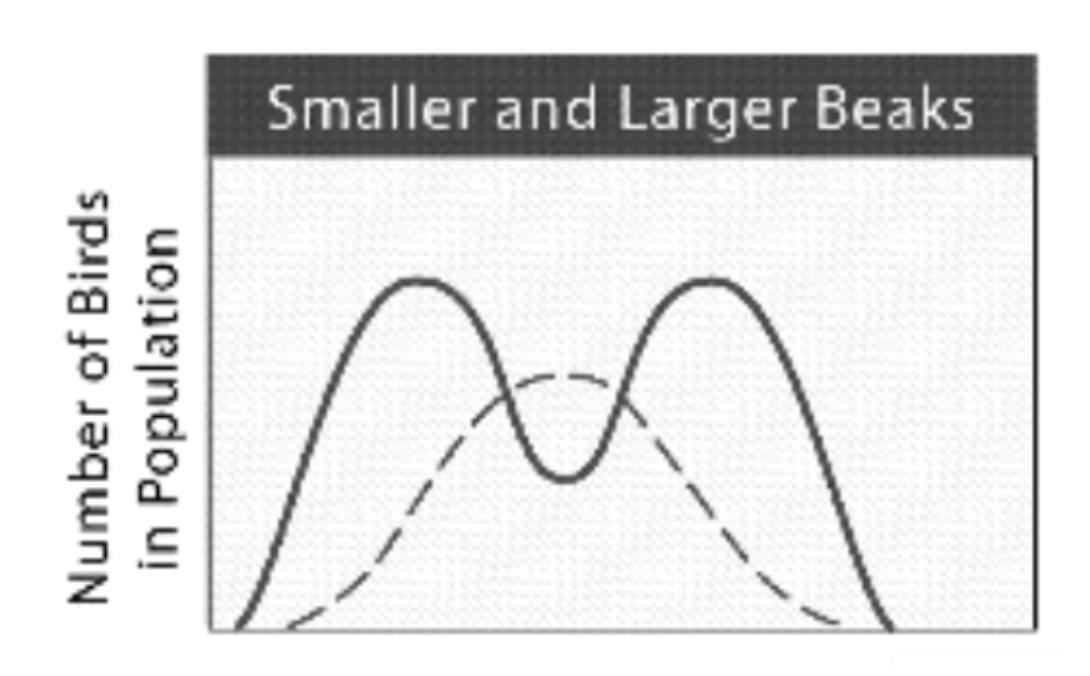
 When more extreme phenotypes within a population have a fitness advantage over intermediate individuals
When more extreme phenotypes within a population have a fitness advantage over intermediate individuals
What is disruptive selection?
Behavior that results in mating and eventual reproduction
What is courtship?
Blue Wildebeest living on the Savannah - seasonal movement to follow food sources.
What is migration?
An animal protects the land where it lives from incursions by others of its species
What is territorial behaviors?
Two different organisms are alike, they share this in their bloodline
What is common ancestor?
A cat, human, bat, and whale all having the same arm bones.
What is a homologous structure?
A population tends to remove the more severe phenotypes, resulting in the reproductive success of the norm or average phenotypes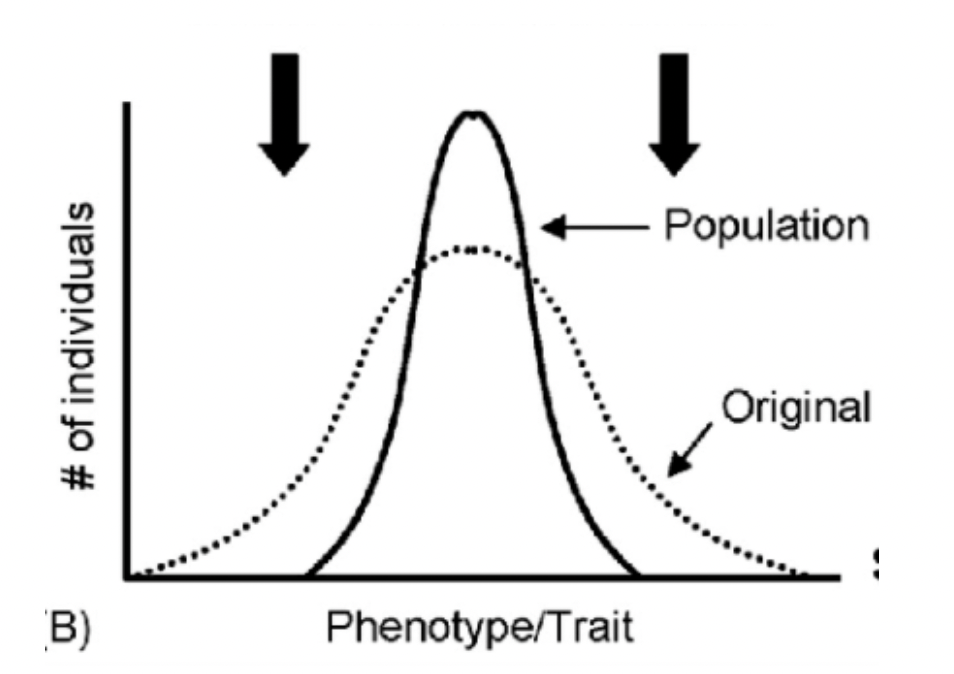
What is stabilizing selection?
