What structures allow us to look at organisms' bones and structures even though they are extinct?
Fossils
Also known as "Survival of the ...."
Fittest
What can cause gene flow?
Overcoming a physical barrier that causes isolation.
Macroevolution are changes that include _________ becoming extinct.
Species
What is it called when an organism changes to the environmental stimuli
Adaptation
This evidence is known as:

Embryological Development
Who was the scientist is known as "the Father of Evolution"?
Charles Darwin
Population
What is the formation of a new species called?
Speciation
A diagram/organizer that shows evolutionary relationships.
Phylogenetic Tree
What is this an example of?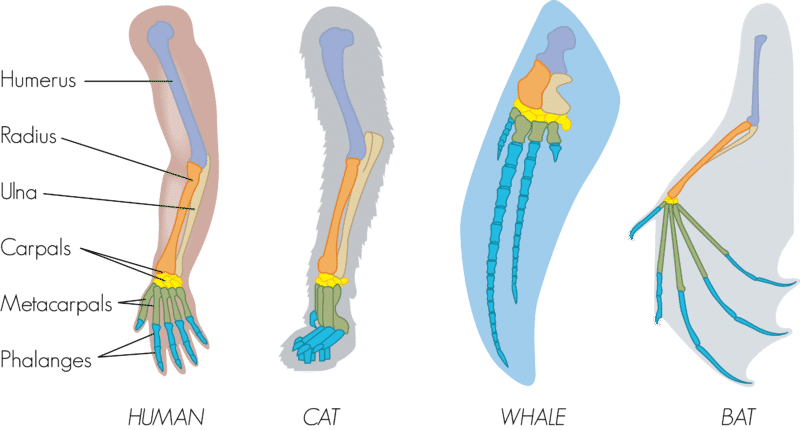
Homologous Structures
Which island did most of evolution's beginning research occur?
Galapagos
What is something that can cause a genetic drift?
Natural Disasters
Migration
Human Disruption
Name 3 forms of evidence that prove Macroevolution.
Speciation
Homologous Structures
Vestigial Organs
Embryonic Development
DNA Sequencing.
Where did the Peppered Moth phenomenon occur?
England
What are analogous structures?
Structures that provide similar functions- not structures.
Explain one of the findings Darwin discovered with the animals and their isolation on different island.
Saddleback vs Dome Turtles
Finches
What type of microevolutionary property is when there is a sudden change in the genetic material?
Mutation
What are organs that no longer have an apparent function called?
Vestigial Organs/Structures
What ship did Darwin take to discover the islands?
HMS Beagle
This form of evidence shows that because of similarities in patterns that all organisms descended from one common ancestor.
DNA Sequencing/Biochemical similarities
Explain one of Darwin's laws of evolution.
Living things increase in number geometrically. (overproduction)
There is no net increase in the number of individuals over a long period of time.
- A “struggle for existence” since not all individuals can survive.
- No two individuals exactly alike (genetic variation).
- In the struggle for existence, those variations which are better adapted to their environment leave behind them proportionately more offspring than those less adapted.
What type of microevolutionary property is when the genes mix between parents showing a mix of traits for the offspring?
EXTRA:
What is the name of the "missing link" that helps (but is not entirely complete) for the evolution of humans and apes?
Lucy
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/93/f8/93f88ad1-a5b2-444b-81bb-09ef520e93c5/42-43539379.jpg)
Why are adaptations/microevolution of mice and rats much easier to see than humans?
Larger populations, smaller lifespan.