Which are examples of homologous structures?
A. The wings of bats and butterflies
B. The fins of fish and whales
C. The hindlimbs of frogs and grasshoppers
D. The forelimbs of primates and penguins
D. The forelimbs of primates and penguins
Which of the adaptations of flowers would be most successful for the survival of a species?
A. Spiny seeds for better wind dispersal
B. Different flowering times for better seed dispersal
C. Sticky pollen for better water dispersal
D. Specific odors for better insect pollination
D. Specific odors for better insect pollination
Which phyla have bilateral symmetry?
A. annelida, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
B. porifera, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
C. cnidaria, porifera, mollusca
D. porifera, annelida, mollusca
A. annelida, arthropoda, platyhelmintha
The diagram represents a cladogram of the family Procyonidae.
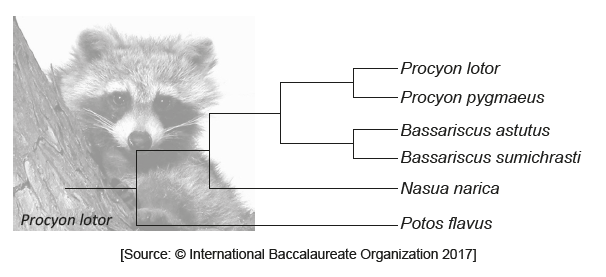
What would justify classifying these organisms into four different genera?
A. They live in different habitats.
B. They do not share any common ancestors.
C. There are enough differences between them.
D. The number of times that the species have split.
C. There are enough differences between them.
Natural selection can operate in different ways. What is the effect of disruptive selection?
A. It eliminates individuals with intermediate forms of a characteristic.
B. It eliminates individuals at random regardless of their characteristics.
C. It favours individuals with intermediate forms of a characteristic.
D. It favours individuals at one extreme of the range of variation in a characteristic.
A. It eliminates individuals with intermediate forms of a characteristic.
Which evidence for evolution do the common features in the bone structure of vertebrate limbs provide?
A. Adaptive radiation
B. Divergent radiation
C. Convergent evolution
D. Discontinuous variation
A. Adaptive radiation
What causes variation within a population?
A. Fertilization and change in the environment
B. Fertilization and mutation
C. Mutation and evolution
D. Evolution and adaptive radiation
B. Fertilization and mutation
If seeds of an unknown species of plant are discovered, what assumption can be made about the species?
A. Its male gametes are contained within pollen.
B. Its seeds are contained within fruits.
C. It is in the domain archaea.
D. It is in the phylum angiospermophyta.
D. It is in the phylum angiospermophyta.
The cladogram includes four marsupial (non-placental mammal) families.
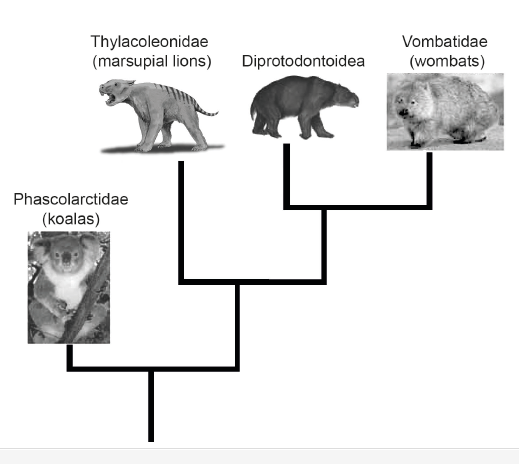
Deduce the family that is most closely related to the Diprotodontoidea.
Vombatidae (wombats)
How do the concepts of gradualism and punctuated equilibrium differ?
A. The timing of evolution
B. The mechanism causing evolution
C. The sequence of evolutionary events
D. The reality of evolution
A. The timing of evolution
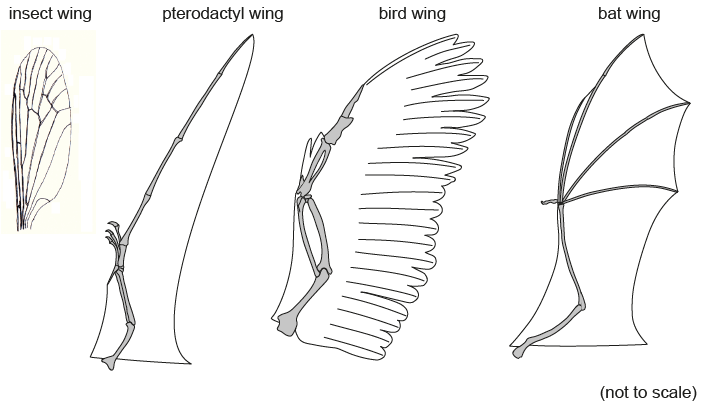
Which statement describes the relationship between the structures of the wings?
