Which of the 4 bonds are broken by boiling temperatures?
Ionic, Hydrogen bonds, & Hydrophobic interactions.
What does CHNOPS stand for?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, & Sulfur.
Draw an example of the streak plate, properly labeled!
Use your imagination for the specific bacteria and media type :)
Must include:
Bacteria name
Name/ Initials
Date
Media type
Group#
What is a microbe?
Microscopic Organism
Which DOMAIN do bacteria belong to?
BACTERIA
What are the DNA and RNA base pairs?
DNA:
Adenine- Thymine
Guanine- Cytosine
RNA:
Adenine- Uracil
Guanine- Cytosine
1) Identify this reaction and then...
2)Draw a Hydrolysis Reaction with this information...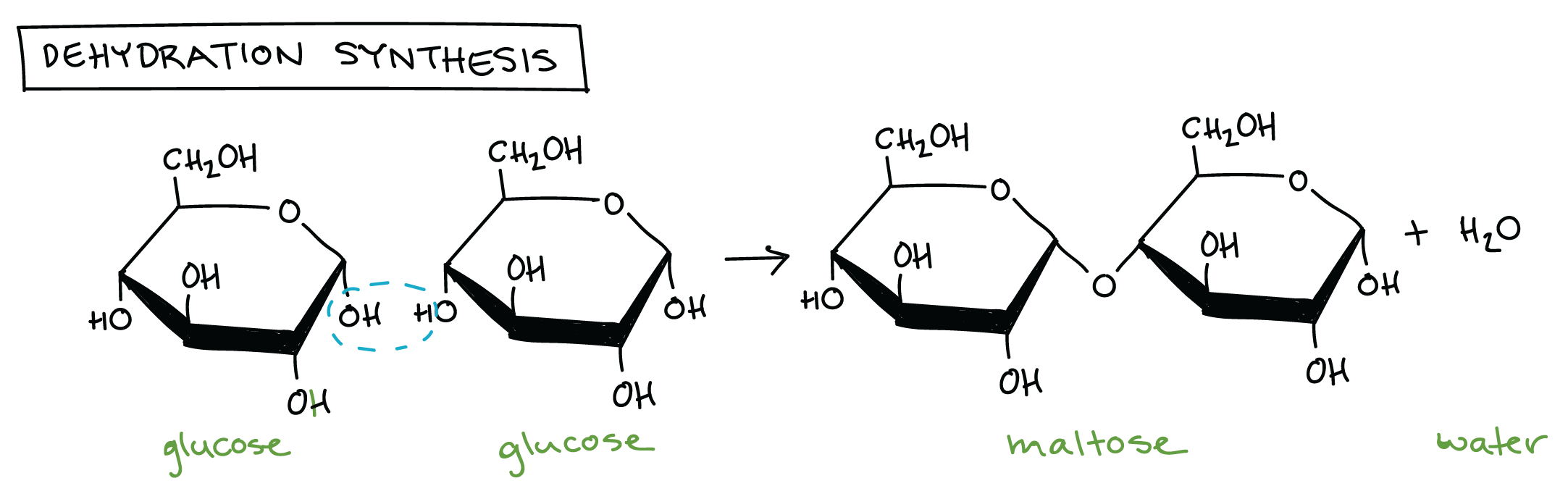
1) Dehydration Synthesis
2) Maltose + Water ->Glucose + Glucose
What is the difference between chemically defined media and complex (rich) media?
In chemically defined the EXACT composition is known.
Which identification method was used to create the three domain system?
Nucleic Acid Testing.
Give an example of a species of bacteria.
Written using both the Scientific name and correct shorthand.
HINT: Include genus and species name
Streptococcus pyogenes
S. pyogenes
(Should use underline only when HANDWRITTING)
Explain the difference between the forces holding water MOLECULES together and the forces holding the hydrogen and oxygen ATOMS together.
BONUS: Which are being broken by boiling?
Polar covalent bonds & Hydrogen bonds.
Why is the polarity of water important to microbial life?
Universal solvent...
List 4 ways to prevent contamination.
Covering the plate, working close to the flame, wearing PPE, dehydrate loop, flaming the loop between every step, flaming the test tubes, opening/pinky technique...
List 3 differences between a Virus and a Bacteria.
Reproduction methods, metabolic abilities, size....
How do bacteria reproduce?
BONUS: How does that differ from eukaryotes? virus?
Binary Fission
Mitosis & Hi-jacking of the host mechanical systems.
Describe 3 differences between saturated and unsaturated fats.
Saturated:
straight, stack, solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated :
Bent, move around easily, liquid at room temperature.
What are the 4 levels of protein structures and which types of bonds hold each type of structure together?
Primary- Covalent (Poly peptide bonds)
Secondary- Hydrogen Bonds
Tertiary- All 4-(Ionic, Hydrogen bond, Covalent, & Hydrophobic Interactions)
Quaternary- All 4 (Ionic, Hydrogen bond, Covalent, & Hydrophobic Interactions)
Which pipette should you use to transfer 250 μL?
Bonus points:
Convert to nL & mL
1,000 μL pipette
.25 nL
250,000 mL
List three differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes:
nucleus
membrane bound organelles
5-100 μm
Prokaryotes:
No nucleus
No organelles
only about 1 μm wide..
List the shapes of bacteria.
Bacillus
Coccus
spirochete
List the 5 specific types of bonds/interactions we have been learning. One way you identify each type on the skeletal structures.
Ionic- +/-
Hydrogen- Dotted line
Polar Covalent- Solid line- Nitrogen or Oxygen
Non-polar Covalent- Solid line- NO NO
Hydrophobic Interactions- Two molecules next to each other W/ both non-polar covalent bonds.
List an example of where one would find each CHNOPS element within a microbial structure.
Carbon- Organic molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids...
Hydrogen- Organic molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids...
Nitrogen- Proteins, nucleic acids..
Oxygen- proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates..
Phosphorus- Nucleic acids, phospholipids
Sulfur- proteins
Write your own experiment using Scientific Method.
HINT: There are FIVE PARTS!
Question
Hypothesis
Experimental control
Positive control
Negative control
Recreate your concept map without looking including the terms:
Microbe
Virus
Eukaryote
Prokaryote
Bacteria
Protist
Archaea
Fungus
Cellular
Acellular
Gram-Positive
Gram-Negative
Microbe
Acellular-virus
Cellular:
Prokaryote- bacteria & archaea (bacteria- + & -)
Eukaryote- Protist & Fungus
Describe the differences between gram positive and gram negative cell walls.
EXTRA BONUS: Draw a picture of both cell walls.
Positive:
stain purple
Plasma membrane, periplasmic space, thick peptidoglycan layer, w/ teichoic acid.
Negative:
stain pink
Plasma membrane, periplasmic space, small peptidoglycan layer, lipopolysaccharide layer.