Where are the tonsils located?
Pharyngeal Tonsils: nasopharynx
Palatine Tonsils: Oropharynx
Describe Inspiration and Expiration.
Breathing in-flattens diaphragm
Breathing out-diaphragm becomes dome-shaped
What are the 3 accessory digestive organs?
Liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Where is the main site of nutrient absorption?
Small Intestine
What does the epiglottis do?
As we swallow, it folds over to seal off the larynx and routes food and liquid properly.
What is the average P O2 in the air and blood?
Air: 100mmHg
Blood: 40mmHg
The GI tract is made of 3 layers. What are they? Deep to Superficial
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis
Does Ghrelin or Gastrin stimulate hunger?
Ghrelin
What is the difference between Stratified Epithelium and Respiratory Epithelium?
Epithelial:
- mult. layers of epithelial cells
- protection
Respiratory
- 1 layer of pseudostratified epithelium
- columnar cells w/cillia
- goblet cells
What does the bicarbonate buffer do? (created in gas transport)
Helps keep blood pH steady (7.35-7.45)
CO2+H2O=H2CO3
What are the 3 salivary glands and where are they?
Parotid: massester muscles
Submandibular: inferior to mandible
Sublingual: on floor of mouth cavity
Which cells secrete pepsinogen that becomes pepsin for protein digestion? And where is this located?
Chief Cells in stomach
What are the 3 ligaments in the Larynx?
1. Thyriodhyoid ligament
2. Crycothyroid Ligament
3. Crycoidtracheal Ligament
When is the diffusion of oxygen most enhanced?
1. When air and blood are WARM
2. When PCO2 of tissues is HIGH
3. Presence of fetal hemoglobin
Which 2 sphincters encapsulate the stomach?
Cardiac Sphincter and Pyloric Sphincter
What does bile do?
In Liver it emulsifies fats (breaks large molecules down into smaller ones)
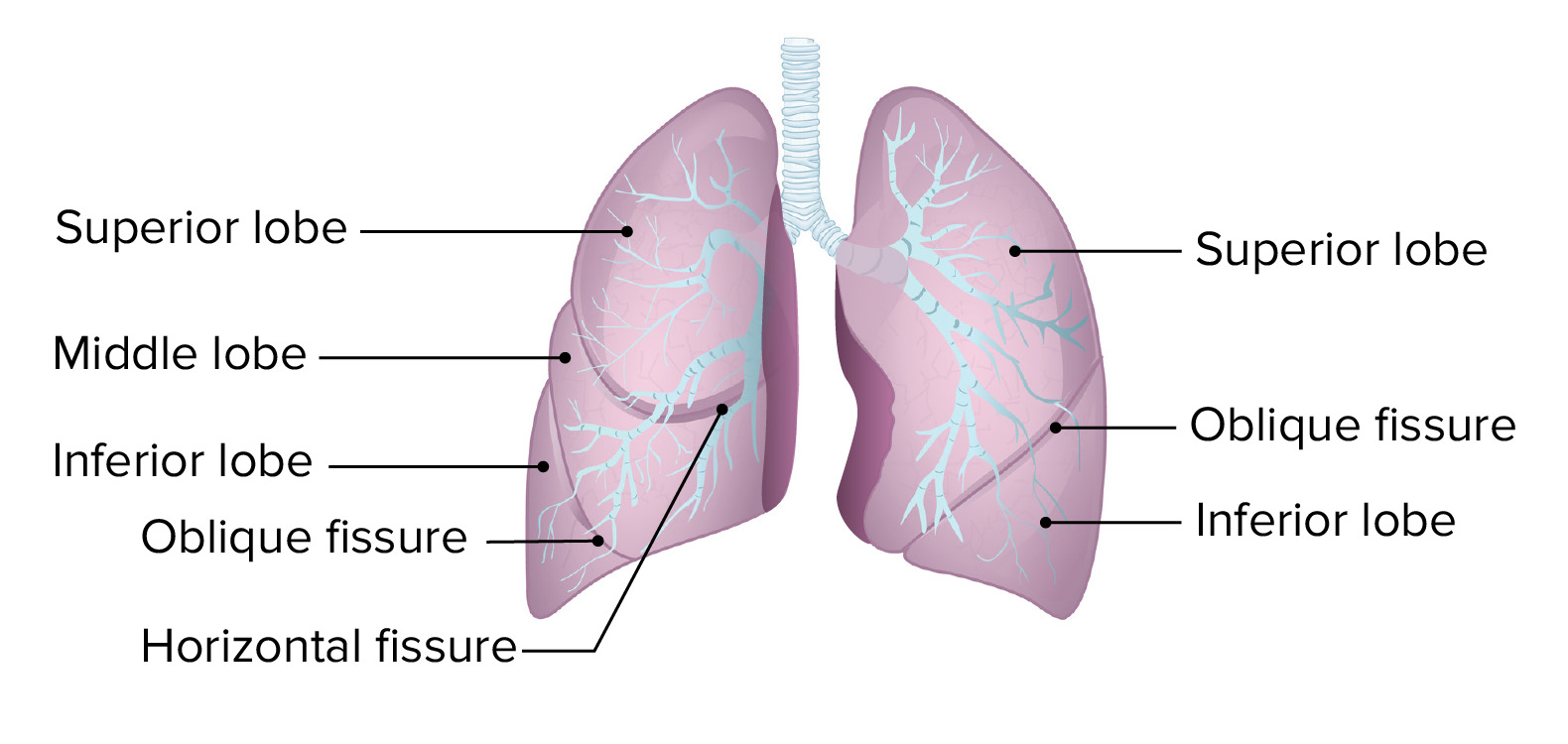
Label the lobes and fissures on the Lungs
How does acidosis occur?
Build up of CO2 in the blood. Making the blood pH too acidic (below 7.35).
Label Digestive Organs


When and how is bile released from Gallbladder?
When fat is in duodenum it contracts.