Give a basic definition of the two types of covalent bonds.
Nonpolar: bond in which electrons are shared equally between two atoms.
Polar: bond in which electrons are shared unequally between two atoms
What is the subunit of proteins?
Amino Acids
What is the general function of carbohydrates?
What is the structure of DNA
double helix
Oxygen has two unpaired valence electrons, how many covalent bonds can oxygen make?
2 bonds
Why is carbon so versatile in organic compounds?
It can form 4 bonds, because it has 4 unpaired electrons
What are the two sub categories of secondary protein structure
Alpha helix and Beta pleated sheet
In a 1,4 beta glycosidic linkage, what does the 1,4 refer to?
The particular carbons in a sugar on the carbon ring that form the bond
To which end a strand of DNA/RNA do new nucleotides add?
new nucleotides add to the 3' end
Which type of covalent bonds have the most potential energy?
Nonpolar covalent
What type of bond holds together the amino acids of protein?
Peptide bonds
What are the four main parts of amino acids?
Amino group, Carboxyl group, Hydrogen atom, and R-group
What is the difference between aldose and ketose carbonyls?
Aldose carbonyls have the c=o bond at a primary carbon/a carbon bonded only to one other carbon.
ketose carbonyls have the c=o bond at a secondary carbon/ a carbon bonded to two other carbons
If a double strand of DNA is 12% G what is the % of A?
38%
What is a glycoprotein?
any protein that has a carbohydrate group attached to it
Define electronegativity
Which level of protein structure is characterized by multiple subunits of polypeptides and is held together by hydrogen bonds, an example is Insulin
Quaternary protein structure
What give structural polysaccharides their strength?
Beta linkages which allow strands of the saccharides to lay parallel
What would be the complimentary strand of DNA?
5' GGATCACTT 3'
What is a dehydration synthesis?
What is the name of the bond that stabilizes the structures of protein & DNA and gives water its critical properties?
Hydrogen Bonds
What are the functions of protein?
Why do fat molecules store more potential energy than carbohydrate molecules?
Because fat molecules have more H-C bonds than carbohydrates
What is the name of the bond that connects the 3' carbon of one sugar molecule to the 5' of another sugar molecule in DNA
Phosphodiester Bond
Which of the following amino acids/r-groups are hydrophilic?
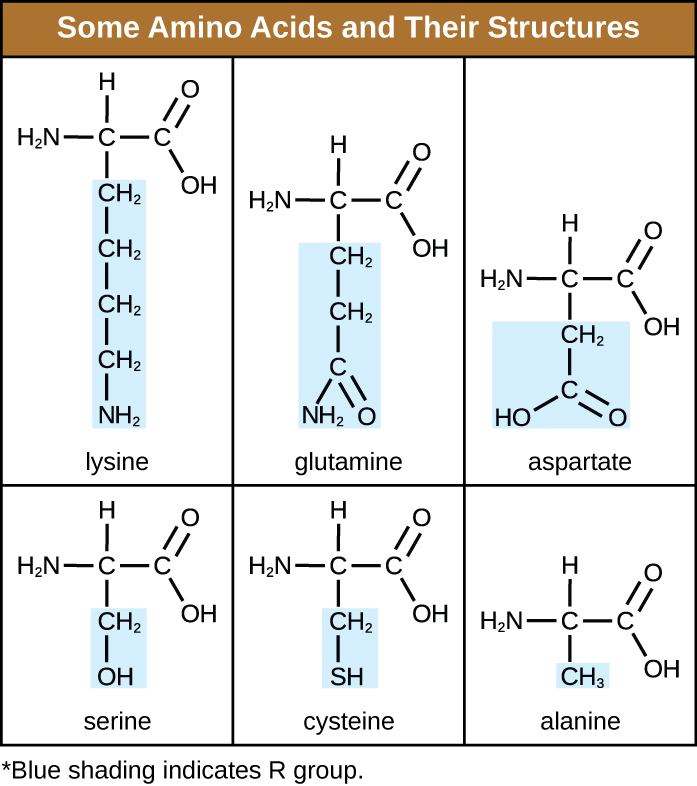
Aspartate, serine, cysteine