1. Who is the founder of psychology?
2. Give the full definition of psychology according to the book.
3. What is the only way to determine causation?
1. Willhelm Wundt
2. The scientific study of mind and behavior
3. True experiment
1. What does the frontal lobe do and what cortex is located inside it?
2. What does the parietal lobe do and what cortex is located inside it?
1. Responsible for executive functions and higher order cognition (planning, thinking, organization). The motor cortex (voluntary movement) is housed inside the frontal
2. Responsible for our senses, i.e. touch. The somatosensory cortex (complex senses, such as heat, cold, pain) is housed inside the parietal
1. What stage of sleep does REM occur?
2. What stage of sleep is the deepest?
1. The 5th stage.
- Muscle paralysis, intense dreaming, rapid eye movements
2. Stage 4, NREM ("Delta wave sleep")

What is the difference between a phenotype and a genotype?
Phenotype we can see, genotype we can't.
1. What is a neuron?
2. How do neurons communicate and what is the advantage of this type of communication?
1. A cell that transmits information through the nervous system.
2. Neurons communicate chemically, the advantage of this communication is neuroplasticity.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/g-neuron-56a792cd5f9b58b7d0ebd043.jpg)
1. In a research experiment, what is a sample supposed to be representative of?
2. What is the specific name of the type of research that gathers detailed, qualitative information about a single individual
1. The population
2. Case study
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-write-a-psychology-case-study-2795722-final-f90b37ae2de34cc29b53e303fc0eef5d.png)
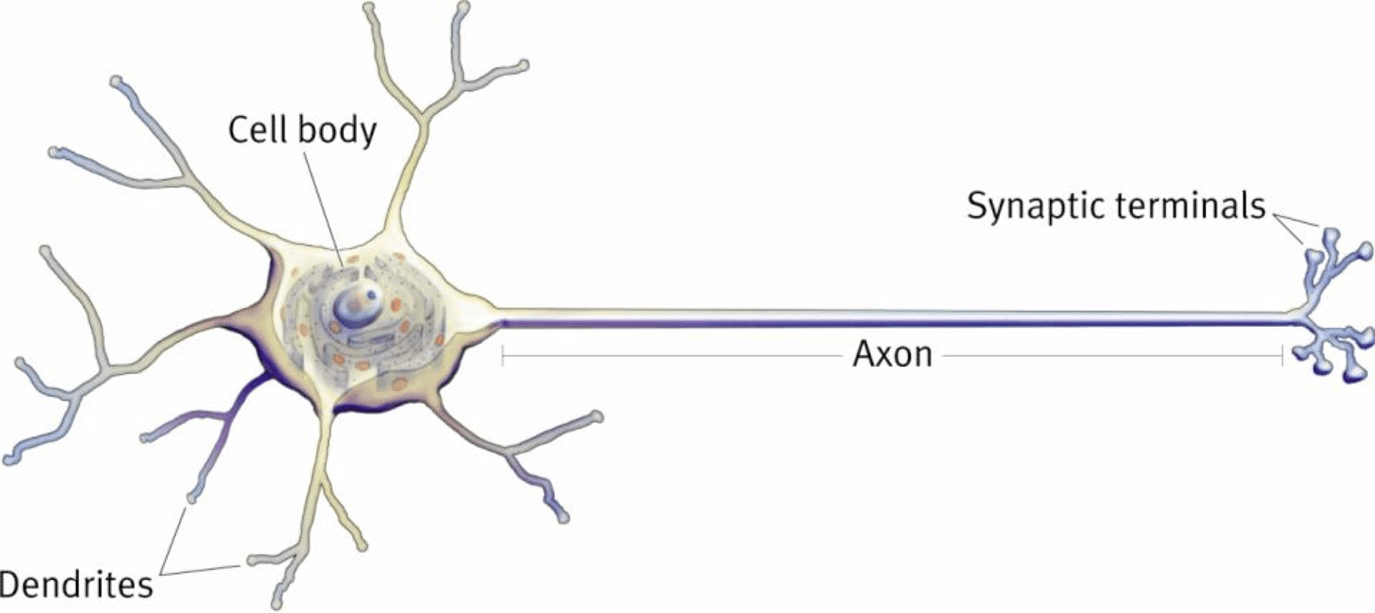
What is the basic anatomy of the neuron and what does each part do?
DAT
1. Dendrites - recieve information
2. Axon - sends information to terminal
3. Terminal/Terminal Buttons - releases information into the synapse to another neuron
Name the three components of consciousness.

