What type of bond involves the sharing of electrons?
(Covalent bond)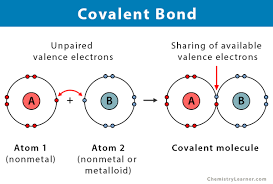
What is the monomer of proteins?
(Amino acids) 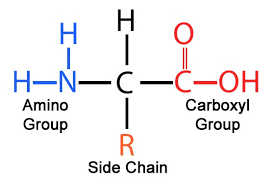
What makes water a polar molecule?
(Unequal sharing of electrons; oxygen is more electronegative.)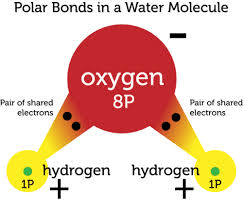
What is the powerhouse of the cell?
(Mitochondria)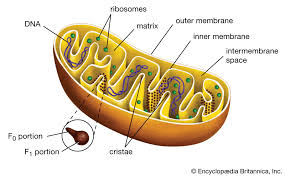
If a cell lacks ribosomes, what process will be disrupted?
(Protein synthesis)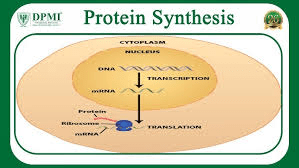
Which type of bond is found between water molecules?
(Hydrogen bond)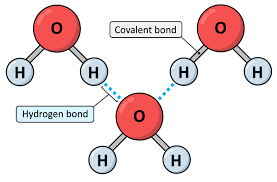
What type of macromolecule is used for long-term energy storage?
(Lipids) Triglyceride
What type of bond holds water molecules together
(Hydrogen bonds)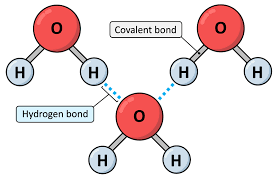
What is the function of ribosomes?
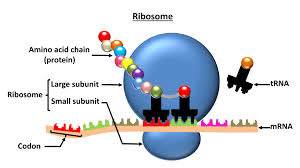 (Protein synthesis)
(Protein synthesis)
A scientist finds a new cell with a nucleus and mitochondria. What type of cell is it?
(Eukaryotic cell)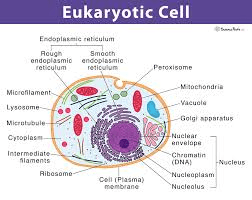
An atom has 8 protons and 10 electrons. What is its charge?
(-2, it’s an anion)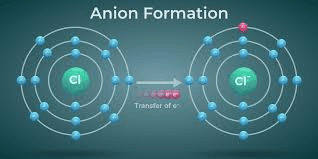
Which carbohydrate is used for energy storage in animals?
(Glycogen)
How many times more acidic is a solution with pH 3 than a solution with pH 6?
(1,000 times more acidic)
What structure controls what enters and exits a cell
Cell membrane/plasma membrane)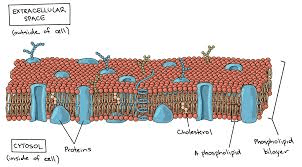
Why does eating too much saturated fat increase the risk of heart disease?
(Saturated fats contribute to plaque buildup in arteries.)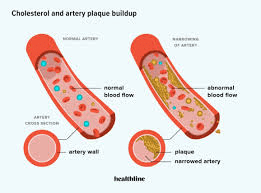
What makes an isotope different from a regular atom?
(Different number of neutrons)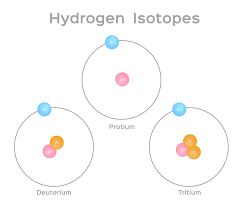
Which macromolecule contains phosphodiester bonds?
(Nucleic acids - DNA & RNA)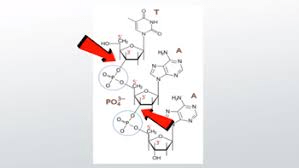
Why does ice float on water?
(Hydrogen bonds create a less dense structure in ice.)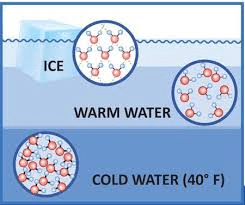
: What are two pieces of evidence supporting the Endosymbiotic Theory
(Mitochondria & chloroplasts have their own DNA, and they divide like bacteria.)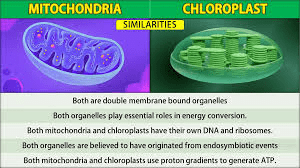
: Why would placing a freshwater fish in saltwater kill it?
Osmosis; water leaves the fish's cells, causing dehydration.)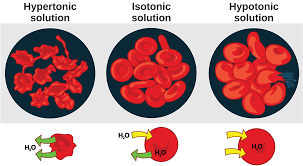
Which type of chemical bond is the strongest in a biological system?
Covalent 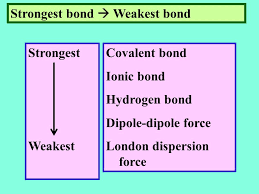
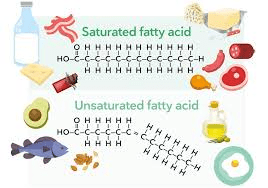
Why are saturated fats solid at room temperature?
(They have no double bonds, so they pack tightly.)
Why does sweating cool your body down?
(Evaporative cooling; high heat of vaporization of water.)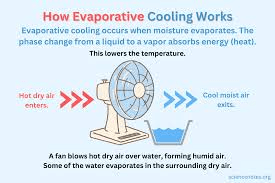
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
(Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids.)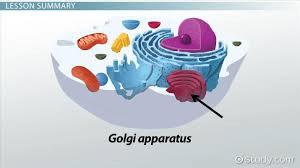
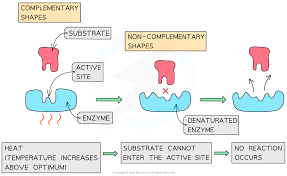
A mutation stops an enzyme from functioning. What might have changed in the enzyme?
(Shape of the active site due to denaturation or genetic mutation.)