Determining whether an object or event is older or younger than other objects or events is called....
Relative Dating
Determining the approximate age of a rock, fossil, or event.
Absolute Dating
A fossil that appears for a short period of time in specific areas.
An Index Fossil
This rock diagram has a line running through with arrows pointing in the direction of rock movement. What does the line represent?
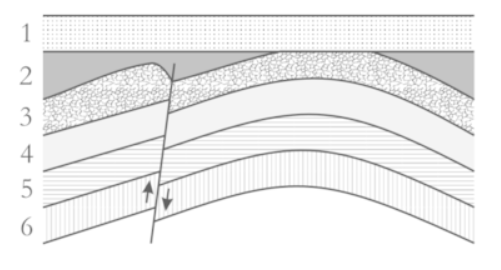
A Fault
What kind of rock is formed in layers?
Sedimentary
Younger rock is found ________ older rock.
Above
Which method would result in an absolute date for a rock that formed billions of years ago?
Radioactive Dating
The remains or impression of a prehistoric organism preserved in petrified form or as a mold or cast in rock
Fossil
When pressure pushes rocks together, this process begins to disturb rock.
Folding
A break or crack in the Earth's crust where rock can move. Rock "slips" down and disrupts the layers
A Fault
A missing layer from the geologic record is called...
An Unconformity
The time needed for half of a sample of a radioactive substance to undergo.
What is Half Life
If a fossil is found in a particular rock layer, what can we say about both the fossil and the rock layer?
The formed at the same time.
An intrusion or fault must be ______________ that the rock that it cuts through.
Younger
Rock layers used to learn about Earth's history
This is called a Geologic column
The Law that states that younger rock is found above older rock as long as the rock layers have not been disturbed.
The Law of Superposition
Process that occurs when the an atom goes through a half life and a new element is formed, giving off energy and an alpha particle.
Radioactive Decay
Helps them determine the date of the rock and the fossil
How does index fossils help geologist
Why might there be a horizontal gap in the layers of sedimentary rock?
Because of weathering and erosion. Over a very long period of time, water flowing across the surface of the rock can break the rock down into sediment and carry it away, leaving a gap.
When igneous rock that forms when magma is injected into rock and then cools and becomes hard, it is called...
An intrusion (keyword: Magma = inside Earth)
In this rock layer diagram there are two unconformities, a fault at E and an intrusion at D. Which unconformity occurred first? How do you know?
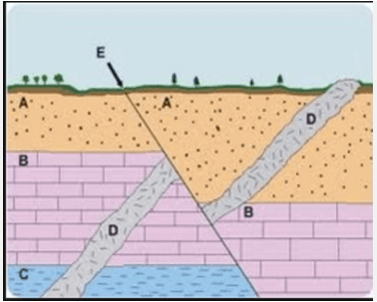
Intrusion D occurred first because the instrusion has been moved by the fault.
Why are isotopes with short half-lives not useful for dating very old rocks?
Not enough of the parent isotope remains to measure accurately
Many mass extinctions took place in the Permian and the Cretaceous periods. Scientists use different methods to determine the causes of the mass extinctions and to find out about the species that died. What is one method scientists use to learn about mass extinctions?
Studying rock layers and the fossil record
What are the five ways that rocks are disturbed?
Folding, Faulting, Tilting, Intrusion, Unconformities
Explain the difference between absolute and relative dating? Why might Scientist need to use both methods to determine the age of a rock?
Relative dating is used to determine the age of a rock layer compared to the layers around it. It gives the sequence in which events occurred in Earth’s history. Absolute dating is used to determine the age of a rock or event in years.
Scientists may not be able to determine the absolute age of some rocks.