1. Qualitativeness - Our conscious experiences have quality.
EX: Eating a good breakfast feels different from learning you that you scored a 100 on your test.
2. Subjectivity - Consciousness can only be experienced by 1 person, its unique to you.
EX: If we are both eating the same ice cream, it's still two different experiences.
3. Unity - Consciousness is a single unified experience, all integrated into one experience.
EX: I sit here typing, I do not just feel the keyboard keys under my fingertips, see the words form on the computer screen, hear the sounds of the computer speakers, and think that it's been raining too long -- I experience all these cognitive and sensory experiences together as one consciousness.
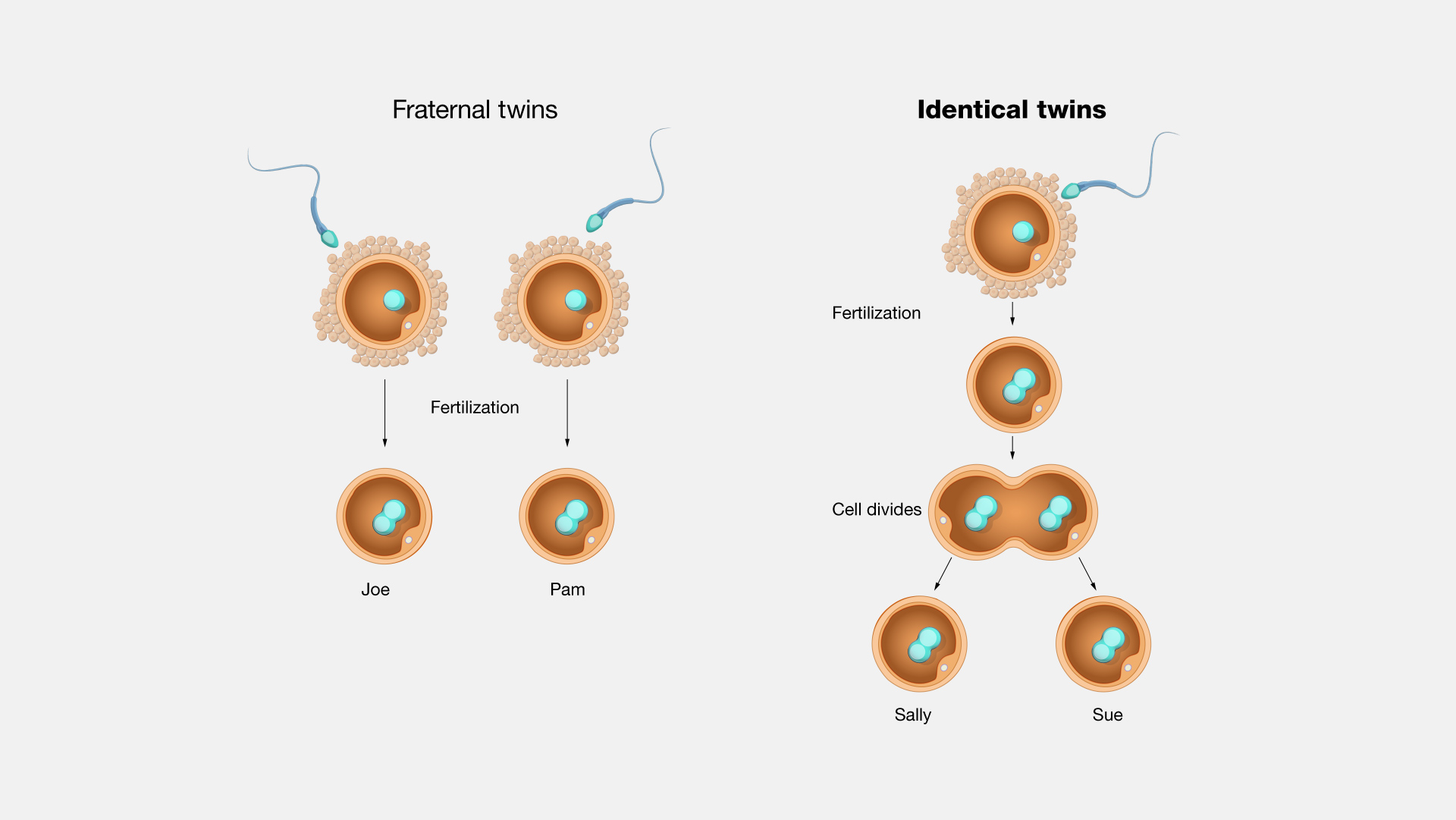
What is the difference between monozygotic and dizygotic twins?
Mono are identical twins that come from one single egg (ovum) and share 100% of their genes
Dio are fraternal twins that come from two eggs and share 50% of their genes
Where does transduction occur in the
1. Eye
2. Ear
3. Nose
1. Cochlea
2. Retina
3. Olfactory
Give an example of
1. A strong negative correlational coefficient
2. A weak positive correlational coefficent
3. A correlational coefficent that can't exist
1. -0.91, -0.99, -0.81
2. +0.20, +0.12, +0.24
3. -1.2, 20, -1.01, 2.5