A. The bat wing and the insect wing are homologous because they have the same function.
B. The limbs of the bird and bat wings are homologous due to convergent evolution.
C. The wings of the pterodactyl and the bat are analogous due to divergent evolution.
D. The bones of the wings of the pterodactyl, bird and bat are homologous as they have a common ancestor.
D. The bones of the wings of the pterodactyl, bird and bat are homologous as they have a common ancestor.
A bacterial population with no resistance to an antibiotic may develop into a bacterial population with some resistance to an antibiotic. Which event could lead to this?
A. Antibiotic resistance was inherited from an ancestral population.
B. An antibiotic resistance plasmid is received from a bacterium in another population.
C. The enzyme needed for antibiotic resistance is received from a bacterium in another population.
D. The bacterial population mutated in response to antibiotics in the environment.
B. An antibiotic resistance plasmid is received from a bacterium in another population.
Which is the hierarchy of taxa in order of increasing numbers of species?
A. genus, family, order, class
B. class, order, genus, family
C. genus, family, class, order
D. class, order, family, genus
A. genus, family, order, class
The cladogram was constructed using DNA base sequences from six species. Which node indicates the greatest difference in base sequences?
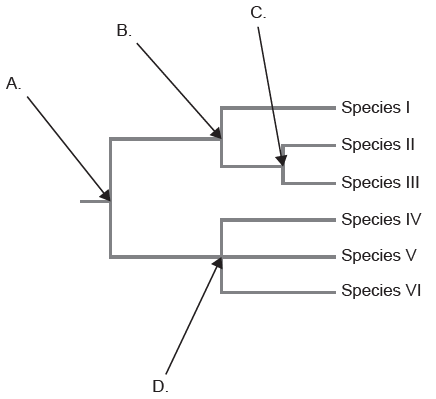
A
The cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) is a large cat found in Africa. It has been discovered that organs could be transferred between any two individuals without rejection of the organ.
What is the probable reason for this?
A. Cheetahs have poor reproductive success.
B. Cheetahs have high heterozygosity.
C. Cheetahs have a large gene pool.
D. Cheetahs have a small gene pool.
D. Cheetahs have a small gene pool.
Which of these structures is not homologous?
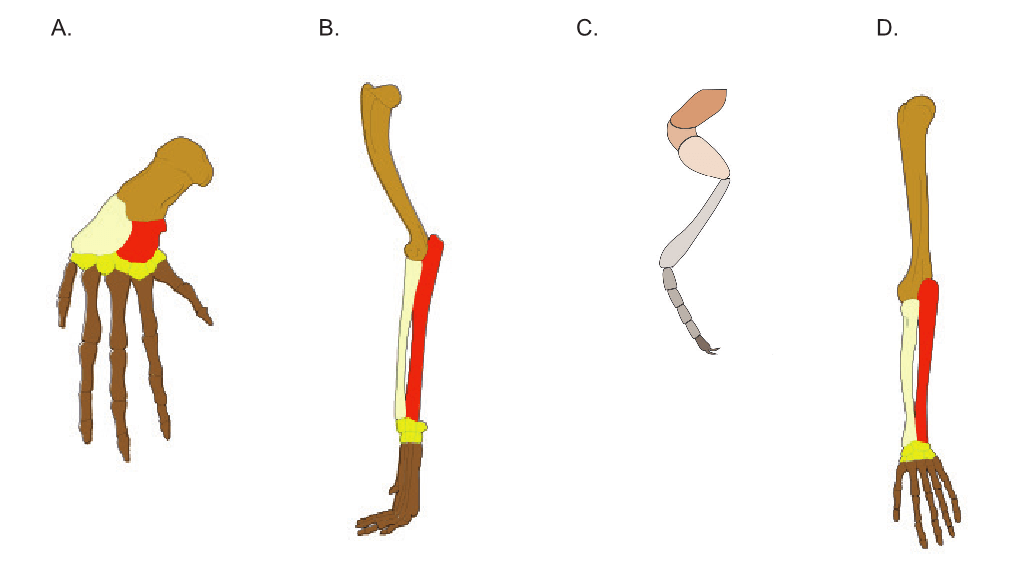
C
Lichens are returning to the forests of the industrial areas of the United Kingdom due to strict pollution control.

What is the expected outcome in the population of peppered moths (Biston betularia)?
A. Increased numbers of light-coloured peppered moths
B. Increased industrial melanism in peppered moths
C. Increased predation of peppered moths
D. Increased speciation of peppered moths
A. Increased numbers of light-coloured peppered moths
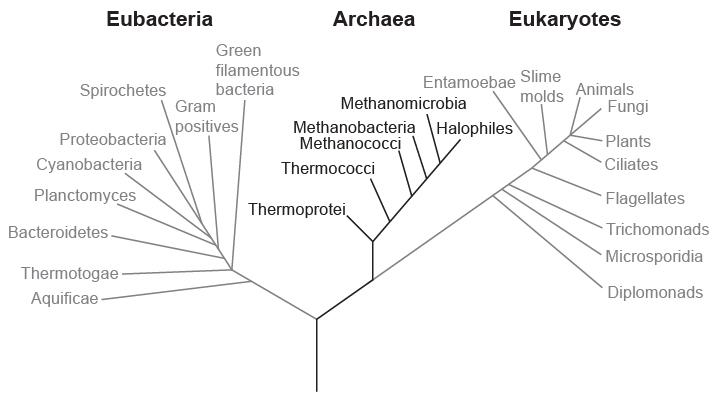 There are important differences between the three domains. Which of these domains have organelles?
