Identify this rhythm
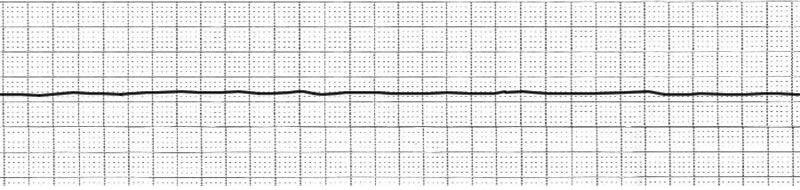
Asystole
Define shock.
Shock is global inadequate tissue perfusion, which causes poor perfusion to the vital organs. Shock is a secondary diagnosis.
Treatment for anaphylaxis
IM Epinephrine, can be IV in ace inhibitors
Define DIC.
Clotting and bleeding
Microthrombi formation is widespread with clots forming that are not needed
Secondary diagnosis
What is the difference between ventilation and oxygenation?
Ventilation: movement of oxygen into the lungs and removal of CO2
Oxygenation: Process of adding oxygen to something (blood in humans)
Identify this rhythm

Ventricular Fibrillation
List the 4 types of shock and an example of each.
Cardiogenic (MI, heart failure, arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy)
Hypovolemic (hemorrhagic (trauma), non-hemorrhagic (pancreatitis, N/V/D)
Obstructive (Pulmonary embolism, tension pneumothorax, superior vena cava)
Distributive (Sepsis, neurogenic, anaphylaxis)
Define thermoregulation.
Homeostatic way your body maintains temperature, and the way our body loses/gains heat.
List 3 risk factors to getting DIC.
Sepsis
Cardiopulmonary arrest
Trauma
OB
Cancer
Define risk factors of OSA.
short neck
Genetics
Obesity
Aging
Smoking
enlarged tonsils
Oropharyngeal edema
The nurse assesses a client to be in this rhythm:
 The client has a pulse and is talking, what can the nurse do to intervene?
The client has a pulse and is talking, what can the nurse do to intervene?
Vagal maneuvers
Adenosine
Beta blocker
Calcium channel blocker
List three things that happen during the compensatory stage of shock.
1. Tachycardia
2. Tachypnea
3. Decrease in pH
4. Increase in lactic acid
5. Decrease urine output
6. Pale skin
7. Widespread vasoconstriction
List the 4 ways we lose/gain heat.
Convection
Radiation
Conduction
Evaporation
List s/s of DIC (not labs)
Mental status changes
Mucosal bleeding
Bleeding at IV sites
Hematuria
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Fever
Retiform purpura, petechiae and acral gangrene
List diagnosis that can cause ARDS.
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Pneumonia
CHF
High altitudes
Smoke inhalation
PE
Hypovolemic shock (trauma)
Hypoventilation
The nurse assesses the client to be in this rhythm:
 The client does not have a pulse. What does the nurse do?
The client does not have a pulse. What does the nurse do?
CPR then defibrillate
List three labs that indicate shock.
1. Increase lactate
2. Low pH on ABG
3. High renal panel (BUN and creatinine)
4. Coag similar to DIC
5. Increase in troponin
What is the difference between heat exhaustion and heat stroke?
Confusion/delirium
No sweat
Rapid heart rate
Loss of consciousness
Temp >104
How do you treat DIC?
TREAT UNDERLYING CAUSE & SUPPORT THE ORGANS
- Oxygenate
- IV fluids
- RBC transfusion
- Platelet transfusion
What is the diagnostic imaging that shows ARDS?
White out chest x-ray
The client is in this rhythm:
 The client has a pulse, is unresponsive and diaphoretic. What does the nurse do?
The client has a pulse, is unresponsive and diaphoretic. What does the nurse do?
Synchoronized cardioversion
Distributive: Vasoconstrictors, and fluids
Obstructive: fix problem (pneumo, PE, etc)
Hypovolemic: Hem = blood, non-hem = fluids
Cardiogenic: Inotropic medications, fluids, can give vasoconstrictors
How do you treat heat stroke?
Remove from heat source
Ice packs on groin/neck
Cooled fluids
Submerge in ice, w/core temperature monitoring
List the labs for DIC.
Decrease fibrinogen
Decrease clotting factors
Increase PT
Increate PTT
Increase D-dimer
Decrease platelets
List the nursing interventions to avoid Ventilator assisted pneumonia?
Turning/repositioning
HOB >30 degrees
Ulcer prophylaxis
Oral care at least every 12 hours