1. What are the two divisions of the central nervous system?
2. What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
1. Brain and spinal cord
2. Sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/brain_spinal_cord-57fe96b15f9b5805c26d5072.jpg)
Give an example of an altered state of consciousness (ASC) and a non-altered state of consciousness.
1. A Buddhist monk who is meditating
- Sleep, dreams, hypnosis, hallucinations, meditations, and drug states (psychoactive and psychedelic drugs)
2. A person who had 8 hours of sleep (baseline state)

TRUE OR FALSE: Nature via nurture
TRUE!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795392-article-what-is-nature-versus-nurture-5a971887eb97de0036685ad3.png)
1. What school/theory does this example demonstrate?
2. Give an example of sensory adaption
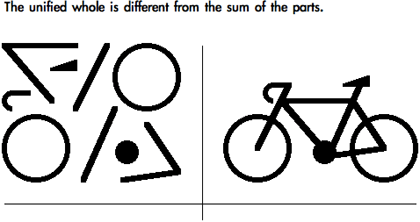
Gestalt School/Theory
- Humans create perceptions of meaningful "wholes" from fragmented and meaningless sensory signals.
A smoker used to the smell of nicotine, the water in a hot tub getting cooler as you stay in longer, putting on your watch and not noticing it is on after 30 seconds
Educators are interested in whether participating in after-school math tutoring can increase scores on standardized math exams. In an experiment, one group of students attends an after-school tutoring session twice a week while another group of students does not receive this additional assistance.
What is the IV, DV, EG, and CG?
IV: After-school tutoring
DV: Scores on standardized math exams
EG: Group that receives tutoring
CG: Group that does not receive additional assistance
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/independent-and-dependent-variable-examples-606828-final1-5b634c5246e0fb008208c528.png)
How do neurons communicate and what is the advantage of this type of communication?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-nerve-cells-587169667-5a4bea3a845b340037919c15.jpg)
Neurons communicate chemically and the advantage of that is plasticity
Give the terms to these two definitions
1. Minimum intensity necessary for a stimulus to be detected, when you are first able to sense something.
2. Smallest difference between two stimuli that can be detected, when you are first able to detect a difference
1. Absolute threshold

2. JND

What is the name of the theory created by Charles Darwin on how evolutionary events shape organisms?
Theory of Natural Selection

What is one of the issues with the experimental method?
Hint: it's a term on the side of the page
External Validity
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/internal-and-external-validity-4584479_final-a1cf2c26ce464856bb86fe5ceb99b17b.png)
What are the four goals of science?
Describe
Classify
Explain
Predict
(DCEP)
Explain what the thalamus and hippocampus do.
1. Gateway to higher functions of the brain, a relay station for sensory information
2. Responsible for our memory
What is the sensation and perception of this image?

Light waves bounce off the image into my retina which are then transducted into neurochemical impulses and sent to my brain.
P: I see a woman with long hair and lipstick on
A + B + transducted + neurochemical impulses + brain
A = light waves, sound waves, odors, food molecules, tactile sensations
B = retina, cochlea, olfactory, taste buds, mechanoreceptors
- But really just focus on visual and sound.
Be familiar with these terms:
** = very important
1. Psychological Adaption**
2. Enviornmental Mismatch**
3. Theory of Parental Investment and Sexual Selection
4. Society
5. Culture
6. Active gene-environment correlation
7. Reactive gene-environment correlation
8. Gene-environment correlation**
9. Heritability**
10. Monozygotic**
11. Dizygotic**
12. Genotype**
13. Phenotype**
14. Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection**
15. RNA
16. Adaptions
17. Chromosomes
18. Gene-environment interaction
Important pages: 113-116, 120-125, 128-131, 133-134, 142
KAHOOT: https://create.kahoot.it/share/exam-1-review/5fd908a0-2df0-42fa-a41a-cc303ea75c05
1. What is the definition of consciousness?
2. Give an example of an apex dream
1. Each person's own subjective experience of themselves and the world.
2. The most intense, bizarre, nonrational, and hallucinatory dreaming, ex: nightmares