The term for when a species no longer exists.
What is extinction?
Traits of certain individuals are favored by the environment, making them more likely to survive and reproduce
What is Natural Selection?
The scientists who created the first classification system for living organisms.
Who is Carl Linnaeus?
This type of evolution can show us the relative or absolute age of species through time and their transitional forms.
What is the fossil record?
This type of selection favors one extreme characteristic, shifting the distribution curve one way or another.
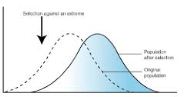
What is directional selection?
The father of Evolution.
Who is Charles Darwin?
The movement of genetic material from one population to another.
What is Gene Flow?
A diagram that shows the relatedness of species based on specific characteristics.
What is a cladogram?
Homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures are all an example of this type of evidence of evolution.
What is comparative anatomy?
This type of fossil is known to have existed for a short period of time and was widespread, helping scientists data other fossils in the record that are found near it.
What is an index fossil?
The process in which inherited characteristics within a population change over generations such that new species sometimes arise.
What is Evolution?
The ultimate source of all genetic variation.
What are mutations?
A tool to identify organisms based on a series of paired statements about their characteristics.
What is a dichotomous key?
Similarities in the DNA of organisms.
What is molecular homology?
This is necessary in order for speciation to occur.
What is reproductive isolation?
The scientist that theorized that individual organisms could evolve within their lifetime and pass on acquired traits.
Who is Lamarck?
What is Nonrandom Mating?
The two taxon used to scientifically name organisms.
What are genus and species?
Evidence of evolution based on similarities in developing embryos
What is comparative embryology?
This type of speciation occurs when two populations are still geographically near each other but they no longer interbreed.
What is sympatric speciation?
Isolation, mutation (variation), natural selection, and time result in this evolutionary change.
What is speciation?
The random rapid decrease in a population's size that shifts the frequency of alleles.
What is Genetic Drift?
The correct order of all the taxa in the Linnaean Classification system (from broad to specific)
What is Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species?
These are the oldest fossils in this diagram

What are trilobites?
This type of genetic drift occurs when a population is suddenly wiped out, possibly from a natural disaster like a fire or tsunami.
What is the bottleneck effect?