Which biomolecule is composed of mostly C, H, O and sometimes P and contains methyl, carboxyl, and phosphate functional groups?
Lipids
In your rough ER, there is a structure made of a chain of amino acids that is folded into a complex 3D shape. This shape is stabilized by disulfide bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions between R groups of the amino acids. What is this biomolecule (and what level of structure does it have)?
Tertiary structure of protein
You ate a 10 carbon long chain of hydrocarbons. There is one carbon=carbon (double bond) and the hydrogens on both side of that double bond are facing different directions. What is this biomolecule?
trans unsaturated fat
What are the parts of the Cell Theory?
Living organisms are made up of cells, that they are the basic unit of life, and that all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Anchors cytoskeleton within and between cells with flexible proteins called Cadherins
Desmosome
Which biomolecule is composed of mostly C, H, and O and contains hydroxyl, carbonyl, and carboxyl functional groups?
Carbohydrates
There is a long, single chain of nucleotides, which include the nitrogenous base Uracil (U), in your cell’s nucleus right now. What is this biomolecule and what kinds of bonds are used to link the monomers together?
RNA, phosphodiester bonds
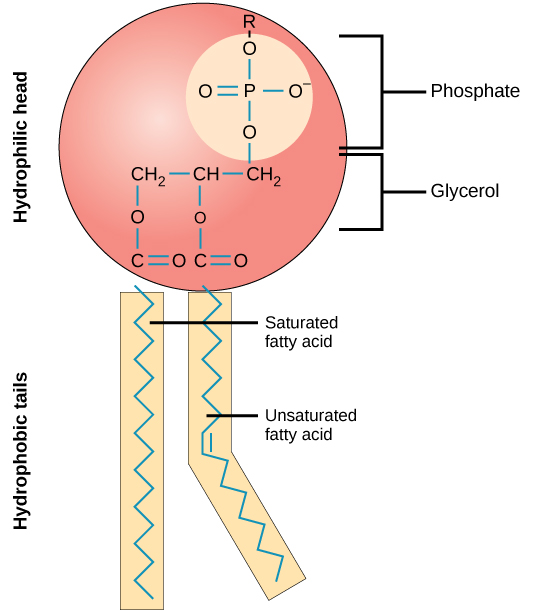
What is this biomolecule? Would a chihuahua from Arizona have more or less unsaturated fatty acid tails in it’s skin cell membranes than a polar bear from the arctic? What property of this molecule causes it to create a bilayer sphere spontaneously when multiple are put in water?
phospholipid, less unsaturated fatty acid tails, it is amphipathic
Why are cells small?
Cells exchange materials through the cell membrane. Cells need to be small so that they have a high surface area to volume ratio and can efficiently take in nutrients and eliminate waste.
Acidic pH breaks down old or invasive things and recycles them
Lysosome
Which biomolecule is composed of mostly C, H, O, N and sometimes S and contains amino, carboxyl, and sufhydryl functional groups?
Proteins
There is a large, branched polymer of alpha glucose in your liver right now. What is this biomolecule and what kinds of bonds are used to link the monomers together?
glycogen, glycosidic bonds

You have long chains of this that are stacked on top of each other and stabilized with hydrogen bonds. What is this biomolecule and what monomer is used to make it?
cellulose, beta glucose monomer
What are the two main types of cells and what are the differences between them?
The two main types of cells are Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic Cells. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles and are much larger than prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and store their DNA in the nucleoid region.
Ca+2 storage, detoxifies drugs and alcohol, makes steroids
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Which biomolecule is composed of mostly C, H, O, N, and P and contains phosphate, hydroxyl, and amino functional groups?
Nucleic acids
You are making a soup from carrots and winter squash such as pumpkins. After boiling the soup for a while there is a layer of oily orange substance floating on the top. What type of biomolecule is that oily orange stuff?
