This is the process by which organisms with traits best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
What is natural selection?
The long tail of a male peacock or the bright colors of a male bird are examples of traits that develop to do this.
What is attracting females?
This is the process where humans decide which plants or animals get to reproduce based on traits we want.
What is artificial selection?
This is the random change in the frequency of alleles in a population over time.
What is genetic drift?
This is a change in the frequency of heritable traits in a population over time.
What is evolution?
Natural selection can only act on traits that can be passed from parents to offspring—also known as these types of traits.
What are heritable traits?
This type of natural selection favors traits that help an organism attract a mate, even if they don’t improve survival.
For artificial selection to create big changes, humans repeat breeding the best individuals over many of these.
What are generations?
When random events (like a natural disaster) drastically reduce a population and change allele frequencies by chance, it’s known as this effect.
What is a genetic bottleneck?
In a population of wildflowers, some plants produce larger flowers with sweeter nectar that attracts more pollinators. Over many generations, what is likely to happen to the population?
More flowers will have larger flowers with sweeter nectar
This is the name for traits that give organisms a survival advantage.
What are adaptations?
Some traits favored by sexual selection, like huge antlers or extravagant feathers, can make survival harder. This shows that sexual selection can act even when it reduces what?
What is survival?
The traits that humans selected for in order to create Collies from wolves.
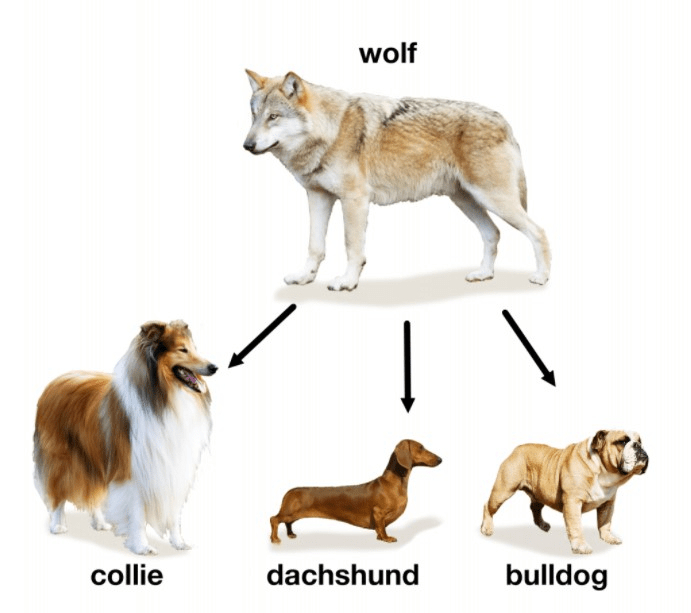
What are long fur, friendliness, etc.?
A few finches from the mainland fly to a small island and start a new population. Over time, their gene frequencies are different (and less varied) than the original population.
What is the founder effect?
This naturalist developed the theory of evolution by natural selection after studying finches on the Galápagos Islands.
Who is Charles Darwin?
This is what causes variation to exist in a population.
What are random mutations?
These 2 individuals are the same species. One is male and one is female. What is the term for differences between the sexes in the same species?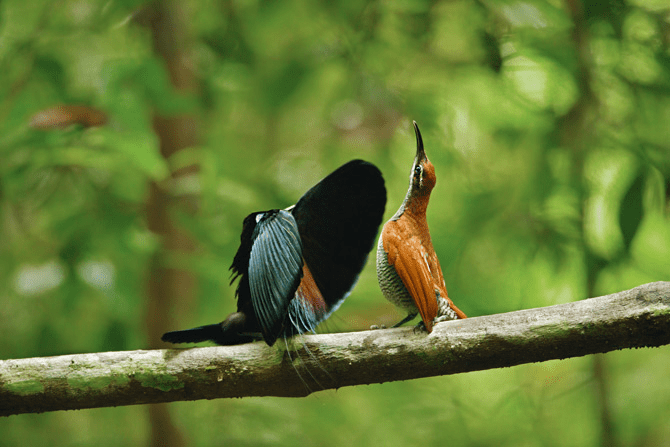
Sexual dimorphism.
The traits that humans selected for in the Brassica oleracea to create kale.
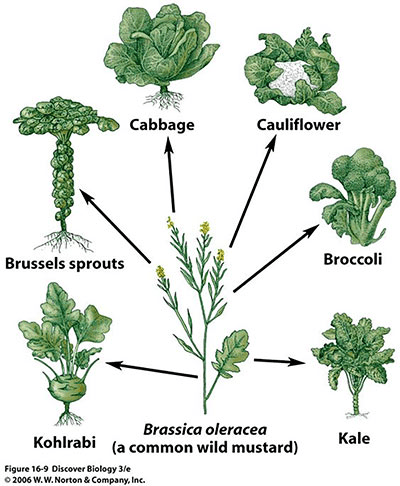
What are large, tasty leaves?
A small pond has a mix of fish with different colors. One year, a storm kills most of the fish randomly, leaving mostly blue ones. Future generations are mostly blue.
Humans have a tailbone and whales have tiny hip bones that serve little or no purpose. These leftover structures are called this.
What are vestigial structures?
When two populations of the same species become separated and can no longer interbreed, they are said to have undergone this evolutionary process.
What is speciation? (a new species is created)
Male crickets make loud chirping sounds to attract females. Some males stay quiet to avoid predators but still try to mate with females near loud males. Why do males still make loud chirps even though it’s risky?
Because louder males attract more females, so they are more likely to have babies. The "sneaky" strategy of the other males wouldn't work anymore if nobody chirped.
What are some problems that could arise from artificial selection?
-Unintended traits could be linked with the desired traits and increase the frequency of diseases
Genetic drift can sometimes cause rare alleles to disappear completely from a population, reducing what?
What is genetic variation?
On an island, some birds have slightly longer beaks that allow them to reach seeds inside deep pods. Over many generations, what will likely happen?
More birds will have longer beaks, and fewer will have short beaks.