How are proteins inserted in the outer membrane for mitochondria?
Proteins destined for the outer membrane or intermembrane space also pass through the Tom complex.
Proteins with single transmembrane domains are inserted via the outer membrane protein Mim1.
How is Chloroplast circular DNA different than those of mitochondria?
Choloroplast circular DNA molecules are present in multiple copies but are larger (contain more genes) than those of mitochondria
What are Leucoplasts? What are the two types and what do they store?
Leucoplasts (nonpigmented) store a variety of energy sources in nonphotosynthetic tissues.
Amyloplasts store starch
Elaioplasts store lipids
What are phospholipid transfer proteins
Lipid transfer between ER and mitochondria is mediated by phospholipid transfer proteins.
Do Chloroplasts use the universal genetic code?
Chloroplast tRNAs are sufficient to translate all the mRNA codons using the universal genetic code.
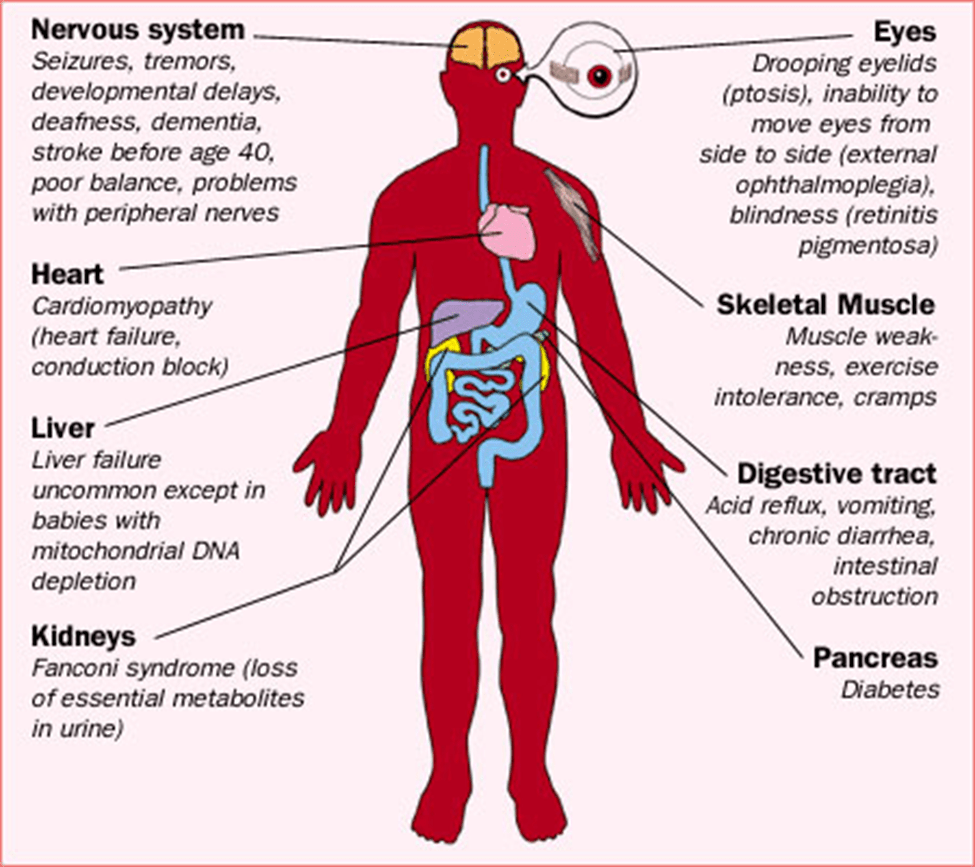
What symptoms are associated with mitochondrial disorders?
Which organs are most affected?
What are transit peptides? Which complex do they direct to?
Transit peptides direct proteins to the translocase of the chloroplast outer membrane (the Toc complex).
How are chloroplasts similar to mitochondria?
Chloroplasts are similar to mitochondria in many ways:
•Both generate metabolic energy
•Both evolved by endosymbiosis
•Both contain their own genetic systems
Both replicate by division (fission)
Which complex do proteins go to after passing the Toc complex? How is the transit peptide cleaved?
Proteins then enter the Tic complex on the inner membrane and are transported to the stroma, drawn by action of an Hsp93 chaperone.
In the stroma, the transit peptide is cleaved by stromal processing peptidase (SPP).
What are Chromoplasts?
Chromoplasts contain carotenoids, resulting in the yellow, orange, and red colors of flowers and fruits.
What are the two different pathways proteins are translocated into the thylakoid lumen?
Sec pathway:
•ATP-dependent; signal sequence is recognized by SecA protein.
•Protein is translocated as an unfolded protein through the Sec translocon.
Tat (twin-arginine translocation):
•Proteins have a twin-arginine signal sequence; translocated in fully-folded state.
•Energy comes from the proton gradient.
•Signal sequences are cleaved by thylakoid processing protease (TPP).