There are important differences between the three domains. Which of these domains have organelles?
A. Eubacteria and archaea
B. Archaea only
C. Eukaryotes and archaea
D. Eukaryotes only
D. Eukaryotes only
The figwort family is a large one consisting of many flowering plants that look similar. For what reason have some members of the family been reclassified into a new family?
A. Cladistic analysis shows the differences in flower structure to be fewer than the shared similarities.
B. DNA analysis shows the similarities in flower shape to be a product of convergent evolution.
C. DNA analysis shows some of the families to have suffered recent mutations in only one gene.
D. DNA analysis shows the similarities between the seed dispersal strategies to be a product of divergent evolution.
B. DNA analysis shows the similarities in flower shape to be a product of convergent evolution.
Which example shows disruptive selection?
A. Giraffe necks have become longer over time.
B. Medium-sized beaks in hummingbirds have decreased in frequency over time.
C. The peppered moth became less common in polluted environments.
D. Human babies with a very high or a very low birth mass have a higher mortality rate.
B. Medium-sized beaks in hummingbirds have decreased in frequency over time.
Describe, using one example, how homologous structures provide evidence for evolution. [4]
a. similar structure but different function «in homologous structures»
b. pentadactyl limbs/limb with five digits/toes / other example
c. similar bone structure/example of similarity of bones «in pentadactyl limbs» but different uses/functions
d. two examples of use of pentadactyl limb by a vertebrate group
e. suggests a common ancestor «and evolutionary divergence»
f. process called adaptive radiation
Describe the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. [4]
a. problem results from excessive use of antibiotics by doctors/veterinarians/in livestock
OR
low antibiotic doses taken by patients (not finishing treatment)
b. natural variation exists in any population of bacteria making some resistant to a specific antibiotic
c. variation arises from mutation
OR
antibiotic resistance can be transferred between bacteria by plasmids
d. antibiotic kills all bacteria except those that are resistant
e. resistant bacteria survive, reproduce and pass on resistance to offspring
f. soon population is made of mainly antibiotic resistant bacteria
g. this is an example of natural selection «increasing frequency of characteristics that make individuals better adapted to environment»
State the phylum of plant X and of plant Y

X - Filicinophyta
Y - Coniferphyta
The image shows part of a cladogram.
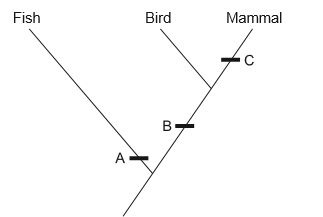
Using the cladogram, identify one diagnostic feature that characterizes the given groups of vertebrates at A, B and C.
A: gills or fins or scales or no limbs or external fertilization
B: homeothermic or warm blooded or endothermic or lungs or tetrapod or four limbs or pentadactyl limbs or internal fertilization
C: hair or fur or mammary glands or milk
The larval stage of the fly Eurosta solidaginis develops in the plant Solidago altissima. The larva secretes a chemical which causes plant tissue to grow around it forming a swelling called a gall. The gall provides the developing insect with protection from predators.
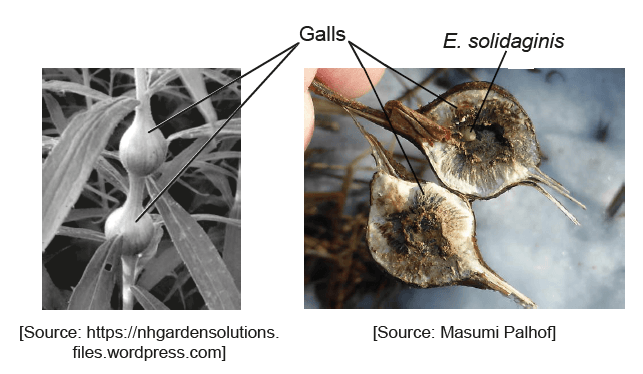
The E. solidaginis fly is preyed upon by the parasitic wasp Eurytoma gigantea. The graph shows the relationship between gall diameter and the percentage of flies that avoid predation by E. gigantea.
Explain the concept of directional selection with respect to this example. [2]
a. directional selection is when an extreme phenotype/characteristic is favoured OWTTE
b. flies that form small galls will be selectively predated OWTTE – accept vice versa
c. over time, flies that produce small galls will become rarer
OR
mean gall size will increase