Which bond is strongest at physiological pH: ionic, covalent, or hydrogen?
Covalent
What is the name of the disaccharide in the image: 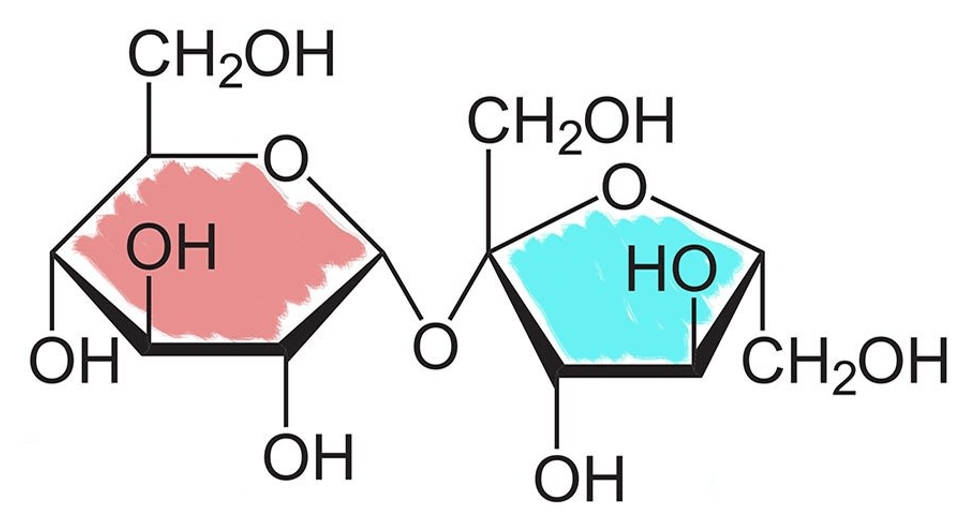
Sucrose
Why are lipids not polymers?
A single lipid is a functional unit
What bond is responsible for the shape of DNA and RNA?
Hydrogen bond
In what conditions will proteins denature?
extreme pH, extreme temperature, or force (but no disulfide!)
Which of the following molecules forms a double bond: CH4, C2H6, C2H4?
C2H4
Which molecule is beta glucose? Where would you find this molecule in nature?
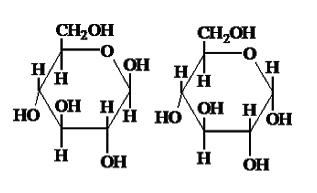
Beta glucose is on the left and can be found in plant cell walls.
How will each type of lipid interact with water?
Fatty acid: hydrophobic
Steroid: hydrophobic (one hydrophilic hydroxyl)
Phospholipid: amphipathic (hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tails)
How does the carbon numbering on the sugar base relate to directionality of DNA/RNA? In which direction do you read DNA/RNA?
The 5' end of the base is where the phosphate group is attached; the 3' end is where the hydroxyl is attached; you read 5' --> 3'
Proteins are diverse. List 3 of the 8 major groups of proteins.
Enzymatic, defensive, storage, transport, hormonal, receptor, contractile/motor, and structural
Name the bonds present in the following image:
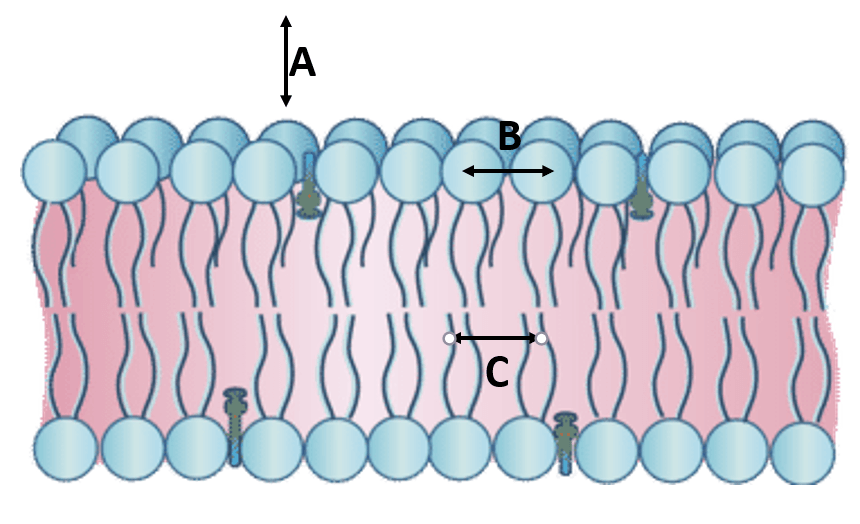
A: hydrogen bonds
B: ionic attractions (NOT BONDS)
C: hydrophobic attractions (van der Waals, london dispersion)
Which form of glucose is easiest to break down and why?
