What is geographic isolation, and how can it lead to the formation of new species?
Geographic isolation occurs when a physical barrier separates populations, preventing gene flow and possibly leading to speciation.
What are homologous structures, and what do they suggest about common ancestry?
Homologous structures are similar in structure but different in function; they indicate a common ancestor.
List the three conditions required for natural selection to occur.
Overproduction, inherited variation, and struggle to survive.
What is an adaptation?
A trait that increases an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce.
How does the overuse of antibiotics contribute to antibiotic-resistant bacteria?
Overuse kills susceptible bacteria; resistant ones survive and reproduce, increasing in frequency.
Explain how fossil evidence supports the theory of evolution.
Fossils show transitional forms and changes in species over time.
Why is inherited variation important for natural selection?
It provides the raw material for selection; without variation, no trait can be favored.
Explain how natural selection can lead to adaptations over time.
Traits that help organisms survive become more common in the population over generations.
Compare and contrast the development of pesticide resistance in insects and antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
Both involve selection pressure: pesticide/antibiotic kills most, resistant individuals survive and reproduce. Different organisms but same evolutionary mechanism.
Compare DNA sequences from three species. How could you determine which two are most closely related?
The two species with the most similar DNA are most closely related.
A species produces hundreds of offspring, but only a few survive. What term describes this concept, and why is it important for natural selection?
Overproduction—leads to competition and selection of traits that improve survival.
A population of rabbits develops longer legs over generations. How might this be an example of adaptation?
Longer legs might help escape predators or travel for food—this trait increases in frequency.
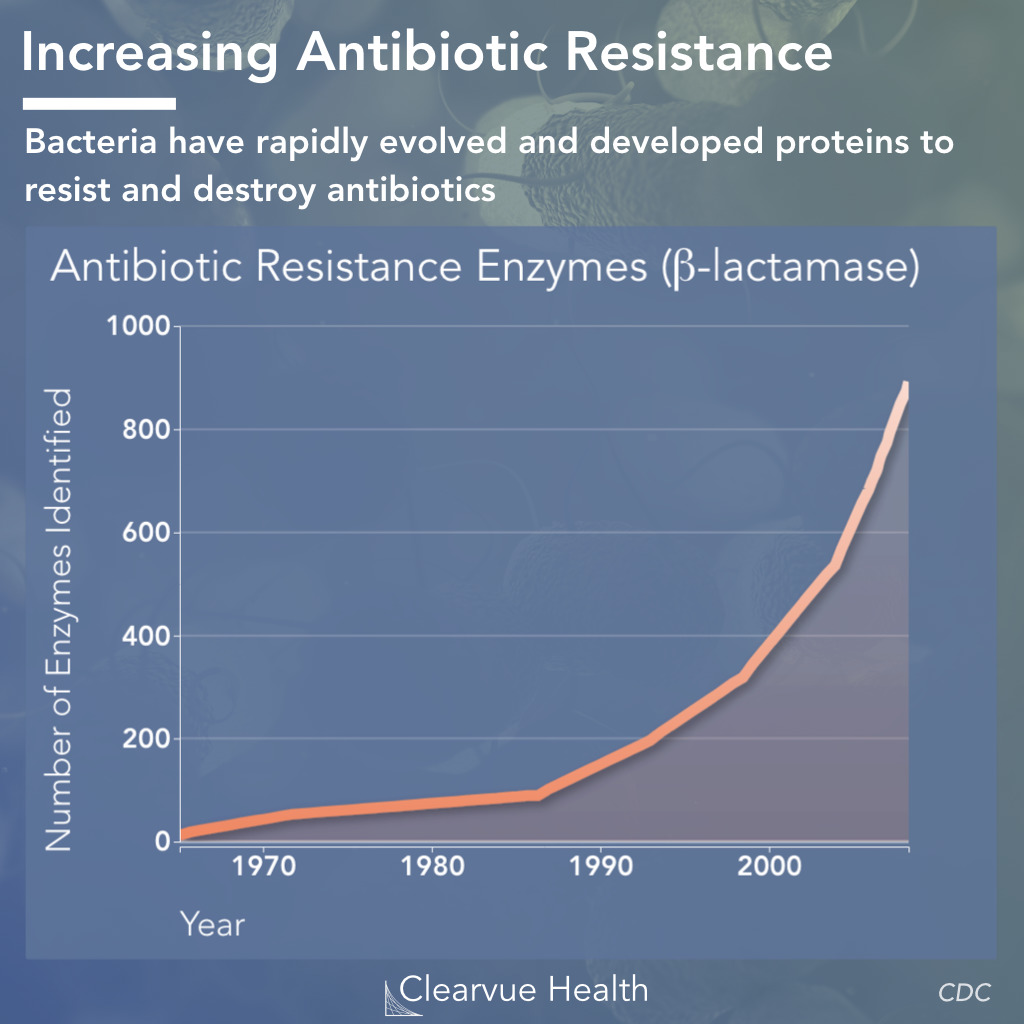
You are given a graph showing the increase in antibiotic resistance over 10 years. What trend do you observe, and how might it impact public health?
Resistance increases over time; fewer infections can be treated effectively. Indicates strong selection pressure.
How do vestigial structures and embryological similarities provide evidence for evolution?
Vestigial structures are remnants of past traits. Embryos of different species show similar developmental stages—both support common ancestry.
In a population of beetles, some are green, and some are brown. Birds can more easily spot and eat green beetles on the forest floor. Over several generations, the population shifts to mostly brown beetles. Explain how the three conditions required for natural selection are demonstrated in this example.
Overproduction, Inherited Variation, Struggle to Survive.
Over time, natural selection favors brown beetles, increasing their frequency in the population.
Given a population of finches with various beak sizes, explain how a drought might change the population over time.
Drought limits food → finches with larger, stronger beaks survive to crack hard seeds → beak size increases in population.
Two populations of the same species of rodents become separated by a newly formed river. After many generations, one population has dark fur and large ears, while the other has light fur and small ears. Explain how natural selection and geographic isolation could have led to these changes and how this situation could eventually result in the formation of two different species.
Data shows divergence in traits/allele frequencies. Suggests reproductive isolation and independent evolution.
You are given genetic, anatomical, and fossil data for four species. Construct an argument for which two species share the most recent common ancestor.
Species with the most similarities across the three types of evidence likely share a recent common ancestor.
Create a model (written description) showing how natural selection could affect a population of moths in a polluted environment.
Model includes: large population, variation in coloration, predators more likely to spot light-colored moths in polluted environment → dark-colored moths survive and reproduce.
You observe a species of fish in two environments: one clear and one murky. Over time, the two populations show different color patterns. Explain how natural selection and environmental pressures led to these adaptations.
Natural selection favors colors that match the environment; over time, the two populations evolve distinct adaptations due to environmental pressure.