carotenoid
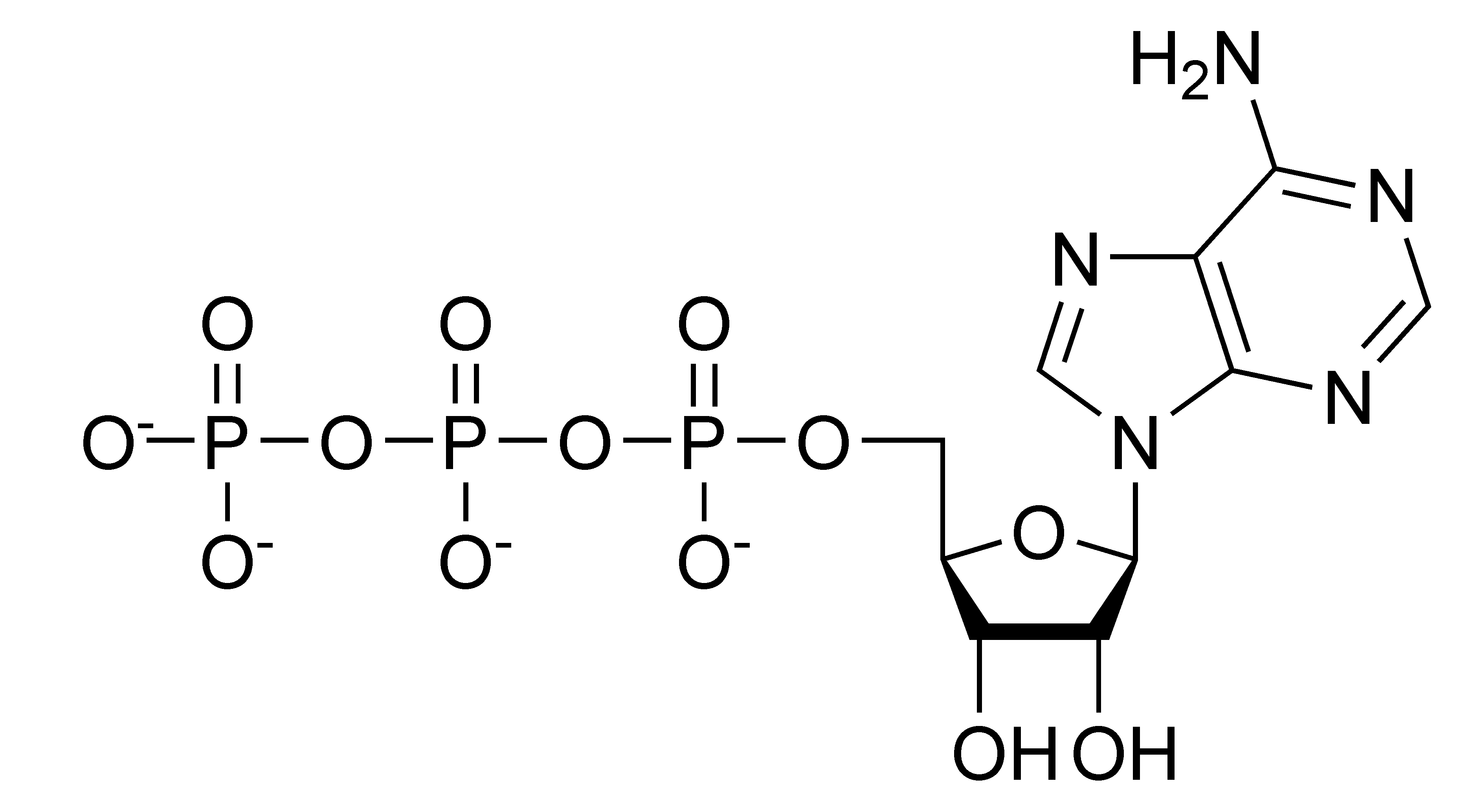
The above molecule is an important molecule that helps to provide energy for cellular work. What kind of biomolecule is this? What are the three components that you find in every monomer of this biomolecule type?
This is ATP which is a type of nucleic acid. The three parts of a nucleotide monomer are a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Which cell parts are found in ALL cells?
Cell membrane, cytosol, DNA, and ribosomes
Made from Connexin proteins that create tube-like structures that can allow small signaling molecules to pass from one cell to another
Gap junctions
What is the relationship between these molecules (be as specific as possible)? What functional groups are present in the molecules?
They are structural isomers of each other. Methyl and aldehyde functional groups are present.
There is a small molecule that has 3, six carbon rings and a five carbon ring. It simply diffuses out of a cell membrane. What is this biomolecule?
steroid

The above image is of a cysteine amino acid. Draw what would happen if two of these monomers bonded together to form a dipeptide polymer. What kind of reaction is this? What regulates and catalyzes this reaction? What is the name of the bond that holds the two monomers together?
This is a dehydration synthesis reaction that is regulated by specific enzymes. Peptide bonds hold the two cysteine monomers together.
Describe the endosymbiont theory and list the evidence that supports it.
The endosymbiotic theory states that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once prokaryotic microbes. Some of the early eukaryotic organisms ingested prokaryotic cells that then survived within the organism and developed a symbiotic relationship. Mitochondria formed when bacteria capable of aerobic respiration were ingested; chloroplasts formed when photosynthetic bacteria were ingested.
Evidence: Mitochandria and chloroplasts are the same size as prokaryotic cells, divide by binary fission, and, have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Breakdown of large chain fatty acids and also building of certain types of lipids
Peroxisome
