These two particles make up the nucleus of an atom.
Protons and neutrons
What are the chemical components of a molecule of water?
2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom
Water is sticking to other water molecules is known as?
Cohesion
Enzymes end in what three letters?
-ase
Define product
The substance that results from a chemical reaction
What three elements make up carbohydrates and Lipids?
carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen
What are the monomers of Lipids?
Fatty acids and Glycerols
List the three parts of a nucleotide.
Phosphate, Sugar, and Nitrogen Bases
What are the 3 charges of the particles that make up an atom?
Protons - positive
Neutron - Neutral
Electrons - negative
What is the difference between cohesion & adhesion?
cohesion: an attraction between molecules of the same substance
adhesion: a force of attraction between different kinds of molecules
The hydrogen end of water has a
slight positive charge
Define active site
The place where the substrate binds
Define Allosteric Site.
When a Noncompetitive inhibitor changes the shape of the enzyme, so the substrate cannot bind to the enzyme.
What is the monomers of Proteins
Amino acids
Name the 4 macromolecules groups.
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucliec acids
Which type of fat is shown below? 
unsaturated and saturated

Letter D is the mass number of an element that tells you the average mass of the isotopes of the element. It also tells you the number of ____________ and ____________ in the nucleus of the atom
protons and neutrons
Water rising in a tube is an example of what property?
capillary action
The oxygen end of a water molecule has a
slight negative charge
Define denature (as it relates to enzymes)
Anything that changes the shape of an enzyme
Define activation energy
The amount of energy it takes for a chemical reaction to occur
What is the main function of carbohydrates?
Short-term energy source
What are the monomers of Nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
Make DNA and RNA
Which two protein folding is shown below?
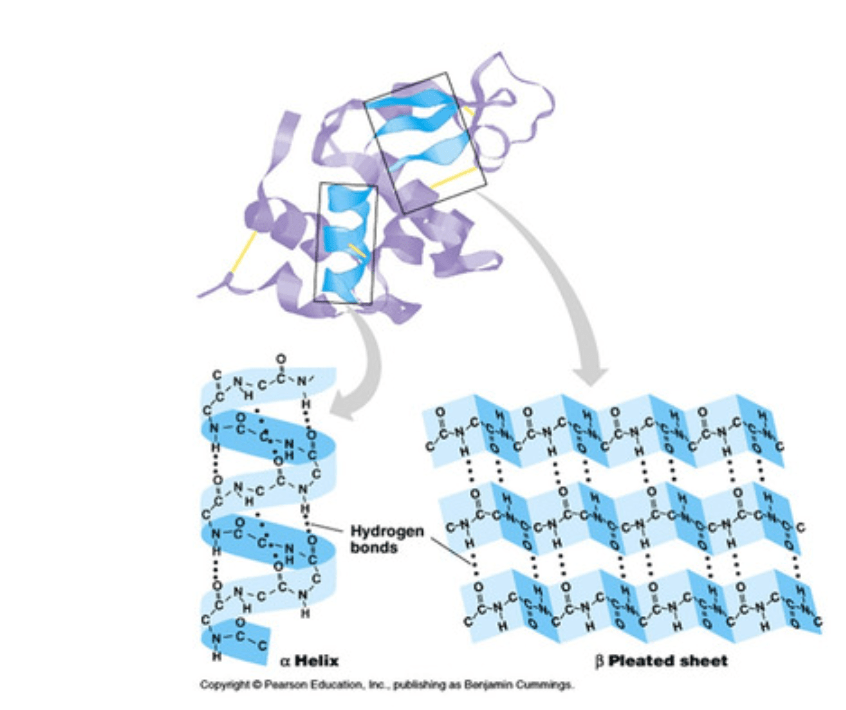
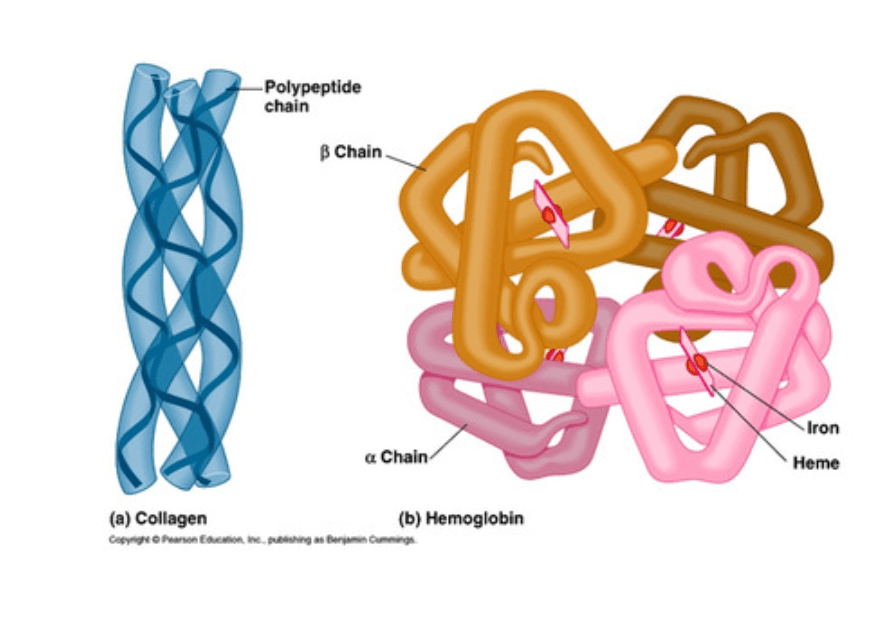
Secondary and Quaternary
What two particles in an atom are equal in number.
electrons and protons
This causes water to stick to other polar substances besides other water molecules.
adhesion
Why are water molecules attracted to each other?
because of polar bonding
Identify the type of inhibition that is taking place. Also, describe this process.