Ants use pheromones to mark a trail to food.
What is chemical communication?
The sound an animal makes
What is auditory communication?
Graylag Goose, rolling egg into nest
What is fixed action patterns?
Organisms that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring
What is a species?
A change in the allelic frequency in a gene pool of a population over time
What is Evolution?
Occurs when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or reproduce more than those on the other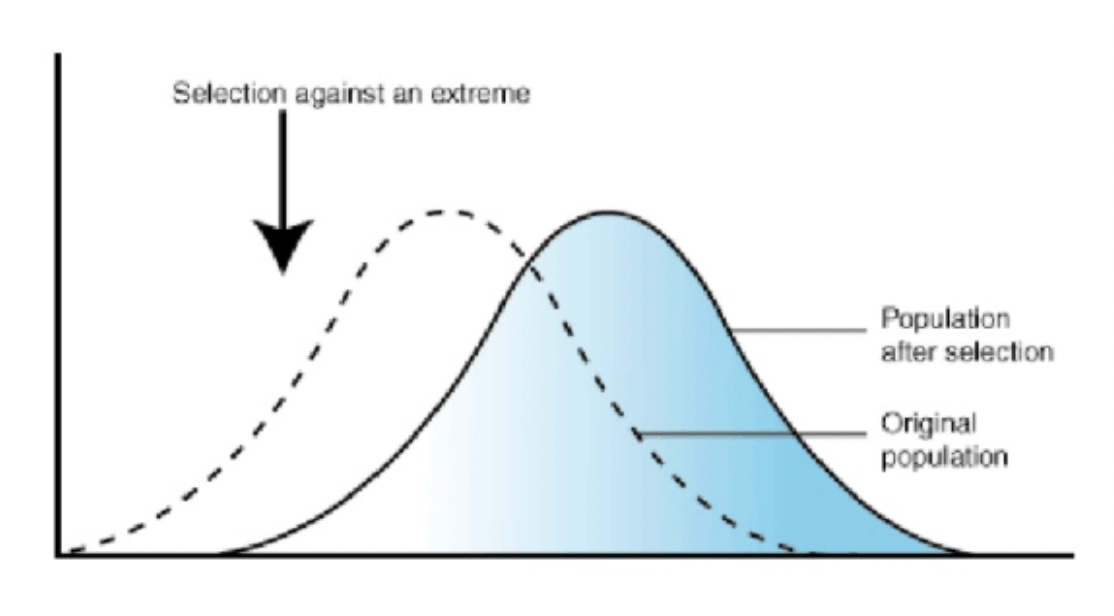
What is directional selection?
A crow using a stick to get food
What is insight learning?
Natural cycle of change in our body’s chemicals or functions
What is biological rhythms?
A Colony of Ants
What is cooperative behaviors?
Humans and bananas being nearly 60% genetically identical
What are DNA from common ancestors?
Geographic, behavioral, and temporal isolation are all examples of
What is reproductive isolation?
An Orb Web Spider building sticky wagon wheel webs.
What is innate behavior?
Group of animals belonging to the same species that work together
What is animal societies?
Come to recognize an animal or object as a parent at first birth/hatch.
What is imprinting?
A little child catches a fly and pulls its wings off. The fly actually lives a better life, but does not pass its lack of wings on to its offspring because the loss of wings is an _________ _______.
What is an Acquired Trait?
In the case of the elephant seals, where humans hunted them nearly to extinction, and their allelic frequencies changed due to the dramatic reduction in the population size
What is the Bottleneck Effect?
Method of Learning that employs rewards and/or punishments for behavior
What is operant conditioning?
Learning Through association - Biological stimulus paired with neutral stimulus
What is classical conditioning?
An animal is able to separate itself from its surroundings, self awareness
What is cognition?