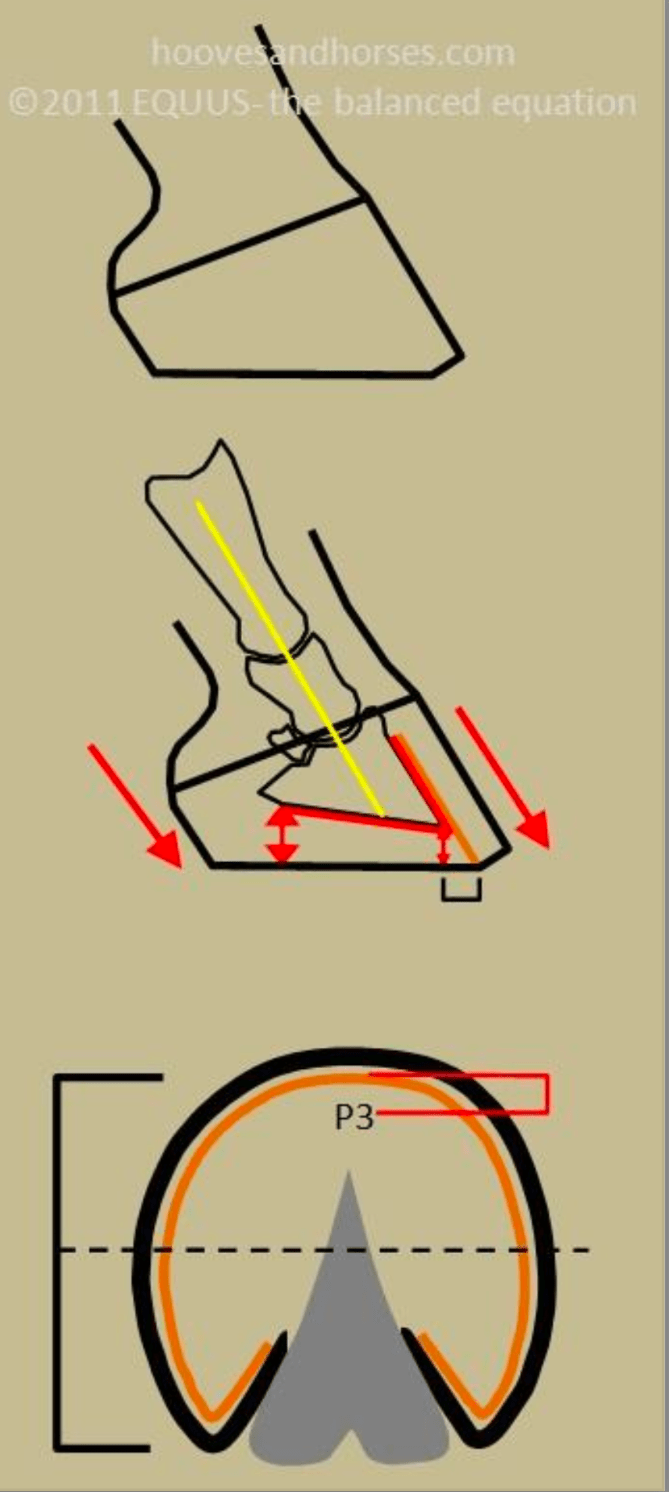
Ideal pastern angle, approximately 45 degree angle when measured from the ground
Name the four conformation flaws that you can see when viewing the horse from the side
Camped Out
Camped Under
Buck Knees/Knee Sprung/Over at the knee
Calf Kneed
What is the ideal conformation when viewing the horse from the side?
You should be able to draw a line starting at the point of buttock, and it should run down the back of the hock and fetlock
Forging is more common in horses with what type of conformation?
Horses with short backs (short-coupled) and relatively long hind legs
Name the five parts of the hoof that absorb/help absorb concussion:
-The high moisture content of the hoof
-The elasticity of the hoof wall
-The collateral cartilages
-Digital Cushion
-Frog
Winging-out or paddling is may be associated with what type of conformation flaw?
Toe-in (pigeon-toed)
Describe a hoof pastern axis that is broken forward
-Heel is high
-Toe appears short
-Hoof angle is steep
Pastern is more horizontal, lowering the fetlock joint
Describe how the front legs should look when observing a horse from the front
-Should be able to draw a straight line from teh point of shoulder to the ground that bisects the leg exactly in half
-Hoof and knee should point forward
-Width of the hooves at the soul should be roughly the same as the width of the legs as they originate from the chest.
Name four conformation flaws you can observe from the rear of the horse
Bow-legged
Cow Hocked
Base wide
Base narrow
What is Brushing?
Contact between opposite (right and left) fore or hind limbs
Most commonly takes places in the lower limb pastern or fetlock
Caused by a lateral gait deficit
Name the three mechanisms of the Hind limbs for absorbing shock:
-The cartilaginous disks between vertebrae
-Hock and stifle joints push the weight of the horse back up
-Hock(Intertarsal) bones
Define Plaiting/Rope Walking
Horse places foot directly in front (sometimes even to the outside) of the opposing foot at the walk or trot
Describe a hoof pastern axis that is broken backward (Negative Palmar Angle)
-heel is low, underrun
-toe is long
-hoof angle is low
Drives the pastern to be more vertical, raising the fetlock
When viewing the conformation of the horse from the front, any deviation in the horse's conformation causes what?
It causes an unequal line of concussion.
The impact from every stride travels up the leg unequally.
The area that absorbs more of the concussion is more likely to be damaged.Describe Sickle Hocks and what they cause
-too much angle to the hocks; feet too far under the body
-put extreme stress on the hock joint and surrounding tendons and ligaments
-can lead to curbed hocks, bog spavin, bone spavin
Over-reaching or grabbing: a type of forging in which the toe of the hind foot contacts the lower forelimb on the same side, usually causing a heel bulb wound or catching the heel of the shoe.
Name the five mechanisms in the Forelimb for absorbing shock:
-Thoracic Sling
-Shoulder, elbow, carpus joints are slightly flexed
-Muscles, tendons, ligaments act like springs
-Carpal bones
-Flexion of the carpus and elbow joints help push horse's weight back up
Poor conformation can lead to....
-Problems related to concussion
-Increased risk of injury and lameness (especially if training hard)
-Gait abnormalities
What are some of the characteristics of a healthy hoof?
-Bony column aligned
-laminae integrity
-hoof is balanced with optimal breakover
-good form of hoof structures (ie bars, heel, frog, digital cushion)
-tight suspensory system and healthy joint function
Name six conformation flaws that can be seen when viewing the horse from the front
Toes out
Toes in
Bow-legged
Knock kneed
Base narrowBase wide
What is this?
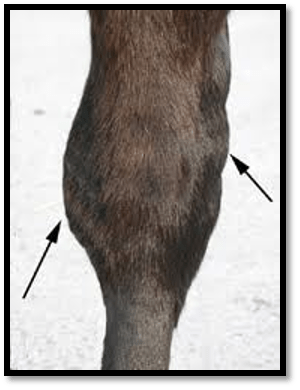
Bog spavin: swelling on the inside and front of the hock
Factors leading to interference - name all seven
Conformation
Lameness
Poor fitness and training
Mechanical gait deficitsNeurologic disease
Improper shoeing or trimmingManagement and riding