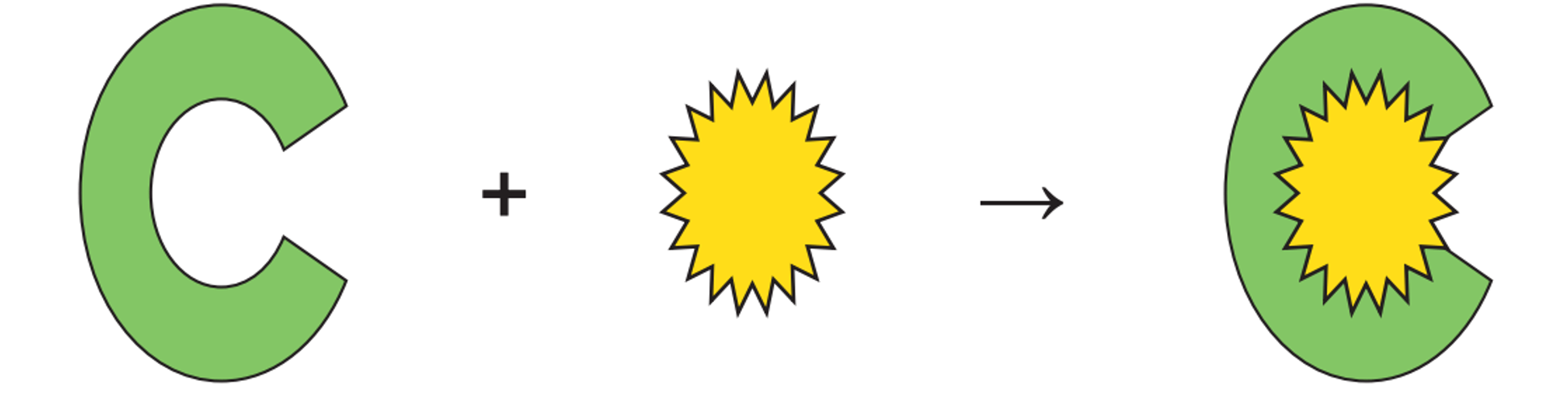
Competitive inhibition. Enzyme active site is blocked causing the substrates unable to bind to the active site.
What are four factors that have an effect on enzymes?
pH, Temperature, Salinity, Substrate Concentration
What is the monomers of carbohydrate?
Monosaccharide
What is the main function of Nucleic acid?
Store genetic information
Transfer and carry genetic information
Identify the DNA structure and label its components A, B, C, and D. 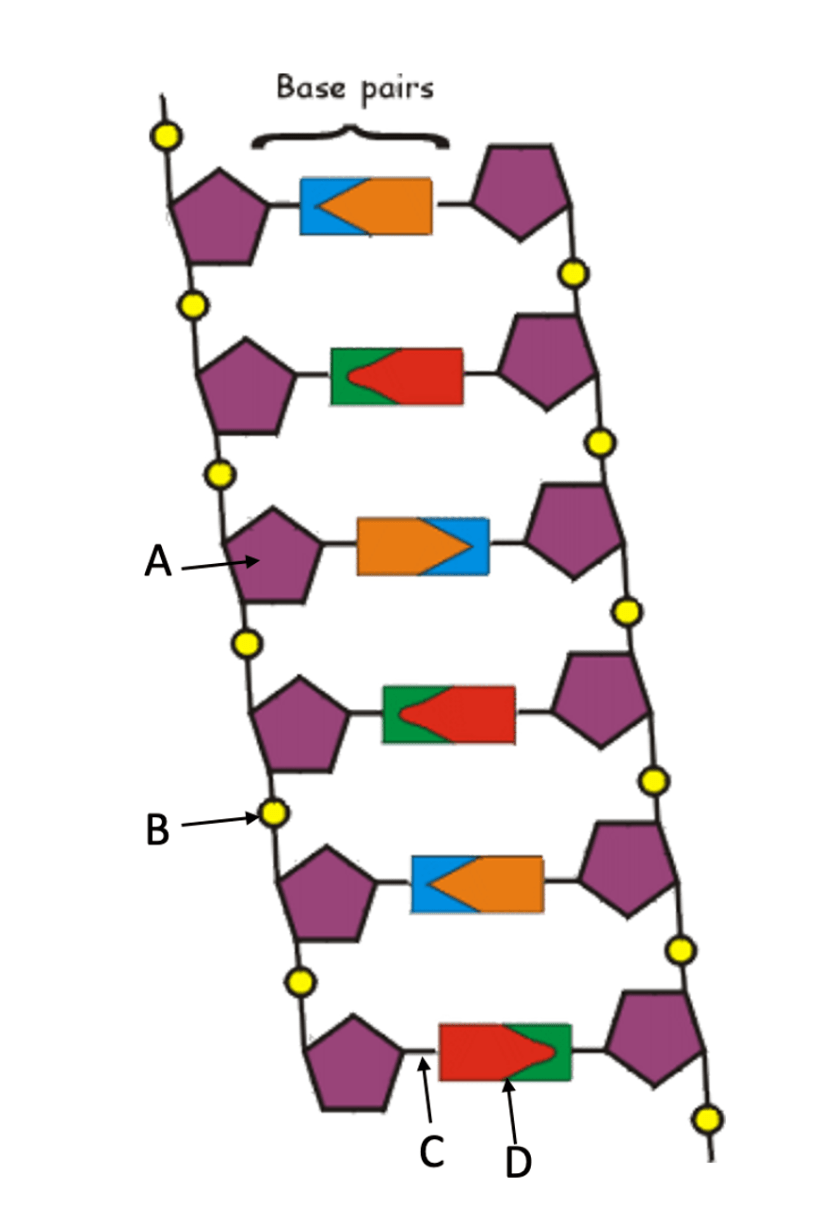
A - Ribose (sugar)
B - Phosphate
C - Hydrogen Bonds
D - Nitrogen Bases
These are atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. (Hint: Same element; different mass)
Isotope(s)
Which property of water allows a water strider to walk on the surface of the water?
Cohesion or Surface Tension
What type of bond is formed from the attraction between the positive end of one water molecule and the negative end of another water molecule?