Alpha glucose is easier to break down because the open structure allows enzymes to get in and them apart.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? What state are they each in at room temperature?
Saturated: no double bonds (all Cs have maximum Hs); solid
Unsaturated: one or more double bonds; liquid
Why is DNA's structure useful for both replication and transcription?
It's complimentarity means that each replication will be identical (barring mutations). Even though it's complimentary, each strand provides unique coding sequences, so it allows for highly variable proteins during transcription.
What bonds make up the secondary structure of protein? What bonds make up the tertiary structure of protein?
2: hydrogen bonds (alpha helix or beta pleated sheets)
3: hydrogen bonds/ionic dipole, ionic bonds, disulfide bridge, hydrophobic interactions
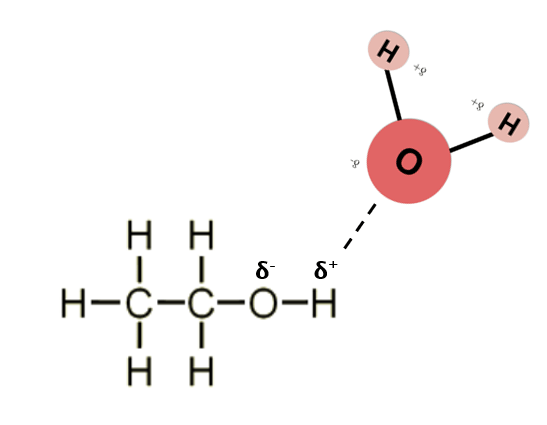
Illustrate the regions of polarity in ethanol. Draw a water molecule and illustrate hydrogen bonding.

What two functional groups interact when forming carb polymers? What's the name of the bond?
Two hydroxyls interact to form glycosidic linkage.
What two functional groups interact when forming fatty acids? What's the name of the bond?
Carboxyl and hydroxyl interact to form ester linkage.
What two functional groups interact when forming nucleic acid polymers? What's the name of the bond?
Hydroxyl and phosphate interact to form phosphodiester bonds
What two functional groups interact when forming amino acid polymers? What's the name of the bond?
Carboxyl and amino interact to form a peptide linkage
Draw one nonpolar, one polar, and one charged functional group.
Nonpolar: methyl
Polar: hydroxyl, carbonyl,
Charged: carboxyl, amino, phosphate
You're at the movies and eat the whole bag of skittles (because that's normal). There are ~4cal/g carb. How many of your calories did you eat?

432 calories
36g *4cal/g = 144 cal per serving
144 *3 = 432 calories
A cell membrane consists of phospholipids with mainly unsaturated tails--how will this membrane act (fluid or viscous)? If you added cholesterol to this membrane, how will it change (more or less fluid/viscous)?
An unsaturated membrane is fluid; adding cholesterol will make it less fluid (or more viscous).
Write the complementary strand of DNA with the correct (readable) directionality:
5' CATCGCTTCC 3'
5' GGAAGCGATG 3'
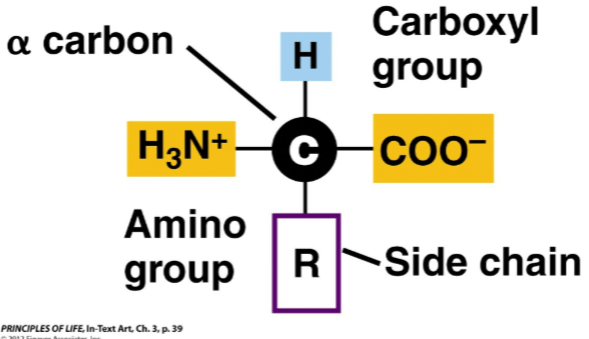
Draw the basic structure of amino acid in physiological pH.