a hydrogen bond
Identify the type of inhibition that is taking place. Also, describe this process.
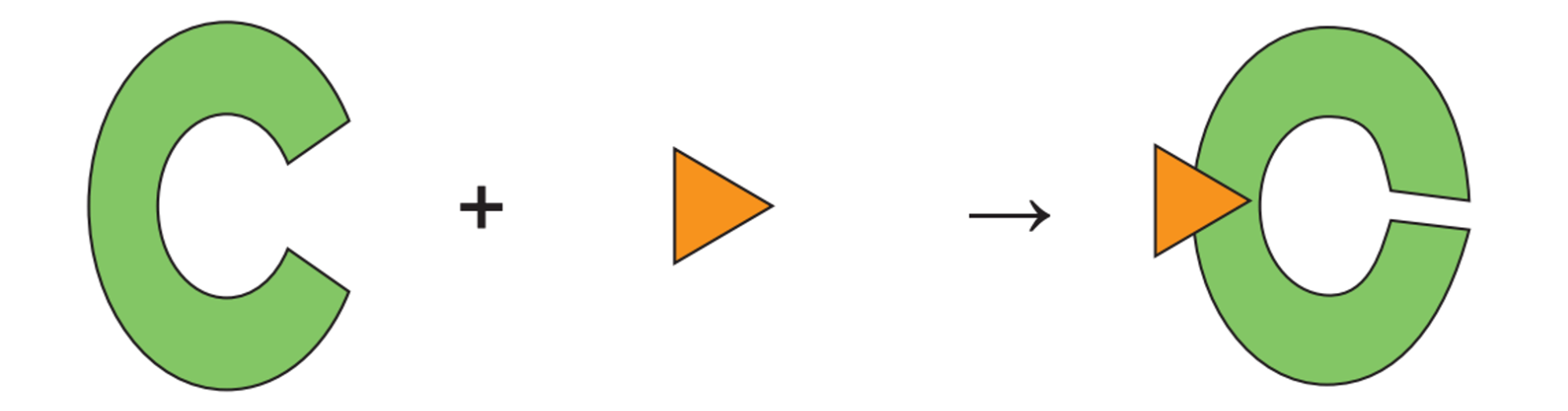
Noncompetitive inhibition. Something other than substrates binding to the alleostric causing the enzyme to change it shape; substrates are not able to bind to the active site.
An enzyme is a catalyst used by living things to promote and regulate chemical reactions. What is the most likely enzyme for the chemical reaction depicted below?

B
Define Hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis is the process breaking macromolecules down into water.
define Polymers:
Polymers many monomers joined together, to form large building.
What macromolecule is depicted in the diagram, and what is the name of its monomer?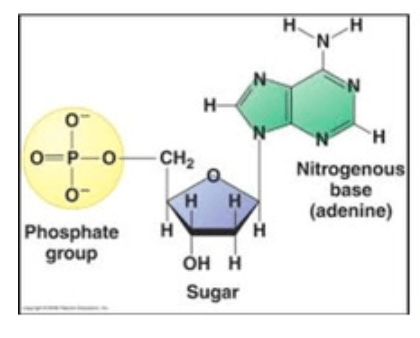
Macromolecule: Nucleic Acid
Monomer: Nucleotide